Press passes now available for Discover BMB to be held March 23–26
Reporters can register to attend in San Antonio or sign up to access press materials online
2024-01-09
(Press-News.org) Complimentary press passes are now available for Discover BMB, the annual meeting of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB). Join us March 23–26 in San Antonio to experience an engaging agenda showcasing the newest developments and current trends in the field.
As the flagship meeting for one of the largest molecular life science organizations in the world, #DiscoverBMB brings together researchers in academia and industry from across the globe.
Explore captivating science stories and connect with leading experts during the scientific symposia, which will encompass 12 themes. Topics include:
Exciting enzymes and their potential role in sustainable chemistry
The secret side of microbes: signaling, communication and metabolism
New natural products derived from genomes, microbiomes and animals
Unlocking how lipids keep cells ticking
The promise of RNA as one of today's hottest biotech tools
Discover BMB will also feature award lectures by scientists recognized for their discoveries, teaching and diversity initiatives.
Qualifying journalists will receive:
Full, complimentary access to all meeting sessions in San Antonio
Opportunities to connect with a global community of top scientists
Early access to embargoed materials featuring high-impact research
Personal introductions for one-on-one interviews with featured scientists
To register for a press pass to attend #DiscoverBMB in San Antionio or access press materials electronically, please check our Media Policies and submit a Press Registration Form.
Follow #DiscoverBMB on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and LinkedIn.
Contact:
Anne Johnson
(571) 271-1986 (mobile)
media@asbmb.org
About the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB)
The ASBMB is a nonprofit scientific and educational organization with more than 12,000 members worldwide. Founded in 1906 to advance the science of biochemistry and molecular biology, the society publishes three peer-reviewed journals, advocates for funding of basic research and education, supports science education at all levels, and promotes the diversity of individuals entering the scientific workforce. www.asbmb.org
Questions? Contact us at media@asbmb.org
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-09
Children and adults with rare, deadly genetic diseases have fresh hope for curative therapies, thanks to a new collaboration between the Innovative Genomics Institute (IGI) and Danaher Corporation, a global life sciences and diagnostics innovator.
The new Danaher-IGI Beacon for CRISPR Cures center will use genome editing to address potentially hundreds of diseases, including rare genetic disorders that have no cure. The goal is to ensure treatments can be developed and brought to patients ...
2024-01-09
DALLAS, Jan. 9, 2024 — A physician-scientist from Massachusetts researching whether chemicals naturally occurring in foods could help treat heart disease, a genetics expert from Pennsylvania exploring the molecular mechanisms of lipid metabolism and cardiovascular diseases and a California-based professor of cardiovascular medicine studying how vaping impacts the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms are the most recent American Heart Association Merit Award recipients. Over the next five years, each researcher will receive a total of $1 million in funding from the Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization focused on heart and brain health and research, ...
2024-01-09
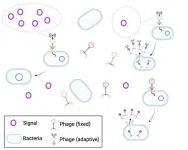
Phages, the viruses that infect bacteria, will pay a high growth-rate cost to access environmental information that can help them choose which lifecycle to pursue, according to a study. Yigal Meir and colleagues developed a model of a bacteria-phage system to investigate how much the viruses should be willing to invest to acquire information about their local environment. A temperate phage, once inside a bacterium, can choose one of two life cycles. In the lytic cycle, the phage turns the bacterium ...
2024-01-09
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Researchers from Binghamton University, State University of New York are unraveling the workings of Group B Strep (GBS) infections in pregnant women, which could someday lead to a vaccine.
One in five pregnant women carry Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Strep or GBS) in the vaginal tract, which is typically harmless — except when it isn’t.
The bacterial infection poses serious and even fatal consequences for newborns, including pneumonia, sepsis and meningitis, which can have long-term effects on the child’s cognitive function.
Researchers ...
2024-01-09
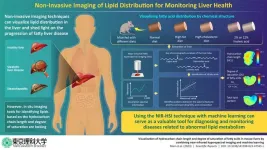
Steatotic liver disease (SLD), previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which includes a range of conditions caused by fat build-up in the liver due to abnormal lipid metabolism, affects about 25% of the population worldwide, making it the most common liver disorder. Often referred to as “silent liver disease,” SLD progresses without noticeable symptoms and can lead to more severe conditions like cirrhosis (liver scarring) and liver cancer.
A liver biopsy—an invasive procedure involving liver tissue sample extraction from the body—is ...
2024-01-09
Robotics and autonomous vehicles are among the most rapidly growing domains in the technological landscape, with the potential to make work and transportation safer and more efficient. Since both robots and self-driving cars need to accurately perceive their surroundings, 3D object detection methods are an active area of study. Most 3D object detection methods employ LiDAR sensors to create 3D point clouds of their environment. Simply put, LiDAR sensors use laser beams to rapidly scan and measure the ...
2024-01-09
Levi Gadye, 628-399-1046
Levi.Gadye@ucsf.edu | @UCSF
Video: https://ucsf.app.box.com/s/i3atd54ye4m1z1spi0qf59axq7tq7640
Subscribe to UCSF News
A high-sugar diet is bad news for humans, leading to diabetes, obesity and even cancer. Yet fruit bats survive and even thrive by eating up to twice their body weight in sugary fruit every day.
Now, UC San Francisco scientists have discovered how fruit bats may have evolved to consume so much sugar, with potential implications for the 37 million Americans with diabetes. The findings, published on Tuesday, Jan. 9, 2024 in Nature Communications, point to adaptations ...
2024-01-09
HOUSTON ― A vaccine showed potential to prevent relapse of KRAS-mutated pancreatic and colorectal cancers for patients who had previously undergone surgery, according to a Phase I trial led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Results were published today in Nature Medicine.
In the trial, patients with pancreatic and colorectal cancer who were considered at high risk of relapse received a maximum of 10 doses of the ELI-002 vaccine targeted toward KRAS G12D and G12R mutations. T cell responses were seen in 84% of all patients and in 100% of those in the two highest dose cohorts, including those who ...
2024-01-09
International research led by the Translational Synthetic Biology Laboratory of the Department of Medicine and Life Sciences (MELIS) at Pompeu Fabra University has succeeded in efficiently engineering Cutibacterium acnes -a type of skin bacterium- to produce and secrete a therapeutic molecule suitable for treating acne symptoms. The engineered bacterium has been validated in skin cell lines and its delivery has been validated in mice. This finding opens the door to broadening the way for engineering non-tractable bacteria to address skin alterations and other diseases using living therapeutics.
The research team is completed by scientists from the Bellvitge Biomedical Research ...
2024-01-09
As the potter works the spinning wheel, the friction between their hands and the soft clay helps them shape it into all kinds of forms and creations. In a fascinating parallel, sea squirt oocytes (immature egg cells) harness friction within various compartments in their interior to undergo developmental changes after conception. A study from the Heisenberg group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), published in Nature Physics, now describes how this works.
The sea is full of fascinating life forms. From algae and colorful fish to marine snails and sea squirts, a completely different world reveals itself underwater. Sea squirts or ascidians in particular are very unusual: ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Press passes now available for Discover BMB to be held March 23–26
Reporters can register to attend in San Antonio or sign up to access press materials online