(Press-News.org)
Images
An insight into preventing perovskite semiconductors from degrading quickly, discovered at the University of Michigan, could help enable solar cells estimated to be two to four times cheaper than today's thin-film solar panels.
Perovskites may also be combined with the silicon-based semiconductors that are prevalent in today's solar panels to create "tandem" solar cells that could surpass the maximum theoretical efficiency of silicon solar cells.
"Silicon solar cells are great because they are very efficient and can last for a very long time, but the high efficiency comes with a high cost," said Xiwen Gong, U-M assistant professor of chemical engineering. "To make high-purity silicon, temperatures over 1,000 degrees Celsius are needed. Otherwise, the efficiency won't be as good."
The high temperature comes with higher economic and environmental costs. But while perovskites can be produced at lower temperatures, they degrade when exposed to heat, moisture and air. As a result, the lifespan of perovskite today is too short to be commercially competitive in solar panels.
Gong's research aims to make hardier perovskite solar cells, and her latest study published in the journal Matter suggests that bulky "defect pacifying" molecules are best at increasing the perovskites' stability and overall lifespan.
Perovskite crystals contain lead atoms that aren't fully bound to the other components within the perovskite. Such "undercoordinated sites" are defects often found on the crystal surfaces and at grain boundaries where there's a break in the crystal lattice. These defects hinder the movement of electrons and speed up the decay of the perovskite material.
Engineers already know that mixing defect pacifying molecules into the perovskites can help lock up the undercoordinated lead, in turn preventing other imperfections from forming at high temperatures. But until now, engineers didn't know exactly how a given molecule affected the hardiness of perovskite cells.
"We wanted to figure out what features on the molecules specifically improve the perovskite's stability," said Hongki Kim, a former postdoctoral researcher in chemical engineering and one of the study's first authors.
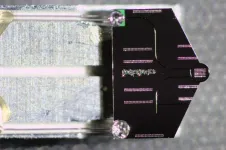
To investigate the problem, Gong's team created three additives with a range of shapes and sizes and added them into thin films of perovskite crystals, which can absorb light and convert it to electricity. Each additive contained the same or similar chemical building blocks, which made size, weight and arrangement the main properties differentiating them.
Then, the team measured how strongly the different additives interacted with perovskites and consequently influenced the formation of defects in the films. Larger molecules by mass were better at sticking to the perovskite because they had more binding sites that interact with perovskite crystals. As a result, they tended to be better at preventing defects from forming.
But the best additives also needed to take up a lot of space. Large but skinny molecules resulted in smaller perovskite grains during the manufacturing process. Smaller grains aren't ideal because they also create perovskite cells with more grain boundaries, or more areas for defects to form. In contrast, bulky molecules forced larger perovskite grains to form, which in turn reduced the density of grain boundaries in the film.
Heating the perovskite films to over 200 degrees Celsius confirmed that bulky additives helped the films retain more of their characteristic slate black color and develop fewer structural defects.
"Both the size and configuration are important when designing additives, and we believe this design philosophy could be implemented across various perovskite formulations to further improve the lifetime of perovskite solar cells, light emitting devices and photodetectors," said Carlos Alejandro Figueroa Morales, a doctoral student in macromolecular science and engineering and one of the study's first authors.
Xiwen Gong is also an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering, materials science and engineering, macromolecular science and engineering, and applied physics. The research was funded by the University of Michigan and relied on a scanning electron microscope funded by the National Science Foundation. Co-author Nancy Muyanja led the microscopy measurements at the Michigan Center for Materials Characterization.
Study: Molecular Design of Defect Passivators for Thermally Stable Metal Halide Perovskite Films (DOI: 10.1016/j.matt.2023.12.003)
END
Bulky additives could make cheaper solar cells last longer
Findings could help engineers methodically find best molecules to increase lifespan of perovskite solar cells, rather than relying on time-consuming trial and error
2024-01-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
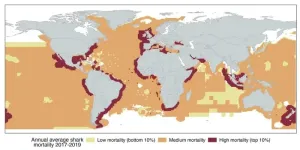
A global study reveals pathways to save threatened sharks, despite rising mortality trends
2024-01-11
Sharks have persisted as powerful ocean predators for more than 400 million years. They survived five mass extinctions, diversifying into an amazing variety of forms and lifestyles. But this ancient lineage is now among the world's most threatened species groups due to overexploitation in poorly regulated fisheries and the proliferation of wasteful finning practices.
Governments around the world have introduced a host of regulations aimed at reducing shark catch and finning, the latter of which typically sees valuable shark fins retained for sale while carcasses are discarded at sea. But until ...
