(Press-News.org)
In recent years, ultrasmall metal nanoclusters have unlocked advances in fields ranging from bioimaging and biosensing to biotherapy thanks to their unique molecular-like properties. In a study published in the journal Polyoxometalates on December 11, 2023, a research team from Qingdao University of Science and Technology proposed a design to synthesize atomically precise, water-soluble alloy nanoclusters.
“The novelty of this study is in a new strategy for the synthesis of water-soluble alloy nanoclusters and a further contribution to the fundamental understanding of the alloying mechanism of metal nanoclusters,” said study author Xun Yuan from Qingdao University of Science and Technology.
“The ultimate goal is to develop such alloy nanoclusters as novel nanomedicine,” Yuan said.
Nanoclusters are made of only a few to tens of atoms, and the size of their cores is usually below 2 nanometers (nm). Since the ultra-small size of the clusters is close to the Fermi wavelength of electrons, the continuous band turns to discontinuous and becomes molecule-like with discrete energy levels. Consequently, the nanoclusters exhibit unique optical and electronic characteristics.
Recent studies have demonstrated how alloy nanoclusters — synthesized by combining two or more different metals into a monometallic nanocluster framework — can generate new geometric structures and additional functionality. Researchers can “tune” the physical and chemical properties (e.g., optical, catalytic, and magnetic) of metal nanoclusters. Moreover, alloy nanoclusters often exhibit synergistic or new properties, which go beyond those of monometallic nanoclusters.
Heightened interest in potential opportunities has spurred recent activity to develop new methods to synthesize alloy nanoclusters. But, while the correlations between size, morphology, and composition of alloy nanoclusters and their physicochemical properties have been well demonstrated, issues surrounding doping processes and the dynamic responses are not well understood, according to Yuan.
“These unresolved issues are mainly due to the technical limitations in characterizing the alloy atom distribution at the atomic level, especially in real-time tracking of the dynamic heteroatom movement in the alloy nanoparticles during the reactions,” Yuan said.
In addition, most of those methods were exploited for hydrophobic alloy nanoclusters, which may preclude synthesis for water-soluble alloy nanoclusters. Given the wide application of water-soluble alloy nanoclusters in biomedicine and environmental protection, developing novel synthetic strategies of water-soluble alloy nanoclusters at the atomic level is significantly important.
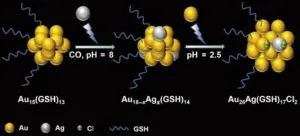
With this goal in mind, Yuan and collaborators found that seeding silver (Ag) ions could trigger the transformation from gold (Au)-based nanoclusters into alloy Au18-xAgx(GSH)14 nanocluster which can be further transformed to composition-fixed Au26Ag(GSH)17Cl2 nanoclusters by gold (Au) ions— with GSH denoting water-soluble glutathione. Moreover, the position of the single Ag atom of Au26Ag(GSH)17Cl2 nanoclusters could be identified on the surface.
“Our results could achieve the atom-level modulation of metal nanoparticles, and provide a platform for producing alloy functional nanomaterials for specific applications,” said Yuan. “Additionally, the acquired alloying mechanism may deepen the understanding on the properties-performance of alloy nanomaterials, contributing to the generation of new knowledge in the fields of nanomaterials, chemistry, and nanocluster science.”
In future studies, the researchers will use these alloy nanoclusters for biomedical applications.
The research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province.
Other contributors include Shuyu Qian, Fengyu Liu, Haiguang Zhu, Yong Liu, Ting Feng and Xinyue Dou from Qingdao University of Science and Technology.
About Polyoxometalates
Polyoxometalates is a peer-reviewed, international and interdisciplinary research journal that focuses on all aspects of polyoxometalates, featured in rapid review and fast publishing, sponsored by Tsinghua University and published by Tsinghua University Press. Submissions are solicited in all topical areas, ranging from basic aspects of the science of polyoxometalates to practical applications of such materials. Polyoxometalates offers readers an attractive mix of authoritative and comprehensive Reviews, original cutting-edge research in Communication and Full Paper formats, Comments, and Highlight.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is a professional open access resource for discovery of scientific and technical content published by the Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners, providing the scholarly publishing community with innovative technology and market-leading capabilities. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, and identity management and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development by offering a range of options across all functions as Journal Layout, Production Services, Editorial Services, Marketing and Promotions, Online Functionality, etc. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
In a recent study, scientists have been investigating the accuracy of AI models that predict whether people with schizophrenia will respond to antipsychotic medication. Statistical models from the field of artificial intelligence (AI) have great potential to improve decision-making related to medical treatment. However, data from medical treatment that can be used for training these models are not only rare, but also expensive. Therefore, the predictive accuracy of statistical models has so far only been demonstrated in a few ...
