(Press-News.org)
When light goes through a material, it often behaves in unpredictable ways. This phenomenon is the subject of an entire field of study called “nonlinear optics”, which is now integral to technological and scientific advances from laser development and optical frequency metrology, to gravitational wave astronomy and quantum information science.
In addition, recent years have seen nonlinear optics applied in optical signal processing, telecommunications, sensing, spectroscopy, light detection and ranging. All these applications involve the miniaturization of devices that manipulate light in nonlinear ways onto a small chip, enabling complex light interactions chip-scale.
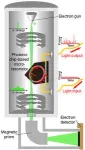
Now, a team of scientists at EPFL and the Max Plank Institute has brought nonlinear optical phenomena into a transmission electron microscope (TEM), a type of microscope that uses electrons for imaging instead of light. The study was led by Professor Tobias J. Kippenberg at EPFL and Professor Claus Ropers, Director of the Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences. It is now published in Science.
At the heart of the study are “Kerr solitons”, waves of light that hold their shape and energy as they move through a material, like a perfectly formed surf wave traveling across the ocean. This study used a particular type of Kerr solitons called “dissipative”, which are stable, localized pulses of light that last tens of femtoseconds (a quadrillionth of a second) and form spontaneously in the microresonator. Dissipative Kerr solitons can also interact with electrons, which made them crucial for this study.
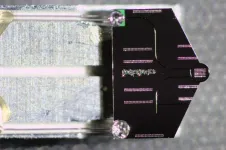
The researchers formed dissipative Kerr solitons inside a photonic microresonator, a tiny chip that traps and circulates light inside a reflective cavity, creating the perfect conditions for these waves. “We generated various nonlinear spatiotemporal light patterns in the microresonator driven by a continuous-wave laser,” explains EPFL researcher Yujia Yang, who led the study. “These light patterns interacted with a beam of electrons passing by the photonic chip, and left fingerprints in the electron spectrum.”
Specifically, the approach demonstrated the coupling between free electrons and dissipative Kerr solitons, which allowed the researchers to probe soliton dynamics in the microresonator cavity and perform ultrafast modulation of electron beams.
“Our ability to generate dissipative Kerr solitons [DKS] in a TEM extends the use of microresonator-base frequency combs to unexplored territories,” says Kippenberg. “The electron-DKS interaction could enable high repetition-rate ultrafast electron microscopy and particle accelerators empowered by a small photonic chip.”
Ropers adds: “Our results show electron microscopy could be a powerful technique for probing nonlinear optical dynamics at the nanoscale. This technique is non-invasive and able to directly access the intracavity field, key to understanding nonlinear optical physics and developing nonlinear photonic devices.”
The photonic chips were fabricated in the Center of MicroNanoTechnology (CMi) and the Institute of Physics cleanroom at EPFL. The experiments were conducted at the Göttingen Ultrafast Transmission Electron Microscopy (UTEM) Lab.
Other contributors
EPFL Center for Quantum Science and Engineering
Reference
Yujia Yang, Jan-Wilke Henke, Arslan S. Raja, F. Jasmin Kappert, Guanhao Huang, Germaine Arend, Zheru Qiu, Armin Feist, Rui Ning Wang, Aleksandr Tusnin, Alexey Tikan, Claus Ropers, Tobias J. Kippenberg. Free-electron interaction with nonlinear optical states in microresonators. Science, 12 January 2024. DOI: 10.1126/science.adk2489
END
Australia is known for its wonderous and unique wildlife. But, just like the rest of the world, Australia is expected to get even hotter because of climate change. This could spell disaster for many of the marsupials that call the drier regions of the country home as it may get too hot for them to handle. To make things even more difficult, many of these marsupials are endangered thanks to habitat loss and introduced species such as domestic cats and red foxes. Therefore, finding a way to study these animals without disturbing them is critical to ensure their survival. This realisation led Christine Cooper (Curtin University, ...