Discovered in the Upper Amazon: 2500-year-old landscape providing evidence for early urbanism in the region
2024-01-11
A dense system of pre-Hispanic urban centers, characterized by constructed platforms and plazas and connected by large, straight roads, has been discovered in the upper Amazon, according to a new study. The research, based on more than 20 years of interdisciplinary research, suggests that this original 2500-year-old society constitutes the earliest and largest low-density agrarian urbanism documented in the Amazon thus far. Such extensive early development in the Upper Amazon resembles similar Maya urban systems in Central America. ...
Machine learning clinical prediction models fail to generalize across trial data
2024-01-11
Clinical prediction models for schizophrenia treatment outcomes that work well within the trials from which they were developed fail to generalize to future trials, according to a new study. “The findings not only highlight the necessity for more stringent methodological standards for machine learning approaches but also require reexamination of the practical challenges that precision medicine is facing,” writes Frederike Petzschner in a related Perspective. Despite receiving the same treatments for the same afflictions, some patients get better while others show no improvement. Precision medicine approaches seek to address this problem by providing tailored treatments for individual ...
Shark fishing mortality on the rise despite regulatory change
2024-01-11
Despite widespread legislation and fishing regulations aimed at reducing wasteful shark finning practices, global shark fishing mortality is still on the rise, researchers report. The findings suggest that improved regulations are needed to reverse the continued overexploitation of these species. Over the last several decades, sharks have been increasingly recognized as some of the planet’s most threatened wildlife. Increasing shark mortality has been driven in part by overfishing – large numbers of sharks are often captured as bycatch in tuna ...
Comprehensive assessment reveals high extinction risks for thousands of Atlantic Forest trees in eastern South America
2024-01-11
A comprehensive analysis of tree species’ conservation statuses across Atlantic Forest trees reveals high extinction risks. According to the report, roughly two-thirds of the 4950 tree species living in this biodiversity hotspot are threatened with extinction. This includes 82% of endemic species, which have quite limited geographic ranges. Based on these findings, the authors suggest that the conservation status of tropical forests worldwide may be worse than previously believed. Conservation efforts and decisions often ...
Lab-grown retinas explain why people see colors dogs can’t
2024-01-11
With human retinas grown in a petri dish, researchers discovered how an offshoot of vitamin A generates the specialized cells that enable people to see millions of colors, an ability that dogs, cats, and other mammals do not possess.
“These retinal organoids allowed us for the first time to study this very human-specific trait,” said author Robert Johnston, an associate professor of biology. “It’s a huge question about what makes us human, what makes us different.”
The findings, published in PLOS Biology, increase understanding of color ...
KAUST scientists unveil blueprint for affordable solar cells to power Saudi Arabia and beyond
2024-01-11
Thuwal, Saudi Arabia, Month Day, Year – Scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) have unveiled a roadmap for bringing perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells to market, paving the way for a future powered by abundant, inexpensive clean energy in Saudi Arabia and the world.
The authors of the article, published in esteemed journal Science, include Prof. Stefaan De Wolf and his research team at the KAUST Solar Center.
The team is working on improving solar efficiency to meet Saudi Arabia’ solar targets.
Perovskite/silicon tandem technology combines the strengths of two materials – perovskite's efficient ...
Quest for personalized medicine hits a snag
2024-01-11
New Haven, Conn. — The quest for personalized medicine, a medical approach in which practitioners use a patient’s unique genetic profile to tailor individual treatment, has emerged as a critical goal in the health care sector. But a new Yale-led study shows that the mathematical models currently available to predict treatments have limited effectiveness.
In an analysis of clinical trials for multiple schizophrenia treatments, the researchers found that the mathematical algorithms were able to predict patient outcomes within the specific ...
Bridging light and electrons
2024-01-11
When light goes through a material, it often behaves in unpredictable ways. This phenomenon is the subject of an entire field of study called “nonlinear optics”, which is now integral to technological and scientific advances from laser development and optical frequency metrology, to gravitational wave astronomy and quantum information science.
In addition, recent years have seen nonlinear optics applied in optical signal processing, telecommunications, sensing, spectroscopy, light detection and ranging. All these applications involve the miniaturization of devices ...
Climate change spells disaster for termite-loving numbats
2024-01-11
Australia is known for its wonderous and unique wildlife. But, just like the rest of the world, Australia is expected to get even hotter because of climate change. This could spell disaster for many of the marsupials that call the drier regions of the country home as it may get too hot for them to handle. To make things even more difficult, many of these marsupials are endangered thanks to habitat loss and introduced species such as domestic cats and red foxes. Therefore, finding a way to study these animals without disturbing them is critical to ensure their survival. This realisation led Christine Cooper (Curtin University, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
[Press-News.org] Bulky additives could make cheaper solar cells last longerFindings could help engineers methodically find best molecules to increase lifespan of perovskite solar cells, rather than relying on time-consuming trial and error