U of A physics professor Paul Thibado received a commitment of $904,000 from the WoodNext Foundation, administered by the Greater Houston Community Foundation. The five-year grant will support Thibado’s development of graphene energy harvesters.
“We have successfully developed a process for building graphene energy harvesting device structures,” Thibado said, “but current structures do not harvest enough power. This proposal will allow us to optimize these structures to harvest nanowatts of power, which is enough energy to run sensors.”
Thibado and his colleagues will develop graphene energy harvesting ...
East Hanover, NJ – January 12, 2024 – A research scientist at Kessler Foundation has been awarded a highly competitive Mentored Patient-Oriented Research Career Development Award (K23) from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities, a part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
This $704,054, five-year grant will support one of the first mixed-methods studies aimed at examining barriers to healthcare, cardiovascular risk factors, and accelerated brain aging in Latinos with multiple sclerosis (MS). The Principal Investigator and grant recipient, Cristina A. F. Román, PhD, is currently a research ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Lifestyle and genetics, and a range of other factors within and outside our control, are known to contribute to development of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that add up to increased risk for serious health problems.
A new study has found that stress, through its propensity to drive up inflammation in the body, is also linked to metabolic syndrome – leading researchers to suggest that cheap and relatively easy stress-management techniques may be one way to help improve biological health outcomes.
“We were specifically examining people in midlife – ...
The National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health has awarded Weill Cornell Medicine a $1.8 million five-year grant to fund a new post-baccalaureate research education program that aims to cultivate scientists and physician-scientists who hail from groups traditionally underrepresented in science and medicine.
Advancing Success and Persistence in Research Education, or ASPiRE, will support college graduates who hope to attend professional and graduate school. The program will train four scholars each year for the first three years, and five scholars in years four and five. The program’s duration is designed to be flexible to the ...
Physicians who are notified that a patient has died of a drug overdose are more judicious in issuing controlled substances if the notification includes a plan for what to do during subsequent patient visits, according to a study published today in Nature Communications.
Compared to a letter with demonstrated effectiveness at improving prescribing safety, physicians who received notifications with additional planning guidance reduced prescriptions of opioids by nearly 13%. They also reduced prescriptions of the anxiety medications benzodiazepines and by more than 8%. Together these drugs constitute the bulk of prescription drug overdoses.
The results suggest that the guidance, known ...
Newcastle University research turns to ancient hot springs to explore the origins of life on Earth.
The research team, funded by the UK’s Natural Environmental Research Council, investigated how the emergence of the first living systems from inert geological materials happened on the Earth, more than 3.5 billion years ago. Scientists at Newcastle University found that by mixing hydrogen, bicarbonate, and iron-rich magnetite under conditions mimicking relatively mild hydrothermal vent results in the formation of a spectrum of organic molecules, most notably including ...
(Boston)—Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading infectious killer worldwide, with 10.6 million cases and 1.6 million deaths in 2021 alone. One in five incident TB cases were attributable to malnutrition, more than double the number attributed to HIV/AIDS. Like HIV/AIDS, malnutrition is a cause of secondary immunodeficiency, known as nutritionally acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (N-AIDS). However, N-AIDS remains the neglected cousin of HIV/AIDS in global TB elimination efforts.
In a review paper led by Madolyn Dauphinais, MPH, researchers at Boston University Chobanian ...
(WASHINGTON, January 12, 2024) – Individuals with obesity are more likely to have monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), a benign blood condition that often precedes multiple myeloma, according to new research published in Blood Advances.
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer of the plasma cells, a type of white blood cells that produce antibodies to fight infection. MGUS, characterized by an abnormal protein produced by plasma cells, is a known precursor to multiple myeloma. Most people with MGUS exhibit no significant symptoms and are not immediately ill. Rather, the presence of MGUS serves as a warning to monitor for the potential ...
Highlights:
Previous studies have connected severe gum disease to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD.
Bacteria play a critical role, but the details remain unclear.
A new study shows how periodontitis, an oral disease, activates immune cells associated with aggravated progression of COPD.
The findings suggest that periodontitis and COPD together worsen COPD, and point to gum disease management as a potential treatment for COPD.
Washington, D.C.—Severe gum disease has been linked to the progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, but an understanding ...