(Press-News.org) (Santa Barbara, Calif.) — The sun has just set on a quiet mudflat in Australia’s Northern Territory; it’ll set again in another 19 hours. A young moon looms large over the desolate landscape. No animals scurry in the waning light. No leaves rustle in the breeze. No lichens encrust the exposed rock. The only hint of life is some scum in a few puddles and ponds. And among it lives a diverse microbial community of our ancient ancestors.
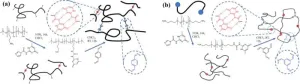
In a new account of exquisitely preserved microfossils, researchers at UC Santa Barbara and McGill University revealed that eukaryotic organisms had already evolved into a diverse array of forms even 1.64 billion years ago. The paper, published in the journal Papers in Paleontology, recounts an assemblage of eukaryotic fossils from an era early in the group’s evolutionary history. The authors describe four new taxa, as well as evidence of several advanced characteristics already present in these early eukaryotes.
“These are among the oldest eukaryotes that have ever been discovered,” explained lead author Leigh Anne Riedman, an assistant researcher in UCSB’s Department of Earth Science. “Yet, even in these first records we’re seeing a lot of diversity.”
Eukarya forms one of the major domains of life, encompassing the plant, animal and fungi clades, as well as all other groups whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus, like protists and seaweeds. Many scientists had thought early eukaryotes were all fairly similar during the late Paleoproterozoic, and that diversification took place around 800 million years ago. But Riedman and her co-authors found fossils of a delightfully diverse, and complex, cast of characters in rock nearly twice as old.
Scientists knew from previous studies that eukaryotes had evolved by this time, but their diversity in this era was poorly understood. So Riedman headed to the Outback in late 2019. Within one week, she had collected about 430 samples from eight cores drilled by a prospecting company; they now reside in the library of the Northern Territory Geological Survey. The two cores used for this study spanned roughly 500 meters of stratigraphy, or 133 million years, with around 15 million years of significant deposition.
Riedman returned to the United States with shale and mudstone: remnants of an ancient coastal ecosystem that alternated between shallow, subtidal mudflats and coastal lagoons. A dip in hydrofluoric acid dissolved the matrix rock, concentrating the precious microfossils which she then analyzed under the microscope.
“We were hoping to find species with interesting and different characteristics to their cell walls,” Riedman said. She hoped that these features could shed light on what was happening within the cells during this time period. Reaching any conclusions about the cellular interior would require a great deal of sleuthing, though, since the fossils preserve only the exterior of the cells.
The researchers were surprised by the diversity and complexity preserved in these fossils. They recorded 26 taxa, including 10 previously undescribed species. The team found indirect evidence of cytoskeletons, as well as platy structures that suggest the presence of internal vesicles in which the plates were formed — perhaps ancestral to Golgi bodies, present in modern eukaryotic cells. Other microbes had cell walls made of bound fibers, similarly suggestive of the presence of a complex cytoskeleton.
The authors also found cells with a tiny trapdoor, evidence of a degree of sophistication. Some microbes can form a cyst to wait out unfavorable environmental conditions. In order to emerge, they need to be able to etch an opening in their protective shell. Making this door is a specialized process. “If you’re going to produce an enzyme that dissolves your cell wall, you need to be really careful about how you use that enzyme,” Riedman said. “So in one of the earliest records of eukaryotes, we’re seeing some pretty impressive levels of complexity.”
Many people in the field had thought this ability emerged later, and the evidence for it in this assemblage further emphasizes how diverse and advanced eukaryotes were even at this early juncture. “The assumption has always been that this is around the time that eukaryotes appeared. And now we think that people just haven’t explored older rocks,” said co-author Susannah Porter, an Earth science professor at UC Santa Barbara.
This paper is part of a larger project investigating early eukaryote evolution. Riedman and Porter want to know in what environments early eukaryotes were diversifying, why they were there, when they migrated to other places, and what adaptations they needed in order to fill those new niches.
A big part of this effort involves understanding when different characteristics of eukaryotes first arose. For instance, the authors are quite interested to learn whether these organisms were adapted to oxygenated or anoxic environments. The former would suggest that they had an aerobic metabolism, and possibly mitochondria. Every modern eukaryote that’s been found descends from ancestors that possessed mitochondria. This suggests that eukaryotes acquired the organelle very early on, and that it provided a significant advantage.
Riedman and Porter are currently working on a fresh account of eukaryote diversity through time. They’ve also collected even older samples from Western Australia and Minnesota. Meanwhile, their geochemist collaborators at McGill are spearheading a study on oxygen levels and preferred eukaryote habitats, aspects that could shed light on their evolution.
“These results are a directive to go look for older material, older eukaryotes, because this is clearly not the beginning of eukaryotes on Earth,” Riedman said.
END
Even the oldest eukaryote fossils show dazzling diversity and complexity
Researchers at UC Santa Barbara and McGill University revealed that eukaryotic organisms had already evolved into a diverse array of forms even 1.64 billion years ago
2024-01-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UTEP researchers discover compound that fights leukemia, lymphoma
2024-01-11
EL PASO, Texas (Jan. 11, 2024) – Researchers at The University of Texas at El Paso have identified a novel pharmaceutical compound that successfully kills leukemia and lymphoma cancer cells, potentially paving the way for new forms of therapy.
Renato Aguilera, Ph.D., a professor in the Department of Biological Sciences, is the principal investigator on the project that identified the promising compound, called thiophene F-8. His team’s findings were recently published in the research journal PLOS One.
