(Press-News.org) In an editorial in the Annals of Internal Medicine, CUNY SPH Distinguished Lecturer Scott Ratzan, Senior Scholar Ken Rabin, and colleagues call for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to “raise its persuasive communications game” on adult immunization to clinicians and the public. They argue that disseminating scientific information alone will not suffice in the present environment of disinformation and low trust in public health.
The editorial is in response to the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) Recommended Adult Immunization Schedule, unveiled in an article in the same journal edition. The authors argue that the schedule misses an opportunity to provide physicians with useful communication guidance around adult vaccines and to address co-administration of influenza, RSV, and COVID-19 vaccines.
Ratzan and team say the recent formation of the Council for Quality Health Communication and the Coalition for Trust in Health and Science, which seek to advance health communication using evidence-based communication and media technologies, is a testament to the need to upgrade health communication.
“Simply ‘informing’ people about immunization schedule changes is not enough,” the authors write. “We need a coordinated, national effort to apply our understanding of current attitudes toward vaccination and implement new health communication strategies that use a full palette of techniques to build vaccine literacy and encourage greater acceptance.”
Read the full editorial here.
END
A call for improved CDC communication on adult immunization
2024-01-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
JMIR Biomedical Engineering has passed the Scientific Quality Review by NLM for PMC
2024-01-11
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce that JMIR Biomedical Engineering has passed the Scientific Quality Review by the US National Library of Medicine (NLM) for PubMed Central (PMC). This decision reflects the scientific and editorial quality of the journal. All articles published from 2021 onward will be found on PMC and PubMed after their technical evaluation.
Launched in 2016, JMIR Biomedical Engineering is a sister journal of Journal of Medical Internet Research (the leading open-access journal in health informatics), focused on the application of engineering principles, ...
Close encounters of the supermassive black hole kind: tidal disruption events and what they can reveal about black holes and stars in distant galaxies
2024-01-11
At the center of most large galaxies lives a supermassive black hole (SMBH). The Milky Way has Sagittarius A*, a mostly dormant SMBH whose mass is around 4.3 million times that of the sun. But if you look deeper into the universe, there are vastly larger SMBHs with masses that can reach up to tens of billions of times the mass of our sun.
Black holes grow in mass by gravitationally consuming objects in their near vicinity, including stars. It’s a catastrophic and destructive end for stars unlucky enough to be swallowed by SMBHs, but fortunate for scientists who now have an opportunity to probe otherwise-dormant centers of galaxies.
TDEs Light the Way
As the name ...
Study reveals new connection between impaired autophagy and heart failure
2024-01-11
A new study sheds light on how autophagy, the body’s process for removing damaged cell parts, when impaired, can play a role in causing heart failure. The research team led by Dr. E. Dale Abel, chair of the Department of Medicine at UCLA and Dr. Quanjiang Zhang, adjunct assistant professor of medicine at UCLA, identified a signaling pathway that links autophagy to the control of cellular levels of a key coenzyme known as NAD+, which is found in all living cells and is central to how our metabolism works. Researchers say these findings may have implications ...
Exploring dimethylsulfoniopropionate production by freshwater phytoplankton in lake Baikal
2024-01-11
Phytoplankton or microalgae found in the ocean are often known to produce a sulfur-containing chemical called dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP). This organic molecule breaks down to release a strong but sweet-smelling gas called dimethyl sulfide (DMS), which plays a major role in the formation of cloud condensation nuclei and is also associated with the smell of the sea. More importantly, DMSP acts as an osmolyte and thus protects the phytoplankton against the osmotic pressure created by saline water.
Scientists have, however, ...
Our surprising magnetic galaxy
2024-01-11
A team of astronomers including those from the University of Tokyo created the first-ever map of magnetic field structures within a spiral arm of our Milky Way galaxy. Previous studies on galactic magnetic fields only gave a very general picture, but the new study reveals that magnetic fields in the spiral arms of our galaxy break away from this general picture significantly and are tilted away from the galactic average by a high degree. The findings suggest magnetic fields strongly impact star-forming regions which means they played a part in the creation of our own solar system.
It might come as a surprise to ...
Oldest known fossilized skin is 21 million years older than previous examples
2024-01-11
Researchers have identified a 3D fragment of fossilized skin that is at least 21 million years than previously described skin fossils. The skin, which belonged to an early species of Paleozoic reptile, has a pebbled surface and most closely resembles crocodile skin. It’s the oldest example of preserved epidermis, the outermost layer of skin in terrestrial reptiles, birds, and mammals, which was an important evolutionary adaptation in the transition to life on land. The fossil is described on January 11 in the journal Current Biology along with several other specimens that were collected from the Richards Spur ...
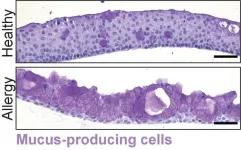
Producing tears in a dish: researchers develop first model of human conjunctiva
2024-01-11
The Organoid group at the Hubrecht Institute produced the first organoid model of the human conjunctiva. These organoids mimic the function of the actual human conjunctiva, a tissue involved in tear production. Using their new model, the researchers discovered a new cell type in this tissue: tuft cells. The tuft cells become more abundant under allergy-like conditions and are therefore likely to play a role in allergies. The organoid model can now be used to test drugs for several diseases affecting the conjunctiva. The study will be published in Cell Stem Cell on 11 January 2024.
Our eyes produce tears to protect themselves from injuries and ...
Palaeontology: New dinosaur species may be closest known relative of Tyrannosaurus rex
2024-01-11
A new species of tyrannosaur from southern North America that may the closest known relative of Tyrannosaurus rex is described in a study published in Scientific Reports.
Sebastian Dalman and colleagues identified the new species — which they have named Tyrannosaurus mcraeensis — by examining a fossilised partial skull, which was previously discovered in the Hall Lake Formation, New Mexico, USA. Although these remains were initially assigned to T. rex and are comparable in size to those of T. rex (which was up to 12 metres long), the authors propose that they belong to a new species due ...
Research shows deadly brain cancer can mimic healthy neurons
2024-01-11
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL JAN. 11, 2024, at 11 AM EST) – Certain cancers are more difficult to treat because they contain cells that are highly skilled at evading drugs or our immune systems by disguising themselves as healthy cells.
Glioblastoma, for example, an incurable brain cancer, is characterized by cells that can mimic human neurons, even growing axons and making active connections with healthy brain neurons. This cancer is usually deadly – average survival time is just over one year from diagnosis ...
High-dose radiotherapy with chemotherapy effective in treating people with non-small cell lung cancer
2024-01-11
A new study led by researchers from the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center shows that using high doses of radiation while integrating an ablative radiotherapy technique called stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) concurrently with chemotherapy is safe and effective in treating people with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer that is not suitable for surgery.
Based on mid-treatment response, researchers found the combination treatment, which involves a second radiation plan to personalize a boost for the last third of radiation treatments, is a viable and promising option that helps reduce the risk of toxic side effects and having the cancer ...