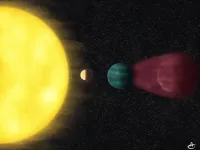
(Press-News.org) MADISON — A team of astronomers have discovered a planet closer and younger than any other Earth-sized world yet identified. It’s a remarkably hot world whose proximity to our own planet and to a star like our sun mark it as a unique opportunity to study how planets evolve.
The new planet was described in a new study published this week by The Astronomical Journal. Melinda Soares-Furtado, a NASA Hubble Fellow at the University of Wisconsin–Madison who will begin work as an astronomy professor at the university in the fall, and recent UW–Madison graduate Benjamin Capistrant, now a graduate student at the University of Florida, co-led the study with co-authors from around the world.
“It’s a useful planet because it may be like an early Earth,” says Soares-Furtado.
Here is what scientists know about the planet:
The planet is known as HD 63433d and it’s the third planet found in orbit around a star called HD 63433.
HD 63433d is so close to its star, it completes a trip all the way around every 4.2 days.
“Even though it's really close-orbiting, we can use follow-up data to search for evidence of outgassing and atmospheric loss that could be important constraints on how terrestrial worlds evolve,” Soares-Furtado says. “But that’s where the similarities end — and end dramatically.”
Based on its orbit, the astronomers are relatively certain HD 63433d is tidally locked, which means one side is perpetually facing its star.
That side can reach a brutal 2,300 degrees Fahrenheit and may flow with lava, while the opposite side is forever dark.
What you should know about the planet’s star:
HD 63433 is roughly the same size and star type as our sun, but (at about 400 million years old) it’s not even one-tenth our sun’s age.
The star is about 73 light years away from our own sun and part of the group of stars moving together that make up the constellation Ursa Major, which includes the Big Dipper.
“On a dark night in Madison,” Soares-Furtado says, “you could see [HD 63433] through a good pair of binoculars.”
How the scientists found the planet:
The study’s authors are collaborating on a planet-hunting project called THYME. In 2020, they used data from NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite to identify two mini-Neptune-sized planets orbiting HD 63433.
Since then, TESS took four more looks at the star, compiling enough data for the researchers to detect HD 63433d crossing between the star and the satellite.
What comes next:
The researchers, including UW–Madison study co-authors graduate student Andrew C. Nine, undergraduate Alyssa Jankowski and Juliette Becker, a UW–Madison astronomy professor, think there is plenty to learn from HD 63433d.
The planet is uniquely situated for further study. Its peppy young star is visible from both the Northern and Southern hemispheres, increasing the number of instruments, like the South African Large Telescope or WIYN Observatory in Arizona (both of which UW–Madison helped design and build) that can be trained on the system.
And the star is orders of magnitude closer than many Soares-Furtado has studied, possibly affording opportunities to develop new methods to study gasses escaping from the planet’s interior or measure its magnetic field.
“This is our solar backyard, and that's kind of exciting,” Soares-Furtado says. “What sort of information can a star this close, with such a crowded system around it, give away? How will it help us as we move on to look for planets among the maybe 100 other, similar stars in this young group it’s part of?”
This research was supported in part by grants from NASA (HST-HF2-51493.001-A, 21-ASTRO21-0068 and XRP 80NSSC21K0393) and the National Science Foundation (AST-2143763, PHY-2210452 and 1745302).
END
Earth-sized planet discovered in ‘our solar backyard’
'It’s a useful planet because it may be like an early Earth'
2024-01-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA analysis confirms 2023 as warmest year on record
2024-01-12
Earth’s average surface temperature in 2023 was the warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. Global temperatures last year were around 2.1 degrees Fahrenheit (1.2 degrees Celsius) above the average for NASA’s baseline period (1951-1980), scientists from NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York reported.
“NASA and NOAA’s global temperature report confirms what billions of people around the world experienced last year; we are facing a climate ...
Incontinence could point to future disability
2024-01-12
If you are one of the 30% to 50% of women experiencing urinary incontinence, new research suggests that it could turn into a bigger health issue.
Having more frequent urinary incontinence and leakage amounts is associated with higher odds of disability, according to RUSH researchers in a study published in the January issue of Menopause.
“Often symptoms from urinary incontinence are ignored until they become bothersome or limit physical or social activities,” said Sheila Dugan, MD, chair of the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation at RUSH. “Because this study suggests that urinary incontinence is associated with disability, ...
