(Press-News.org) School connectedness – the degree to which students feel part of their school community – influences more than grades. For Black students, it’s a protective factor against depression and aggressive behavior later in life, according to a Rutgers University-New Brunswick study.
“Our data provide fairly strong evidence for the idea that the experiences Black adolescents have in their school impacts their long-term mental health,” said Adrian Gale, an assistant professor in the Rutgers School of Social Work, and lead author of the study published in the Journal of Youth and Adolescence.
Researchers have long understood the benefits of school connectedness for youth well-being and physical health outcomes. But most research into the topic has been focused on White adolescents, with limited research exploring the relationship among Black youth, Gale said.
To address this gap, Gale and Lenna Nepomnyaschy, an associate professor in the Rutgers School of Social Work, analyzed longitudinal data from the Future of Families and Child Wellbeing Study (FFCWS), a population-based birth cohort study following children born in large United States cities between 1998 and 2000.
From the total cohort of nearly 5,000 children included in the FFCWS, Gale and Nepomnyaschy identified 1,688 who self-identified as Black or African American, were interviewed at ages 9 and 15, and whose primary caregivers were interviewed at the 15-year follow-up.
At age 9, participants were asked about their connectedness to schools. Participants were asked to rate the frequency they felt “part of your school, close to people at your school, happy to be at your school, and safe at school.” Six years later, caregivers were asked about their children’s propensity for aggressive behaviors, and youth reported their experiences of depression.
Using these data as inputs, the researchers then used linear regression models to control for variables that could influence the association between school connectedness, depression and aggressive behaviors. Covariates included family characteristics, mother’s education, neighborhood characteristics and perceived neighborhood disorder – such as the presence of garbage.
Even with this “rich set of child, parent, family, neighborhood and school-district characteristics that could potentially confound the associations between school connectedness and mental health,” the researchers said they found evidence that early school connectedness may reduce depressive symptoms and aggressive behaviors later in life. The association was strongest for girls.
“These findings demonstrate that when Black children felt connected to their school at age 9, they had fewer depressive symptoms and less aggressive behavior issues as adolescents,” Gale said. “Simply put, when Black kids feel closely tied to their school, their mental health benefits.”
Gale said these findings have implications for school districts nationwide and should be viewed as more evidence to support increased school funding.
“School connectedness, no matter how it's defined, is about the relationships people in school have with one another,” he said. “The extent that you can improve the quality of those individual relationships – with funding for smaller classes, for example – is what will lead to improved school connectedness and better student outcomes.”
END
For black adolescents, feeling connected to school has long-lasting mental health benefits
Students who reported higher levels of school connectedness showed lower levels of aggressive behaviors and depression six years later, Rutgers researchers find
2024-01-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mechanisms and management of atrial fibrillation: Updates from a Chinese Medical Journal Review
2024-01-08
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a major global health concern impacting millions and causing symptoms like palpitations, dyspnea, fatigue, dizziness, and chest discomfort. Furthermore, these symptoms reduce patients’ quality of life and lead to increased mortality and morbidity. The medical community agrees that epicardial adipose tissue (EAT), chronic inflammation, imbalances in the autonomic nervous system (ANS), stretch-induced fibrosis, and genetic alterations are the main factors that influence AF pathogenesis. Despite extensive research efforts focused on uncovering the underlying mechanisms ...
Study from ECNU Review of Education redevelops framework for teaching artificial intelligence and robotics
2024-01-08
Just like computers, the Internet, and smartphones have become commonplace in our daily lives, artificial intelligence and robotics (AIR) are the next technologies in line set to drastically change how we interact with the world and among ourselves. Various AI-driven applications are already in widespread use, such as Siri, Google Assistant, and ChatGPT, and both industrial- and consumer-grade robots are becoming increasingly capable and accessible.
In our modern societies, where people rely more and more on AIR systems to perform tasks, it’s essential to prepare children and teenagers to understand ...
