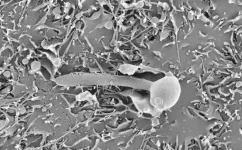
(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C.—The American Society for Microbiology (ASM) announces the launch of its new fully open access journal, ASM Case Reports, which will begin publishing case reports in 2025 and accepting submissions starting mid-2024. ASM Case Reports will be a dedicated platform for the prompt publication of high-quality case reports in clinical microbiology and infectious diseases, an extensive and rapidly growing body of research.
ASM Case Reports will explore new diseases, elaborate disease progressions, the detailed actions and effects of pharmaceuticals, and the emerging frontiers of clinical microbiology and infectious diseases. The journal will publish case reports that elucidate aspects of pathogen diagnosis, pathogen roles in diseases and the dynamics of infectious outbreaks. Case reports will undergo rigorous review and swift publication.
ASM Case Reports will be anchored by 2 highly successful and established ASM journals, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy and Journal of Clinical Microbiology. Together with existing multidisciplinary open access titles, this new forum for important research findings will significantly broaden the ecosystem of clinically relevant research published by ASM Journals.
“Case studies are an established and integral forum of communication, and the launch of ASM Case Reports will allow ASM to capture essential information about newly emerging diseases and diseases that affect a limited number of patients. ASM is committed to joining the larger scientific discourse about the new diseases, drug actions and effects, and outbreaks,” said Melissa Junior, ASM’s Executive Publisher.
ASM Journals has begun their search for an Editor in Chief (EiC), who will begin their 5-year renewable term on July 1, 2024. The EiC will be instrumental in shaping the journal's direction, complementing ASM's existing research journals. We encourage scientists and physicians to apply or nominate a peer for this exciting new role as inaugural EiC. While previous editorial experience is beneficial, it is not mandatory. Nominations, including self-nominations, will be accepted until Feb. 8.
###
The American Society for Microbiology is one of the largest professional societies dedicated to the life sciences and is composed of 36,000 scientists and health practitioners. ASM's mission is to promote and advance the microbial sciences.
ASM advances the microbial sciences through conferences, publications, certifications, educational opportunities and advocacy efforts. It enhances laboratory capacity around the globe through training and resources. It provides a network for scientists in academia, industry and clinical settings. Additionally, ASM promotes a deeper understanding of the microbial sciences to diverse audiences.
END
ASM expands clinically relevant research with launch of ASM Case Reports
2024-01-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rice researchers revolutionizing 5G network testing
2024-01-12
With the potential to transform the future of global wireless networks, Rice University engineers are developing a cutting-edge testing framework to assess the stability, interoperability, energy efficiency and communication performance of software-based machine learning-enabled 5G radio access networks (RANs).
As 5G networks evolve toward more software-centric architectures, there is a critical need for advanced testing methods to ensure robust real-time performance. Funded by a $1.9 million grant from the U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information ...
Candida evolution disclosed: new insights into fungal infections
2024-01-12
Barcelona, 12 January 2024 – Global fungal infections, which affect one billion people and cause 1.5 million deaths each year, are on the rise due to the increasing number of medical treatments that heighten vulnerability. Patients undergoing chemotherapy or immunosuppressive treatments after organ transplant often present compromised immune systems. Given the emergence of resistant strains, the limited variety of current antifungal drugs as well as their cost and side effects, the treatment of these infections is challenging and brings about an urgent need for more effective treatments.
In this context, a team from the Institute for ...
Study reveals function of little-understood synapse in the brain
2024-01-12
New research from Oregon Health & Science University for the first time reveals the function of a little-understood junction between cells in the brain that could have important treatment implications for conditions ranging from multiple sclerosis to Alzheimer’s disease, to a type of brain cancer known as glioma.
The study published today in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
Neuroscientists focused on the junction, or synapse, connecting neurons to a non-neuronal cell, known as oligodendrocyte precursor cells, or OPCs. OPCs can differentiate into oligodendrocytes, which produce a sheath around nerves known as myelin. Myelin is ...
