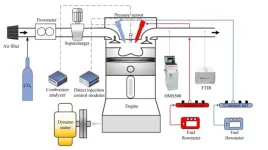
A methodology for regulating fuel stratification and improving fuel economy of GCI mode via double main-injection strategy
2024-01-11
(Press-News.org)
Exploring advanced combustion mode with high efficiency and low emissions has been the dream of successive generations of researchers. Conventional diesel engines have high compression ratios thus with thermal efficiencies of 35%–45%, but the diffusion combustion
characteristics of diesel make NOx and soot emissions high. Gasoline compression ignition (GCI) is an advanced combustion mode in the field of internal combustion engines, which combines the advantages of the high efficiency of diesel engines and the low emissions of gasoline engines. Although the GCI mode can achieve a high efficiency while maintaining low NOx and soot emissions, the GCI combustion still faces problems such as high maximum pressure rise rate (MPRR) and combustion deterioration at high loads.
A research group of Yong QIAN from Shanghai Jiao Tong University proposes a new methodology to improve the problems of high MPRR and combustion deterioration of the GCI mode at high loads. The new methodology called double main-injection (DMI) strategy was that two direct injectors were used for the simultaneously main-injection. By comparing DMI strategy with the single main-injection (SMI) strategy and conventional diesel combustion at high loads, they found that ① the simultaneous main-injection of the two direct injectors can achieve a rapid fuel supply and control of fuel stratification in the DMI mode, ② exhaust gas recirculation has a significant effect on the combustion and emissions of the DMI mode, ③ the DMI strategy achieves a highly efficient and stable combustion of the GCI mode, ④ the DMI strategy can alleviate the requirement of the GCI
mode on injection pressure and improve the problems of high MPRR and combustion deterioration.
The proposed new methodology-DMI strategy can improve the fuel economy and reduce MPRR at high loads, and it is of great significance to GCI mode. These findings were published in Frontiers in Energy on Jan. 10, 2023.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-11
Organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) have matured to commercial level. Yet, their widespread market adoption is hindered due to high costs and complicated device architecture. Researchers are actively exploring innovative device engineering strategies to circumvent these issues.
Narayanan Unni and co-workers have tried to address the above challenges by exploiting a concept called exciplex. Exciplex emission is possible at the interface of two different materials which may not be luminescent themselves. This provides an opportunity to use relatively cheaper materials instead of costly fluorescent or phosphorescent emitter materials. They ...
2024-01-11
OAKLAND, CA – The California Energy Commission (CEC) has selected PSE Healthy Energy to support their development of social cost and non-energy benefit metrics for the deployment of clean energy resources. These metrics will be used to evaluate scenarios for achieving California’s clean energy goals, including through California’s 100 percent clean energy target, as defined in Senate Bill 100 (SB100).
“Transitioning to 100 percent renewable and zero-carbon electricity resources by 2045 will reshape California’s energy systems,” ...
2024-01-11
People taking medical cannabis for chronic pain have a slightly increased risk of arrhythmia, according to research published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Thursday). Arrhythmia is when the heart beats too slowly, too quickly or irregularly. It includes conditions like atrial fibrillation.
Recreational use of cannabis has been linked to cardiovascular disease but there has been very little research on the side effects of medical cannabis.
Researchers say the new study is important as a growing number of countries now permit medical cannabis as a treatment for chronic pain.
The study was ...
2024-01-11
Researchers from The University of Queensland have launched the world’s biggest drug survey, to gain insight into drug use around the globe.
The Global Drug Survey was founded by Professor Adam Winstock from University College London and has been running annually since 2012.
This year the survey is led by Dr Cheneal Puljevic from UQ’s School of Public Health.
“The aim of the Global Drug Survey is to make drug use safer for people, regardless of the drug’s legality,” Dr Puljevic said.
“We hope to gain insight ...
2024-01-11
Sixty percent of US physicians serving as panel and task force members for the American Psychiatric Association’s official manual of psychiatric disorders received payments from industry totalling $14.24m, finds a study published by The BMJ.
Because of the enormous influence of diagnostic and treatment guidelines, the researchers say their findings “raise questions about the editorial independence of this diagnostic manual.”
Often referred to as the ‘bible’ of psychiatric disorders, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition, text revision (DSM-5-TR) ...
2024-01-11
Women who suffer depression during or after pregnancy have a higher risk of death by both natural and unnatural causes, a new study of childbirth in Sweden published in The BMJ reports. The increased risk peaks in the month after diagnosis but remains elevated for as long as 18 years afterwards.
Women who develop perinatal depression, which is to say depression during pregnancy or shortly after childbirth, are generally twice as likely to die of natural or, as in most cases, unnatural causes. They are six times more likely to commit than women without this form of depression. The increase ...
2024-01-11
Study shows that combining whole genome sequence and clinical data together at scale supports the delivery of precision cancer care, where cancer diagnosis and treatment is tailored to the individual patient
Results support increased use of genomic testing in cancer care via the NHS Genomic Medicine Service
The research shows the value of data from the ground-breaking 100,000 Genomes Project to improve understanding of cancer and help researchers to develop new treatments.
In the largest study of its kind, scientists today report how combining health data with whole genome sequence (WGS) data in patients with cancer can help doctors provide more tailored care for ...
2024-01-11
A Rutgers biophysical chemist and his brother, a political scientist on the West Coast, have joined intellectual forces, realizing a long-standing dream of co-authoring an article that bridges their disciplines involving cells and society.
In their paper, they have proposed that powerful parallels exist between the microscopic, natural world of cells and molecules and the human-forged realm of organizations and political systems.
Taking it a step further, the brothers – eminent scholars who have served as top leaders of their respective institutions – have proposed that humankind can draw lessons from what the microscopic and macroscopic worlds have in common. Ideally, ...
2024-01-11
A new wave of communication technology is quickly approaching and researchers at UBC Okanagan are investigating ways to configure next-generation mobile networks.
Dr. Anas Chaaban works in the UBCO Communication Theory Lab where researchers are busy analyzing a theoretical wireless communication architecture that will be optimized to handle increasing data loads while sending and receiving data faster.
Next-generation mobile networks are expected to outperform 5G on many fronts such as reliability, coverage and intelligence, explains Dr. Chaaban, an Assistant Professor ...
2024-01-11
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Jan. 10, 2024) – Researchers with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have received funding to better understand how personalized nutrition and exercise programs can improve quality of life after cancer treatment.
The three-year, approximately $700,000 grant from the Applebaum Foundation with added support by Sylvester, will fund the On Precision Oncology Interventions in Nutrition and Training (OnPOINT) clinical study to develop individualized diet and activity programs ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A methodology for regulating fuel stratification and improving fuel economy of GCI mode via double main-injection strategy