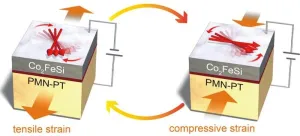
(Press-News.org) Controlling the direction of magnetization using low electric field is necessary for developing efficient spintronic devices. In spintronics, properties of an electron’s spin or magnetic moment are used to store information. The electron spins can be manipulated by straining orbital magnetic moments to create a high-performance magnetoelectric effect.
Japanese researchers, including Jun Okabayashi from the University of Tokyo, revealed a strain-induced orbital control mechanism in interfacial multiferroics. In multiferroic material, the magnetic property can be controlled using an electric field—potentially leading to efficient spintronic devices. The interfacial multiferroics that Okabayashi and his colleagues studied consist of a junction between a ferromagnetic material and a piezoelectric material. The direction of magnetization in the material could be controlled by applying voltage.
The team showed the microscopic origin of the large magnetoelectric effect in the material. The strain generated from the piezoelectric material could change the orbital magnetic moment of the ferromagnetic material. They revealed element-specific orbital control in the interfacial multiferroic material using reversible strain and provided guidelines for designing materials with a large magnetoelectric effect. The findings will be useful in developing new information writing technology that consumes less power.
###
The article, “Strain-induced specific orbital control in a Heusler alloy-based interfacial multiferroics,” was published in NPG Asia Materials at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41427-023-00524-6
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
END
Toward efficient spintronic materials
Researchers reveal how magnetization direction can be controlled using strain in an interfacial multiferroic material.
2024-01-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds hospital surfaces can harbor harmful microbes even after routine disinfection
2024-01-11
Study Finds Hospital Surfaces Can Harbor Harmful Microbes Even After Routine Disinfection
Microbial contamination, including harmful pathogens, was found on bed rails, workstations, and other frequently-touched surfaces
Arlington, Va. — January 11, 2024 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) reports microbial contamination — including pathogenic and potentially pathogenic bacteria — on high-touch hospital surfaces despite compliance with recommended disinfection protocols. The findings shed light on the persistent challenge of reducing healthcare-associated infections ...
Researchers develop prime editors using Cas12a and circular RNAs in human cells
2024-01-11
In a study published in Nature Biotechnology, GAO Caixia's group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a series of new prime editors based on the Cas12a protein, further expanding the targeting scope and applications of precision genome editing.
Prime editing (PE) enables precise, targeted DNA insertions, deletions, and replacements. To date, all efficient prime editors have been based on Cas9. However, the Cas9 has certain disadvantages that limit the broad application of prime editors. For example, it is too large, experiences higher levels of off-target editing, and has limited effectiveness ...
A methodology for regulating fuel stratification and improving fuel economy of GCI mode via double main-injection strategy
2024-01-11
Exploring advanced combustion mode with high efficiency and low emissions has been the dream of successive generations of researchers. Conventional diesel engines have high compression ratios thus with thermal efficiencies of 35%–45%, but the diffusion combustion
characteristics of diesel make NOx and soot emissions high. Gasoline compression ignition (GCI) is an advanced combustion mode in the field of internal combustion engines, which combines the advantages of the high efficiency of diesel engines and the low emissions of gasoline engines. Although the GCI mode ...
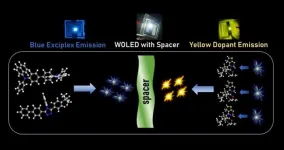
Exciplex route to white OLEDs: the role of spacer
2024-01-11
Organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) have matured to commercial level. Yet, their widespread market adoption is hindered due to high costs and complicated device architecture. Researchers are actively exploring innovative device engineering strategies to circumvent these issues.
Narayanan Unni and co-workers have tried to address the above challenges by exploiting a concept called exciplex. Exciplex emission is possible at the interface of two different materials which may not be luminescent themselves. This provides an opportunity to use relatively cheaper materials instead of costly fluorescent or phosphorescent emitter materials. They ...
PSE Healthy Energy awarded grant from the California Energy Commission
2024-01-11
OAKLAND, CA – The California Energy Commission (CEC) has selected PSE Healthy Energy to support their development of social cost and non-energy benefit metrics for the deployment of clean energy resources. These metrics will be used to evaluate scenarios for achieving California’s clean energy goals, including through California’s 100 percent clean energy target, as defined in Senate Bill 100 (SB100).
“Transitioning to 100 percent renewable and zero-carbon electricity resources by 2045 will reshape California’s energy systems,” ...
Nationwide study suggests link between medical cannabis for chronic pain and abnormal heart rhythm
2024-01-11
People taking medical cannabis for chronic pain have a slightly increased risk of arrhythmia, according to research published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Thursday). Arrhythmia is when the heart beats too slowly, too quickly or irregularly. It includes conditions like atrial fibrillation.
Recreational use of cannabis has been linked to cardiovascular disease but there has been very little research on the side effects of medical cannabis.
Researchers say the new study is important as a growing number of countries now permit medical cannabis as a treatment for chronic pain.
The study was ...
UQ leads the world’s largest drug survey
2024-01-11
Researchers from The University of Queensland have launched the world’s biggest drug survey, to gain insight into drug use around the globe.
The Global Drug Survey was founded by Professor Adam Winstock from University College London and has been running annually since 2012.
This year the survey is led by Dr Cheneal Puljevic from UQ’s School of Public Health.
“The aim of the Global Drug Survey is to make drug use safer for people, regardless of the drug’s legality,” Dr Puljevic said.
“We hope to gain insight ...
Panel members for new psychiatric ‘bible’ received over $14M from industry
2024-01-11
Sixty percent of US physicians serving as panel and task force members for the American Psychiatric Association’s official manual of psychiatric disorders received payments from industry totalling $14.24m, finds a study published by The BMJ.
Because of the enormous influence of diagnostic and treatment guidelines, the researchers say their findings “raise questions about the editorial independence of this diagnostic manual.”
Often referred to as the ‘bible’ of psychiatric disorders, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition, text revision (DSM-5-TR) ...
Perinatal depression linked to increased risk of death
2024-01-11
Women who suffer depression during or after pregnancy have a higher risk of death by both natural and unnatural causes, a new study of childbirth in Sweden published in The BMJ reports. The increased risk peaks in the month after diagnosis but remains elevated for as long as 18 years afterwards.
Women who develop perinatal depression, which is to say depression during pregnancy or shortly after childbirth, are generally twice as likely to die of natural or, as in most cases, unnatural causes. They are six times more likely to commit than women without this form of depression. The increase ...
Landmark national study supports use of whole genome sequencing in standard cancer care
2024-01-11
Study shows that combining whole genome sequence and clinical data together at scale supports the delivery of precision cancer care, where cancer diagnosis and treatment is tailored to the individual patient
Results support increased use of genomic testing in cancer care via the NHS Genomic Medicine Service
The research shows the value of data from the ground-breaking 100,000 Genomes Project to improve understanding of cancer and help researchers to develop new treatments.
In the largest study of its kind, scientists today report how combining health data with whole genome sequence (WGS) data in patients with cancer can help doctors provide more tailored care for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
[Press-News.org] Toward efficient spintronic materialsResearchers reveal how magnetization direction can be controlled using strain in an interfacial multiferroic material.