(Press-News.org) An international team of scientists provide an overview of the latest research on light-matter interactions. A team of scientists from the Fritz Haber Institute, the City University of New York and the Universidad de Oviedo has published a comprehensive review article in the scientific journal Nature Reviews Materials. In this article, they provide an overview of the latest research on polaritons, tiny particles that arise when light and material interact in a special way.
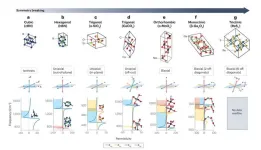
In recent years, researchers worldwide have discovered that there are different types of polaritons. Some of them can trap light in a very small space, about the size of a nanometer. That's about 80,000 times thinner than a human hair!
The scientists report in their article that these special polaritons can arise in certain crystals. When the light in these crystals generates special vibrations - the researchers call this "phonons" - these special polaritons are created. Interestingly, they also found that the less symmetric the crystal is, the better the whole thing works. This leads to new and exciting possibilities for controlling light in the smallest space.
In their article, the scientists provide an overview of the latest research findings and discuss how these new insights could be used in the future. They believe that this work could help develop new materials that can use light in innovative ways.
This fundamental research could therefore have a major impact on many areas, from the development of new technologies to the improvement of existing devices. It's an exciting step forward in the world of nanotechnology!
END
Light-matter interaction: broken symmetry drives polaritons
2024-01-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Neuroscientists identify 'chemical imprint of desire'
2024-01-12
Hop in the car to meet your lover for dinner and a flood of dopamine— the same hormone underlying cravings for sugar, nicotine and cocaine — likely infuses your brain’s reward center, motivating you to brave the traffic to keep that unique bond alive. But if that dinner is with a mere work acquaintance, that flood might look more like a trickle, suggests new research by University of Colorado Boulder neuroscientists.
“What we have found, essentially, is a biological signature of desire that helps us explain why we want to be with some people more than other people,” said senior author Zoe Donaldson, associate professor ...
Trends in cancer mortality disparities between Black and white individuals in the US
2024-01-12
About The Study: Although U.S. age-adjusted cancer mortality rates declined significantly between 2000 and 2020, substantial racial and ethnic disparities persisted for many common and preventable cancers, including female breast and male colorectal cancer. Cancer disparities arise from a confluence of factors, including structural racism, medical mistrust, health care access inequities, poor socioenvironmental conditions, aggressive tumor biology, and genetic ancestry.
Authors: Tomi Akinyemiju, Ph.D., M.S., of the Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Medicaid expansion under the Affordable Care Act and early mortality following lung cancer surgery
2024-01-12
About The Study: In this study of nearly 15,000 adults with non–small cell lung cancer, Medicaid expansion was associated with declines in 30- and 90-day postoperative mortality following hospital discharge. These findings suggest that Medicaid expansion may be an effective strategy for improving access to care and cancer outcomes in this population.
Authors: Leticia M. Nogueira, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the American Cancer Society in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.51529)
Editor’s ...
Researchers create light-powered yeast, providing insights into evolution, biofuels, cellular aging
2024-01-12
You may be familiar with yeast as the organism content to turn carbs into products like bread and beer when left to ferment in the dark. In these cases, exposure to light can hinder or even spoil the process.
In a new study published in Current Biology, researchers in Georgia Tech’s School of Biological Sciences have engineered one of the world’s first strains of yeast that may be happier with the lights on.
“We were frankly shocked by how simple it was to turn the yeast into phototrophs (organisms that ...
2023: the warmest year on record globally
2024-01-12
Globally 2023 was the warmest year in a series stretching back to 1850, according to figures released today by the Met Office and the University of East Anglia.
2023 is the tenth year in succession that has equalled or exceeded 1.0 °C above the pre-industrial period (1850-1900).
The global average temperature for 2023 was 1.46 °C above the pre-industrial baseline; 0.17 °C warmer than the value for 2016, the previous warmest year on record in the HadCRUT5 global temperature dataset which runs from 1850.
Dr Colin Morice is a Climate ...
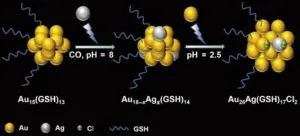
Researchers develop technique to synthesize water-soluble alloy nanoclusters
2024-01-12
In recent years, ultrasmall metal nanoclusters have unlocked advances in fields ranging from bioimaging and biosensing to biotherapy thanks to their unique molecular-like properties. In a study published in the journal Polyoxometalates on December 11, 2023, a research team from Qingdao University of Science and Technology proposed a design to synthesize atomically precise, water-soluble alloy nanoclusters.
“The novelty of this study is in a new strategy for the synthesis of water-soluble alloy nanoclusters and a further contribution ...
Clinical predictive models created by AI are accurate but study-specific
2024-01-12
In a recent study, scientists have been investigating the accuracy of AI models that predict whether people with schizophrenia will respond to antipsychotic medication. Statistical models from the field of artificial intelligence (AI) have great potential to improve decision-making related to medical treatment. However, data from medical treatment that can be used for training these models are not only rare, but also expensive. Therefore, the predictive accuracy of statistical models has so far only been demonstrated in a few ...
$900,000 awarded to optimize graphene energy harvesting devices
2024-01-12
U of A physics professor Paul Thibado received a commitment of $904,000 from the WoodNext Foundation, administered by the Greater Houston Community Foundation. The five-year grant will support Thibado’s development of graphene energy harvesters.
“We have successfully developed a process for building graphene energy harvesting device structures,” Thibado said, “but current structures do not harvest enough power. This proposal will allow us to optimize these structures to harvest nanowatts of power, which is enough energy to run sensors.”
Thibado and his colleagues will develop graphene energy harvesting ...
Kessler Foundation scientist awarded prestigious federal grant for novel, mixed-method study on Latinos with multiple sclerosis
2024-01-12
East Hanover, NJ – January 12, 2024 – A research scientist at Kessler Foundation has been awarded a highly competitive Mentored Patient-Oriented Research Career Development Award (K23) from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities, a part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
This $704,054, five-year grant will support one of the first mixed-methods studies aimed at examining barriers to healthcare, cardiovascular risk factors, and accelerated brain aging in Latinos with multiple sclerosis (MS). The Principal Investigator and grant recipient, Cristina A. F. Román, PhD, is currently a research ...
Stress, via inflammation, is linked to metabolic syndrome
2024-01-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Lifestyle and genetics, and a range of other factors within and outside our control, are known to contribute to development of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that add up to increased risk for serious health problems.
A new study has found that stress, through its propensity to drive up inflammation in the body, is also linked to metabolic syndrome – leading researchers to suggest that cheap and relatively easy stress-management techniques may be one way to help improve biological health outcomes.
“We were specifically examining people in midlife – ...