(Press-News.org) The boundary between everyday reality and the quantum world remains unclear. The more massive an object, the more localized it becomes when being made quantum through cooling down its motion to the absolute zero. Researchers, led by Oriol Romero-Isart from the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW) and the Department of Theoretical Physics at the University of Innsbruck, propose an experiment in which an optically levitated nanoparticle, cooled to its ground state, evolves in a non-optical (“dark”) potential created by electrostatic or magnetic forces. This evolution in the dark potential is expected to rapidly and reliably generate a macroscopic quantum superposition state.
Laser light can cool a nanoscale-sized glass sphere to its motional ground state. Left alone, bombarded by air molecules and scattering incoming light, such glass spheres quickly heat up and leave the quantum regime, limiting quantum control. To avoid this, the researchers propose letting the sphere evolve in the dark, with the light switched off, guided solely by nonuniform electrostatic or magnetic forces. This evolution is not only fast enough to prevent heating by stray gas molecules but also lifts the extreme localization and imprints unequivocally quantum features.
The recent paper in Physical Review Letters also discusses how this proposal circumvents the practical challenges of these type of experiments. These challenges include the need for fast experimental runs, minimal use of laser light to avoid decoherence, and the ability to quickly repeat experimental runs with the same particle. These considerations are crucial in mitigating the impact of low-frequency noise and other systematic errors.
This proposal has been extensively discussed with experimental partners in Q-Xtreme, an ERC Synergy Grant project financially supported by the European Union. “The proposed method is aligned with current developments in their labs and they should soon be able to test our protocol with thermal particles in the classical regime, which will be very useful to measure and minimize sources of noise when lasers are off,” says the theory team of Oriol Romero-Isart. “We believe that while the ultimate quantum experiment will be unavoidably challenging, it should be feasible as it meets all the necessary criteria for preparing these macroscopic quantum superposition states.”
Publication: Macroscopic Quantum Superpositions via Dynamics in a Wide Double-Well Potential. M. Roda-Llordes, A. Riera-Campeny, D. Candoli, P. T. Grochowski, and O. Romero-Isart. Physical Review Letters 2023 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.023601 [arXiv: 2303.07959]
END
Observing macroscopic quantum effects in the dark
How to make a nanoscale-sized glass bead show quantum effects at macroscopic scales
2024-01-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI discovers that not every fingerprint is unique
2024-01-10
Columbia engineers have built a new AI that shatters a long-held belief in forensics–that fingerprints from different fingers of the same person are unique. It turns out they are similar, only we’ve been comparing fingerprints the wrong way!
New York, NY—January 12, 2024—From “Law and Order” to “CSI,” not to mention real life, investigators have used fingerprints as the gold standard for linking criminals to a crime. But if a perpetrator leaves prints from different fingers in two different crime scenes, these scenes are very difficult to link, and the trace can go ...
JMIR Mental Health accepted for MEDLINE indexing
2024-01-10
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce that JMIR Mental Health (JMH) has been accepted for inclusion in MEDLINE, which is the U.S. National Library of Medicine's premier bibliographic database.
JMIR Mental Health had already been indexed in PubMed previously. MEDLINE is a more selective subset of PubMed, consisting of the top 5,200 biomedical journals. Indexing in MEDLINE also means that articles are now also indexed with NLM Medical Subject Headings (MeSH terms) and other metadata.
Selection for MEDLINE is a result of a thorough review of the ...
Reduced drug use is a meaningful treatment outcome for people with stimulant use disorders
2024-01-10
Reducing stimulant use was associated with significant improvement in measures of health and recovery among people with stimulant use disorder, even if they did not achieve total abstinence. This finding is according to an analysis of data from 13 randomized clinical trials of treatments for stimulant use disorders involving methamphetamine and cocaine. Historically, total abstinence has been the standard goal of treatment for substance use disorders, however, these findings support the growing recognition that a more nuanced perspective on measuring treatment success may be beneficial.
The study, published in Addiction, was led by scientists at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public ...
Blood test distinguishes neuroendocrine subtype of advanced prostate cancer
2024-01-10
Boston – Like a criminal entering a witness protection program, cancer cells can shed their past and take on a new identity. Detecting such an identity-switch is particularly challenging when metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) advances from adenocarcinoma to neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC), a very difficult cancer to treat.