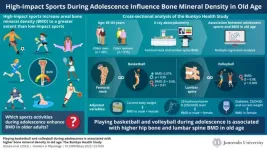
Adolescent sports activities help improve bone health in older adults, new study finds
2024-01-08
Loss of bone mineral density (BMD) with age is an important cause of osteoporosis (deterioration of bone tissue), which has been reported as one of the leading causes of falls among older adults in Japan. This leads to fractures that require long-term nursing. Prevention of osteoporosis in the aging population can thus help decrease the burden of disease and healthcare costs substantially.
Early lifestyle habits can largely influence health and disease onset in old age. In this regard, physical activities ...
Bariatric surgery may slow cognitive decline for people with obesity
2024-01-08
Within the next 10 years, it’s projected that up to 50% of United States adults will be affected by obesity, which is associated with cognitive impairment and dementia.
Investigators at Michigan Medicine found that people with obesity who underwent bariatric surgery had stable cognition two years later.
Researchers say it suggests that bariatric surgery may mitigate the natural history of cognitive decline expected in people with obesity.
The results are published in the Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging.
“Since individuals with obesity ...
Exploring dimensions of justice in climate science
2024-01-08
How can climate policy be made more just and fair? IIASA researchers have synthesized different dimensions of justice into a framework that can be used by climate scientists and policymakers, explaining how previous research has neglected many potential justice positions and how these can be implemented in policy contexts.
Dealing with climate change is not just about the environment – it is also about justice and fairness. This includes how we transition to cleaner ways of living, the different impacts on various groups of people, and who is responsible ...
CHOP researchers develop algorithm to determine how cellular “neighborhoods” function in tissues
2024-01-08
Philadelphia, January 8, 2024 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have developed a new AI-powered algorithm to help understand how different cells organize themselves into particular tissues and communicate with one another. This new tool was tested on two types of cancer tissues to reveal how these “neighborhoods” of cells interact with one another to evade therapy, and more studies could reveal more information about the function of these cells in the tumor ...
Researchers engineer in vivo delivery system for prime editing, partially restoring vision in mice
2024-01-08
Prime editing, a versatile form of gene editing that can correct most known disease-causing genetic mutations, now has a new vehicle to deliver its machinery into cells in living animals.
A team of researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard has engineered virus-like particles to deliver prime editors to cells in mice at a high enough efficiency to rescue a genetic disorder. In the new work published today in Nature Biotechnology, the team adapted engineered virus-like particles (eVLPs) that they had previously designed to carry base editors — ...
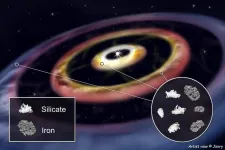
Three iron rings in a planet-forming disk
2024-01-08
The origin of Earth and the Solar System inspires scientists and the public alike. By studying the present state of our home planet and other objects in the Solar System, researchers have developed a detailed picture of the conditions when they evolved from a disk made of dust and gas surrounding the infant sun some 4.5 billion years ago.
Three rings hinting at two planets
With the breathtaking progress made in star and planet formation research aiming at far-away celestial objects, we can now investigate the conditions in environments around young stars and compare them to the ones derived for the early Solar System. Using the European Southern Observatory’s (ESO) Very Large ...
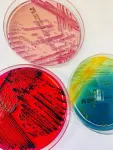
More than thirty new species of bacteria discovered in patient samples
2024-01-08
Unknown germs are a common occurrence in hospitals. Researchers at the University of Basel have spent many years collecting and analyzing them. They have identified many new species of bacteria, some of which are significant for clinical practice.
Bacterial infections can be treated more efficiently if the cause of the disease is known. In most cases, all it takes to identify a pathogen is an analysis in a medical laboratory. Sometimes, however, the standard methods are insufficient – for example, if the species of bacteria has not yet been classified or ...
Where do patients choose to undergo breast cancer surgery, and do these choices drive health care inequality?
2024-01-08
Including patients as partners for making decisions about their medical treatments is an important aspect of patient-centered care. A new study from England examined choices that patients with breast cancer make when considering where to have surgery for their condition and assessed how policies that offer such choices might affect inequalities in the health care system. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, investigators analyzed data from the National Health Service (NHS), the publicly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] For black adolescents, feeling connected to school has long-lasting mental health benefitsStudents who reported higher levels of school connectedness showed lower levels of aggressive behaviors and depression six years later, Rutgers researchers find