Core-shell ‘chemical looping’ boosts efficiency of greener approach to ethylene production
2024-01-12
Ethylene is sometimes called the most important chemical in the petrochemical industry because it serves as the feedstock for a huge range of everyday products. It’s used in the production of antifreeze, vinyl, synthetic rubber, foam insulation, and plastics of all kinds.
Currently, ethylene is produced through an energy- and resource-intensive process called steam cracking, where extremes of temperature and pressure produce ethylene from crude oil in the presence of steam—and in the process, emit tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Another way ...
Targeting Microbiota 2024: Shaping the future of medicine – International leaders unite at the 11th World Congress
2024-01-12
The International Society of Microbiota (ISM) is pleased to announce its 11th World Congress, Targeting Microbiota 2024. This congress is scheduled to take place on October 17-18 in Malta, and will convene international leading experts, researchers, and professionals to explore and discuss the latest advancements in the field of microbiota. Under the new presidency of Maria Cecilia Giron, University of Padova, we anticipate a transformative era, propelling the ISM to new heights in microbiota research.
Thorough Investigation through Specialized Tracks
Recent Advances & Challenges in Microbiota
Microbiota-Host Cross-Talk and Signaling
Metabolomics: Innovations ...
How should boards handle visionary CEOs?
2024-01-12
AUSTIN, Texas — The recent firing and rapid rehiring of Sam Altman, the co-founder and CEO of ChatGPT creator OpenAI, illustrates the delicate dance between visionary CEOs and the boards who oversee them.
Some CEOs — often founders — are fueled by strong convictions about the strategic direction their companies should take. But their boards sometimes don’t share their visions.
When that happens, what is the board’s role in governance? Should it monitor or advise the CEO? Should it back off and approve the CEO’s strategy?
The answer depends on how deeply the CEO is invested in the strategy, says Volker Laux, professor of accounting at Texas ...
Drinkable, carbon monoxide-infused foam enhances effectiveness of experimental cancer therapy
2024-01-12
Did smokers do better than non-smokers in a clinical trial for an experimental cancer treatment? That was the intriguing question that led University of Iowa researchers and their colleagues to develop a drinkable, carbon monoxide-infused foam that boosted the effectiveness of the therapy, known as autophagy inhibition, in mice and human cells. The findings were recently published in the journal Advanced Science.
Looking for ways to exploit biological differences between cancer cells and healthy cells ...
Light-matter interaction: broken symmetry drives polaritons
2024-01-12
An international team of scientists provide an overview of the latest research on light-matter interactions. A team of scientists from the Fritz Haber Institute, the City University of New York and the Universidad de Oviedo has published a comprehensive review article in the scientific journal Nature Reviews Materials. In this article, they provide an overview of the latest research on polaritons, tiny particles that arise when light and material interact in a special way.
In recent years, researchers worldwide have discovered that there are different types of polaritons. Some of them can trap light in a very small space, about the size of a nanometer. That's ...
Neuroscientists identify 'chemical imprint of desire'
2024-01-12
Hop in the car to meet your lover for dinner and a flood of dopamine— the same hormone underlying cravings for sugar, nicotine and cocaine — likely infuses your brain’s reward center, motivating you to brave the traffic to keep that unique bond alive. But if that dinner is with a mere work acquaintance, that flood might look more like a trickle, suggests new research by University of Colorado Boulder neuroscientists.
“What we have found, essentially, is a biological signature of desire that helps us explain why we want to be with some people more than other people,” said senior author Zoe Donaldson, associate professor ...
Trends in cancer mortality disparities between Black and white individuals in the US
2024-01-12
About The Study: Although U.S. age-adjusted cancer mortality rates declined significantly between 2000 and 2020, substantial racial and ethnic disparities persisted for many common and preventable cancers, including female breast and male colorectal cancer. Cancer disparities arise from a confluence of factors, including structural racism, medical mistrust, health care access inequities, poor socioenvironmental conditions, aggressive tumor biology, and genetic ancestry.
Authors: Tomi Akinyemiju, Ph.D., M.S., of the Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Medicaid expansion under the Affordable Care Act and early mortality following lung cancer surgery
2024-01-12
About The Study: In this study of nearly 15,000 adults with non–small cell lung cancer, Medicaid expansion was associated with declines in 30- and 90-day postoperative mortality following hospital discharge. These findings suggest that Medicaid expansion may be an effective strategy for improving access to care and cancer outcomes in this population.
Authors: Leticia M. Nogueira, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the American Cancer Society in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.51529)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
[Press-News.org] Earth-sized planet discovered in ‘our solar backyard’'It’s a useful planet because it may be like an early Earth'