Now, however, researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and the University of Trento, Italy, have developed a blood test, described in Cancer Discovery, that can ...
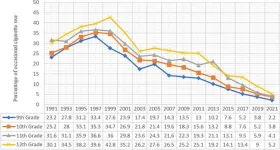
Dramatic decline in cigarette use among U.S. teens over three decades
2024-01-10
Cigarette smoking remains the leading avoidable cause of premature death in the United States, accounting for approximately 500,000 deaths or 1 in 5 deaths annually. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, most adults who smoke cigarettes started before age 18, so preventing cigarette smoking in adolescents is important to reducing smoking in adults.
In a new study, researchers from Florida Atlantic University’s Schmidt College of Medicine and collaborators explored overall trends in cigarette smoking among a large sample of U.S. adolescents in grades nine to 12 from 1991 to 2021. They ...
Finding a home for the wandering mushrooms —— Phylogenetic and taxonomic updates of Agaricales
2024-01-10
Many edible, medicinal, and poisonous mushrooms that we are familiar with belong to the order Agaricales, which is a group of fungi with important economic and ecological value. Understanding the phylogenetic relationships of Agaricales can help us to know their evolutionary history and diversity, as well as their interactions with other organisms. Moreover, the phylogenetic framework of Agaricales can provide a basis for conserving biodiversity, such as measuring phylogenetic diversity and assessing the uniqueness and importance of different species.
Previous studies divided Agaricales into 8 suborders and 46 families, but the systematic position and phylogenetic relationship ...
ALS: blocking inflammation to reduce symptoms
2024-01-10
Québec, January 10, 2024 – In people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), changes in neurons appear to activate immune cells. Lowering the inflammation could reduce the symptoms of the disease, according to a study led by Chantelle Sephton, a professor at Université Laval's Faculty of Medicine.
ALS is caused by the loss of upper motor neurons, located in the brain, and lower motor neurons, which extend from the spinal cord to the muscles. Using a genetically modified mouse ...
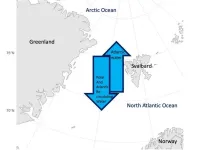
PFAS flow equally between Arctic Ocean and Atlantic Ocean, study finds
2024-01-10
The frigid Arctic Ocean is far removed from the places most people live, but even so, “forever chemicals” reach this remote landscape. Now, research in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters suggests that per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) won't stay there indefinitely. Instead, they are transported in a feedback loop, with the Arctic Ocean potentially exporting as many PFAS to the North Atlantic Ocean as it receives, circulating the compounds around the world.
To ...
Rice University Engineer Ashok Veeraraghavan, Ph.D., recognized for revolutionary imaging technology that seeks to make the invisible visible
2024-01-10
Trailblazing engineer Ashok Veeraraghavan, Ph.D., Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Computer Science, George R. Brown School of Engineering at Rice University, is the recipient of the 2024 Edith and Peter O’Donnell Award in Engineering from TAMEST (Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology). He was chosen for his revolutionary imaging technology that seeks to make the invisible visible. View a video on Dr. Veeraraghavan's groundbreaking research here.
Imagine taking a pristine picture through fog, smoke and rain. Imagine taking interior images of the human body through skin, bone ...
UT Southwestern Medical Center biochemist Vincent Tagliabracci, recognized for potentially life-saving research in understanding how enzymes work
2024-01-10
Forward-thinking biochemist Vincent Tagliabracci, Ph.D., Associate Professor at UT Southwestern Medical Center, is the recipient of the 2024 Edith and Peter O’Donnell Award in Biological Sciences from TAMEST (Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology). He was chosen for his potentially life-saving research in understanding how enzymes work. View a video on Dr. Tagliabracci's groundbreaking research here.
Dr. Tagliabracci and his team at UT Southwestern Medical Center have shined a new light on an array of physiological processes that rely on enzymes called protein kinases (PKs) and their biological cousins called ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Observing macroscopic quantum effects in the darkHow to make a nanoscale-sized glass bead show quantum effects at macroscopic scales