Between building and unbuilding: An interdisciplinary design approach to cohabitation, material cycles, and traditional ecological knowledge
2024-01-12
(Press-News.org)
In recent history, built environment practices have accepted a paradigm which underlines the land’s static quality, prioritizes immediate utility, and consequently adopts design processes that inevitably accelerate assimilation. With the capitalist propensity to obtain control and enhance efficiency, those processes nevertheless privilege certain cultures while rejecting other forms of knowledge or living specific to the land. The design discourse, confronted with the rising pressure of global climate challenges and environmental inequity, suggests a shift of design pattern from static to responsive as a means to an end that is part of nature’s transformation.
Located amid the semi-arid play a of Nevada in the USA, Fly Ranch sits on land remote yet crisscrossed by industrial activity, with extreme climatic conditions yet teeming with life and traditions. Working with these contradictions, “Lodgers,” the project to be constructed in Fly Ranch, is grounded in three key approaches to challenging contemporary architectural practice. Firstly, prioritize the well-being of all plants and animals species, including humans, by creating cohabitation spaces. Secondly, utilize local or nearby building resources to minimize waste, maintain ecological balance, and rebuild the material cycle. Finally, integrate Traditional Ecological Knowledge with modern building practices and employ low-tech construction techniques to encourage community participation. As a pilot project goes into construction, the authors offer critical reflection on contemporary architecture practice, the design process, and the meaning of “unbuilding” as a response to climate challenge.
The work entitled “Between Building and Unbuilding: An Interdisciplinary Design Approach to Cohabitation, Material Cycles, and Traditional Ecological Knowledge” was published on the journal of Landscape Architecture Frontiers.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-12
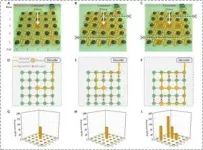
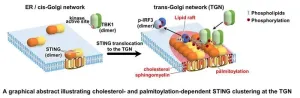
When pathogens attack the body, the innate immune system goes to work protecting against the invading disease. The innate immune system is the first line of defense. It detects precisely what the virus or bacteria is and then activates the proteins that fight the pathogens. Wanting to better understand how the body’s innate immune system works, a team of scientists undertook a study of STING, a protein that plays a vital role in innate immunity.
The team provides quantitative results, showing how STING, an acronym for stimulator of interferon genes, works in innate immune signaling.
Their work is published in the journal Nature Communications on Jan ...
2024-01-12
Petaluma, CA--Newly published research by Petaluma-based non-profit, Point Blue Conservation Science, shows how Adélie penguins within the Ross Sea, Antarctica use sea ice in their annual migrations. The results were published in the journal Ecology, a publication of the Ecological Society of America.
Adélie penguins, though flightless, can undertake extraordinary migrations like their flying relatives, traveling thousands of kilometers out to sea from their on-land breeding colonies in Antarctica, tracking daylight and food during the long Antarctic winter. Many other species are known to use wind ...
2024-01-12
For the first time, researchers have analysed the impact of antibiotic use on the rise of treatment-resistant bacteria over the last 20 years in the UK and Norway. They show that while the increase in drug use has amplified the spread of superbugs, it is not the only driver.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Oslo, the University of Cambridge, and collaborators, conducted a high-resolution genetic comparison of bacteria. They compared over 700 new blood samples with nearly 5,000 ...
2024-01-12
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – January 11, 2024) Data from the St. Jude lifetime cohort study (St. Jude LIFE) revealed that two common biomarkers of cardiac function and damage could better predict cardiomyopathy within five years than routine clinical evaluations in high-risk, asymptomatic childhood cancer survivors. Early detection through screening using these two biomarkers may lead to earlier treatment to prevent and protect against further heart damage. The findings were published today in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Cardiomyopathy is often asymptomatic at onset and thus “invisible” to routine clinical evaluations. St. Jude ...
2024-01-12
Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania have discovered key insights into the molecular basis of skin color variations among African populations. Their findings, published in Nature Genetics, broaden the understanding of human evolution and the genetics underpinning contemporary human skin color diversity.
“Despite the abundant genetic diversity within African populations, they have been historically underrepresented in genetic studies,” says senior author Sarah Tishkoff, a Penn Integrates ...
2024-01-12
Media contacts:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
BOSTON, MA – January 11, 2024 marks the 22nd anniversary of the opening of the Guantanamo Bay detention camp, a facility shrouded in controversy and synonymous with indefinite detention and alleged human rights abuses. Established in the wake of the 9/11 attacks, Guantanamo has held hundreds of individuals suspected of terrorism, many without charge or trial, and under conditions widely condemned by international human rights organizations.
A Legacy of Controversy:
Indefinite Detention: Over ...
2024-01-11
The University of California, Davis, is leading the establishment of a new Integrative Center for Alternative Meat and Protein, or iCAMP. The center will work toward large-scale commercialization and technological advancement of alternative proteins, including cultivated meat (from animal cells grown in large fermentors), plant- and fungal-based foods, and innovative hybrids that combine conventional meat products with alternative proteins.
Bringing together leading researchers and academic institutions, industry ...
2024-01-11
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — The sun has just set on a quiet mudflat in Australia’s Northern Territory; it’ll set again in another 19 hours. A young moon looms large over the desolate landscape. No animals scurry in the waning light. No leaves rustle in the breeze. No lichens encrust the exposed rock. The only hint of life is some scum in a few puddles and ponds. And among it lives a diverse microbial community of our ancient ancestors.
In a new account of exquisitely preserved microfossils, researchers at UC Santa Barbara and McGill University revealed that eukaryotic organisms had already evolved into a diverse array ...
2024-01-11
EL PASO, Texas (Jan. 11, 2024) – Researchers at The University of Texas at El Paso have identified a novel pharmaceutical compound that successfully kills leukemia and lymphoma cancer cells, potentially paving the way for new forms of therapy.
Renato Aguilera, Ph.D., a professor in the Department of Biological Sciences, is the principal investigator on the project that identified the promising compound, called thiophene F-8. His team’s findings were recently published in the research journal PLOS One.
“The main ...
2024-01-11
TUCSON, Ariz., January 11, 2024 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) today announced the launch of a task force focused on accelerating drug development for mitochondrial and inherited metabolic diseases. The task force will lay the groundwork for specific solutions, offering valuable insights that aim to contribute to regulatory decision-making.
C-Path’s demonstrated expertise will be leveraged to ensure success, specifically its track record in generating tangible solutions that have accelerated drug development in rare and pediatric ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Between building and unbuilding: An interdisciplinary design approach to cohabitation, material cycles, and traditional ecological knowledge