Embargoed for release until 1:00 p.m. ET on Thursday 11 January 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find a summary for new article that will be published in of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summary is not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
-------------------------------------------------
ACIP ...
Curtin University research using thermal imaging of numbats in Western Australia has found that during hot weather the endangered animals are limited to as little as ten minutes of activity in the sun before they overheat to a body temperature of greater than 40°C.
Lead author Dr Christine Cooper, from Curtin’s School of Molecular and Life Sciences, said despite using techniques such as raising or flattening their fur to regulate body temperature, numbats were prone to overheating, which was an important consideration for future conservation efforts, particularly given our warming climate.
“Active only during ...
In an editorial in the Annals of Internal Medicine, CUNY SPH Distinguished Lecturer Scott Ratzan, Senior Scholar Ken Rabin, and colleagues call for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to “raise its persuasive communications game” on adult immunization to clinicians and the public. They argue that disseminating scientific information alone will not suffice in the present environment of disinformation and low trust in public health.
The editorial is in response to the CDC’s ...
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce that JMIR Biomedical Engineering has passed the Scientific Quality Review by the US National Library of Medicine (NLM) for PubMed Central (PMC). This decision reflects the scientific and editorial quality of the journal. All articles published from 2021 onward will be found on PMC and PubMed after their technical evaluation.
Launched in 2016, JMIR Biomedical Engineering is a sister journal of Journal of Medical Internet Research (the leading open-access journal in health informatics), focused on the application of engineering principles, ...
At the center of most large galaxies lives a supermassive black hole (SMBH). The Milky Way has Sagittarius A*, a mostly dormant SMBH whose mass is around 4.3 million times that of the sun. But if you look deeper into the universe, there are vastly larger SMBHs with masses that can reach up to tens of billions of times the mass of our sun.
Black holes grow in mass by gravitationally consuming objects in their near vicinity, including stars. It’s a catastrophic and destructive end for stars unlucky enough to be swallowed by SMBHs, but fortunate for scientists who now have an opportunity to probe otherwise-dormant centers of galaxies.
TDEs Light the Way
As the name ...
A new study sheds light on how autophagy, the body’s process for removing damaged cell parts, when impaired, can play a role in causing heart failure. The research team led by Dr. E. Dale Abel, chair of the Department of Medicine at UCLA and Dr. Quanjiang Zhang, adjunct assistant professor of medicine at UCLA, identified a signaling pathway that links autophagy to the control of cellular levels of a key coenzyme known as NAD+, which is found in all living cells and is central to how our metabolism works. Researchers say these findings may have implications ...
Phytoplankton or microalgae found in the ocean are often known to produce a sulfur-containing chemical called dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP). This organic molecule breaks down to release a strong but sweet-smelling gas called dimethyl sulfide (DMS), which plays a major role in the formation of cloud condensation nuclei and is also associated with the smell of the sea. More importantly, DMSP acts as an osmolyte and thus protects the phytoplankton against the osmotic pressure created by saline water.
Scientists have, however, ...
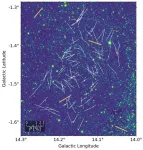
A team of astronomers including those from the University of Tokyo created the first-ever map of magnetic field structures within a spiral arm of our Milky Way galaxy. Previous studies on galactic magnetic fields only gave a very general picture, but the new study reveals that magnetic fields in the spiral arms of our galaxy break away from this general picture significantly and are tilted away from the galactic average by a high degree. The findings suggest magnetic fields strongly impact star-forming regions which means they played a part in the creation of our own solar system.
It might come as a surprise to ...
Researchers have identified a 3D fragment of fossilized skin that is at least 21 million years than previously described skin fossils. The skin, which belonged to an early species of Paleozoic reptile, has a pebbled surface and most closely resembles crocodile skin. It’s the oldest example of preserved epidermis, the outermost layer of skin in terrestrial reptiles, birds, and mammals, which was an important evolutionary adaptation in the transition to life on land. The fossil is described on January 11 in the journal Current Biology along with several other specimens that were collected from the Richards Spur ...