“The main ...
C-path to lead new task force aimed at accelerating drug development for mitochondrial and inherited metabolic diseases
2024-01-11
TUCSON, Ariz., January 11, 2024 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) today announced the launch of a task force focused on accelerating drug development for mitochondrial and inherited metabolic diseases. The task force will lay the groundwork for specific solutions, offering valuable insights that aim to contribute to regulatory decision-making.
C-Path’s demonstrated expertise will be leveraged to ensure success, specifically its track record in generating tangible solutions that have accelerated drug development in rare and pediatric ...
Molecularly designing polymer networks to control sound damping
2024-01-11
The world is filled with a myriad of sounds and vibrations—the gentle tones of a piano drifting down the hall, the relaxing purr of a cat laying on your chest, the annoying hum of the office lights. Imagine being able to selectively tune out noises of a certain frequency. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have synthesized polymer networks with two distinct architectures and crosslink points capable of dynamically exchanging polymer strands to understand how the network connectivity and bond exchange mechanisms govern the overall damping behavior of the network. The incorporation of dynamic bonds into the polymer network demonstrates ...
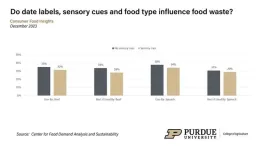
Year-end survey spotlights food safety, age-related consumer behavior, out-of-stock trends
2024-01-11
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Building off the previous month’s survey, the December 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report digs deeper into the relationships between food-date labels and the decision to discard food. The report also explores generational differences in food behaviors and reviews 2023 trends for out-of-stock items and common foods that people reported limiting in their diets over the year.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support ...
Mike Norvell named 2023 Paul “Bear” Bryant Coach of the Year
2024-01-11
HOUSTON, January 10, 2024 – Mike Norvell, head coach at Florida State University, was named college football Coach of the Year at the American Heart Association’s Paul “Bear” Bryant Awards, presented by Marathon Oil. The 38th annual awards program benefits the American Heart Association, the world’s leading voluntary health organization devoted to a world of longer, healthier lives for all.
In his fourth season as the head coach at Florida State, Norvell led the Seminoles to a 13-1 overall record and an 8-0 mark in the Atlantic Coast Conference (ACC). Norvell was previously honored as the ACC Coach of the Year and was ...
Study reveals wastewater surveillance is key tool in keeping schools open during public health emergencies
2024-01-11
Wastewater surveillance is a potent tool in understanding COVID-19 transmission within school settings, according to a ground-breaking study led by epidemiologist David Larsen from Syracuse University.
The research team’s work that was published recently in PLOS Global Public Health establishes the pivotal role of wastewater analysis in managing the public health response to COVID-19 at schools.
The study focused on a middle and high school campus in Jefferson County, New York, serving 600 students and compared results from wastewater surveillance to COVID-19 case trends. The surveillance ...
Loss of executive function may signal onset of neurodegenerative condition FXTAS
2024-01-11
New UC Davis research shows that men with an FMR1 premutation who experienced reduced executive function were at higher likelihood of developing fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS).
FXTAS is a progressive genetic condition that causes movement issues and cognitive decline. These findings, published in the journal Movement Disorders, could help clinicians determine which premutation carriers will eventually develop FXTAS.
“There's converging evidence that the premutation is affecting certain circuits in the brain ...
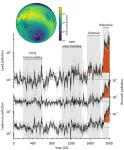
The first assessment of toxic heavy metal pollution in the Southern Hemisphere over the last 2,000 years
2024-01-11
Human activity, from burning fossil fuels and fireplaces to the contaminated dust produced by mining, alters Earth’s atmosphere in countless ways. Records of these impacts over time are preserved in everlasting polar ice that serves as a sort of time capsule, allowing scientists and historians to link Earth’s history with that of human societies. In a new study, ice cores from Antartica show that lead and other toxic heavy metals linked to mining activities polluted the Southern Hemisphere as early as the 13th century.
“Seeing evidence that early Andean ...
Bulky additives could make cheaper solar cells last longer
2024-01-11
Images
An insight into preventing perovskite semiconductors from degrading quickly, discovered at the University of Michigan, could help enable solar cells estimated to be two to four times cheaper than today's thin-film solar panels.
Perovskites may also be combined with the silicon-based semiconductors that are prevalent in today's solar panels to create "tandem" solar cells that could surpass the maximum theoretical efficiency of silicon solar cells.
"Silicon solar cells are great because they are very efficient and can last for a very long time, but the high efficiency comes with a high cost," ...
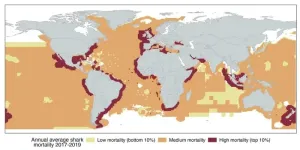
A global study reveals pathways to save threatened sharks, despite rising mortality trends
2024-01-11
Sharks have persisted as powerful ocean predators for more than 400 million years. They survived five mass extinctions, diversifying into an amazing variety of forms and lifestyles. But this ancient lineage is now among the world's most threatened species groups due to overexploitation in poorly regulated fisheries and the proliferation of wasteful finning practices.
Governments around the world have introduced a host of regulations aimed at reducing shark catch and finning, the latter of which typically sees valuable shark fins retained for sale while carcasses are discarded at sea. But until ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Even the oldest eukaryote fossils show dazzling diversity and complexityResearchers at UC Santa Barbara and McGill University revealed that eukaryotic organisms had already evolved into a diverse array of forms even 1.64 billion years ago