Spying on a shape-shifting protein
2024-01-12
NEW YORK, January 12, 2024 — Proteins do the heavy lifting of performing biochemical functions in our bodies by binding to metabolites or other proteins to complete tasks. To do this successfully, protein molecules often shape-shift to allow specific binding interactions that are needed to perform complex, precise chemical processes.
A better understanding of the shapes proteins take on would give researchers important insight into stopping or treating diseases, but current methods for revealing these dynamic, three-dimensional forms offer scientists limited information. To address this knowledge ...
Researchers sequence the first genome of myxini, the only vertebrate lineage that had no reference genome
2024-01-12
An international scientific team made up of more than 40 authors from seven different countries, led by the researcher at the University of Malaga Juan Pascual Anaya, has managed to sequence the first genome of the myxini –also known as ‘hagfish’–, the only large group of vertebrates for which there was no reference genome of any of its species yet.
This finding, published in the scientific journal ‘Nature Ecology & Evolution’, has allowed deciphering the evolutionary history of genome duplications –number of times a ...
Researchers uncover blood flow regulation of brain pericyte development
2024-01-12
In a study published online in Cell Reports, DU Jiulin’s group at the Institute of Neuroscience, Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the collaborators, created a zebrafish model for in vivo labeling of brain pericytes and systematically explored the developmental dynamics of brain pericytes during the early embryonic stage. The researchers revealed the promoting effect of blood flow on the proliferation of pericytes after ingress into the brain and showed that this process ...
Divergent responses of growth rate and antioxidative system of ten Bacillus strains to acid stresses
2024-01-12
Soil aciditification is widely occurring in diverse terrestrial ecosystems and soil microbial communities have been reported to be highly sensitive to changes in soil pH. Soil microbes could regulate their physiological conditions to make them survive under the aciditifying conditions. This study demonstrates that ten Bacillus strains are able to regulate the antioxidative system differently in response to the decreasing environmental pH condition, and therefore have different acid tolerance capacity. The researchers’ ...
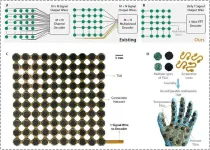
HKUST researchers develop a versatile, reconfigurable, and damage-tolerant single-wire sensor array
2024-01-12
Researchers from The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have developed a sensor array design technology inspired by the human auditory system. By mimicking the human ear's ability to distinguish sounds through tonotopy, this innovative sensor array approach could optimize the application of sensor arrays in fields such as robotics, aviation, healthcare, and industrial machinery.
Traditional sensor arrays face challenges such as complex wiring, limited reconfigurability, and low damage resistance. The design developed by the HKUST team, led by Associate Professor YANG Zhengbao from the Department of Mechanical & Aerospace ...
Between building and unbuilding: An interdisciplinary design approach to cohabitation, material cycles, and traditional ecological knowledge
2024-01-12
In recent history, built environment practices have accepted a paradigm which underlines the land’s static quality, prioritizes immediate utility, and consequently adopts design processes that inevitably accelerate assimilation. With the capitalist propensity to obtain control and enhance efficiency, those processes nevertheless privilege certain cultures while rejecting other forms of knowledge or living specific to the land. The design discourse, confronted with the rising pressure of global climate challenges and environmental inequity, suggests a ...
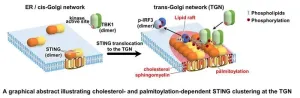
Team explores role of STING – stimulator of interferon genes – in body’s innate immune system
2024-01-12
When pathogens attack the body, the innate immune system goes to work protecting against the invading disease. The innate immune system is the first line of defense. It detects precisely what the virus or bacteria is and then activates the proteins that fight the pathogens. Wanting to better understand how the body’s innate immune system works, a team of scientists undertook a study of STING, a protein that plays a vital role in innate immunity.
The team provides quantitative results, showing how STING, an acronym for stimulator of interferon genes, works in innate immune signaling.
Their work is published in the journal Nature Communications on Jan ...