(Press-News.org) MIAMI, FLORIDA (Jan. 10, 2024) – Researchers with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have received funding to better understand how personalized nutrition and exercise programs can improve quality of life after cancer treatment.
The three-year, approximately $700,000 grant from the Applebaum Foundation with added support by Sylvester, will fund the On Precision Oncology Interventions in Nutrition and Training (OnPOINT) clinical study to develop individualized diet and activity programs for cancer survivors with complex needs.
“Initially, the study will focus on adults treated for breast, prostate and colorectal cancers,” said multiple principal investigator Tracy E. Crane, PhD, RDN, co-lead of Cancer Control and director of lifestyle medicine, prevention and digital health at Sylvester. “Those are the three most common cancer types among U.S. survivors today.”
According to the National Cancer Institute (NCI), breast, prostate and colorectal cancer patients represent more than half of all cancer survivors – about 9 million people nationwide.
Precision Interventions
Sylvester researchers named the trial OnPOINT because of its focus on individualized plans. While all study patients will participate in an eight-week diet and exercise program, the interventions will differ for survivors based on their needs, said co-investigator Paola Rossi, MD, clinical program director of lifestyle medicine at Sylvester.
“The Oncology field is moving toward the delivery of precise interventions – getting the right intervention at the right time, for the right patient,” she explained. “This study aims to do that with lifestyle strategies.”
Researchers will use data from 300 study recruits to develop and refine an algorithm that will help guide decision-making about precision lifestyle support. At baseline, researchers will evaluate patients’ physical fitness and diet using digital biometrics from wearable trackers, proven tests and self-reports of diet, exercise, sleeping habits and other activity. They’ll also assess survivors’ symptoms and quality of life to develop the interventions.
The algorithm will classify patients into one of three groups based on complexity, with varying intervention levels for each group. “For those whose needs fall into the high-complexity category, they will have one-on-one support with a dietitian and an exercise physiologist,” Crane explained. “Conversely, the low-complexity group may only need text-messaging support with a wearable device and journaling to keep on track.”
Researchers will reassess participants after eight weeks and again at six months.
“Our primary objective with this trial is to determine the feasibility of several approaches,” she continued. “We’re assessing wearable data and how it impacts clinical decision-making. “We’re assessing the algorithm. And we’re testing six different ways of delivering nutrition and exercise information.”
Provider Feedback
Another vital study component is learning what healthcare providers want to know about their patients and how involved they want to be with lifestyle modifications, Crane said. That’s where Sylvester’s proprietary My Wellness Research platform comes into play. It collects the data for researchers to transform into meaningful decision tools.
“We will create different visuals of patient-generated data in the electronic health record to obtain provider feedback on these presentations and what they think is most valuable to them,” Crane explained.
She added that there are plans to expand OnPoint study recruitment to include blood-cancer survivors.
“We are excited to offer this study and additional support for Sylvester patients,” Crane said. “It’s a big undertaking with a big goal to better predict where to focus interventions and services to help survivors live healthy, quality lives after cancer treatment.”
about the study on the InventUM blog and follow @SylvesterCancer for the latest in cancer research and care.
# # #
END
January 10, 2024, New Orleans, LA - College students interested in pursuing a career in cancer research are urged to apply to The Louisiana Cancer Research Center’s 8-week Summer Undergraduate Cancer Research Experience, SUCRE.
Selected students can explore and develop their interests by working in a research lab with an assigned faculty mentor from member institutions Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center - New Orleans, Tulane School of Medicine and Xavier University of Louisiana.
The program runs from Thursday, June 3 through Friday, July 26, 2024. ...
Beta Pictoris, a young planetary system located just 63 light-years away, continues to intrigue scientists even after decades of in-depth study. It possesses the first dust disk imaged around another star — a disk of debris produced by collisions between asteroids, comets, and planetesimals. Observations from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope revealed a second debris disk in this system, inclined with respect to the outer disk, which was seen first. Now, a team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to image the Beta Pictoris system (Beta Pic) has discovered a new, previously unseen structure.
The ...
Texas A&M AgriLife Research received more than $5.2 million in grant funding from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture for a project to address multiple aspects of the southern U.S. onion harvest system.
Subas Malla, Ph.D., Texas A&M AgriLife Research associate professor at the Texas A&M AgriLife Research and Extension Center in Uvalde, will serve as director for a short-day onion project. (Texas A&M AgriLife photo by Paul Schattenberg)
The director for the “Ensuring Future Economic Viability of U.S. Short-Day ...
Key points:
According to two trials of 11,000 pregnant women in India and in Tanzania, low-dose calcium supplementation (500 milligrams per day) appears as effective at reducing the risk of preeclampsia and preterm birth as high-dose calcium supplementation (1,500 milligrams per day).
The World Health Organization currently recommends high-dose calcium supplementation—equivalent to three calcium pills a day—for pregnant women in contexts with low-calcium diets, predominantly low- and middle-income countries. Lowering the pill burden to one 500mg ...
EAST LANSING, Mich. – The U.S. health care response during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic unveiled challenges in public health reporting systems and electronic clinical data exchange.
A new study led by John (Xuefeng) Jiang, Eli Broad Endowed Professor of Accounting in MSU’s Broad College of Business, examines U.S. hospitals’ experiences in public health reporting, accessing clinical data from external providers for COVID-19 patient care, and their success in reporting vaccine-related ...
The holidays may be over, but neuroscientists are getting a special gift to kick off the new year: access to a greatest hits collection from one of Janelia’s longest running and successful Project Teams.
Janelia’s FlyLight Project Team, which has worked for more than a decade to create tools to study the fly brain, is making a core collection of their best genetically engineered fly strains available to researchers worldwide through the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center. The brain images of these flies, along with hundreds of thousands of images from thousands of additional fly lines, are also now freely accessible through Janelia websites.
These ...
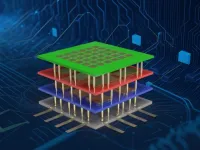
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Moore's Law, a fundamental scaling principle for electronic devices, forecasts that the number of transistors on a chip will double every two years, ensuring more computing power — but a limit exists.
Today's most advanced chips house nearly 50 billion transistors within a space no larger than your thumbnail. The task of cramming even more transistors into that confined area has become more and more difficult, according to Penn State researchers.
In a study ...
Hummingbirds use two distinct sensory strategies to control their flight, depending on whether they’re hovering or in forward motion, according to new research by University of British Columbia (UBC) zoologists.
“When in forward fight, hummingbirds rely on what we call an ‘internal forward model’—almost an ingrained, intuitive autopilot—to gauge speed,” says Dr. Vikram B. Baliga, lead author of a new study on hummingbird locomotion published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B. ...
Environmental epidemiologists at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, in collaboration with an interdisciplinary team of researchers at Oregon State University, Pacific Northwest National Labs, and Mt. Sinai School of Medicine, report on the findings of a new study of air pollution exposures collected using personal wristband monitors worn by pregnant individuals in New York City matched with data from a questionnaire. Factors predictive of exposures to air pollution include income, time spent outdoors, maternal age, country of birth, transportation type, and season.
The researchers examined an unprecedented number ...
URBANA, Ill. — Urban agriculture has the potential to decentralize food supplies, provide environmental benefits like wildlife habitat, and mitigate environmental footprints, but researchers have identified knowledge gaps regarding both the benefits and risks of urban agriculture and the social processes of growing more food in urban areas.
In a new paper published in Nature Food, an interdisciplinary group of experts, including a researcher from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, survey ...