(Press-News.org) You may be familiar with yeast as the organism content to turn carbs into products like bread and beer when left to ferment in the dark. In these cases, exposure to light can hinder or even spoil the process.
In a new study published in Current Biology, researchers in Georgia Tech’s School of Biological Sciences have engineered one of the world’s first strains of yeast that may be happier with the lights on.
“We were frankly shocked by how simple it was to turn the yeast into phototrophs (organisms that can harness and use energy from light),” says Anthony Burnetti, a research scientist working in Associate Professor William Ratcliff’s laboratory and corresponding author of the study. “All we needed to do was move a single gene, and they grew 2% faster in the light than in the dark. Without any fine-tuning or careful coaxing, it just worked.”
Easily equipping the yeast with such an evolutionarily important trait could mean big things for our understanding of how this trait originated — and how it can be used to study things like biofuel production, evolution, and cellular aging.
Looking for an energy boost
The research was inspired by the group’s past work investigating the evolution of multicellular life. The group published their first report on their Multicellularity Long-Term Evolution Experiment (MuLTEE) in Nature last year, uncovering how their single-celled model organism, “snowflake yeast,” was able to evolve multicellularity over 3,000 generations.
Throughout these evolution experiments, one major limitation for multicellular evolution appeared: energy.
“Oxygen has a hard time diffusing deep into tissues, and you get tissues without the ability to get energy as a result,” says Burnetti. “I was looking for ways to get around this oxygen-based energy limitation.”
One way to give organisms an energy boost without using oxygen is through light. But the ability to turn light into usable energy can be complicated from an evolutionary standpoint. For example, the molecular machinery that allows plants to use light for energy involves a host of genes and proteins that are hard to synthesize and transfer to other organisms — both in the lab and naturally through evolution.
Luckily, plants are not the only organisms that can convert light to energy.
Keeping it simple
A simpler way for organisms to use light is with rhodopsins: proteins that can convert light into energy without additional cellular machinery.
“Rhodopsins are found all over the tree of life and apparently are acquired by organisms obtaining genes from each other over evolutionary time,” says Autumn Peterson, a biology Ph.D. student working with Ratcliff and lead author of the study.
This type of genetic exchange is called horizontal gene transfer and involves sharing genetic information between organisms that aren’t closely related. Horizontal gene transfer can cause seemingly big evolutionary jumps in a short time, like how bacteria are quickly able to develop resistance to certain antibiotics. This can happen with all kinds of genetic information and is particularly common with rhodopsin proteins.
“In the process of figuring out a way to get rhodopsins into multi-celled yeast,” explains Burnetti, “we found we could learn about horizontal transfer of rhodopsins that has occurred across evolution in the past by transferring it into regular, single-celled yeast where it has never been before.”
To see if they could outfit a single-celled organism with solar-powered rhodopsin, researchers added a rhodopsin gene synthesized from a parasitic fungus to common baker’s yeast. This specific gene is coded for a form of rhodopsin that would be inserted into the cell’s vacuole, a part of the cell that, like mitochondria, can turn chemical gradients made by proteins like rhodopsin into energy.
Equipped with vacuolar rhodopsin, the yeast grew roughly 2% faster when lit — a huge benefit in terms of evolution.
“Here we have a single gene, and we're just yanking it across contexts into a lineage that's never been a phototroph before, and it just works,” says Burnetti. “This says that it really is that easy for this kind of a system, at least sometimes, to do its job in a new organism.”
This simplicity provides key evolutionary insights and says a lot about “the ease with which rhodopsins have been able to spread across so many lineages and why that may be so,” explains Peterson, who Peterson recently received a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Gilliam Fellowship for her work. Carina Baskett, grant writer for Georgia Tech’s Center for Microbial Dynamics and Infection, also worked on the study.
Because vacuolar function may contribute to cellular aging, the group has also initiated collaborations to study how rhodopsins may be able to reduce aging effects in the yeast. Other researchers are already starting to use similar new, solar-powered yeast to study advancing bioproduction, which could mark big improvements for things like synthesizing biofuels.
Ratcliff and his group, however, are mostly keen to explore how this added benefit could impact the single-celled yeast’s journey to a multicellular organism.
“We have this beautiful model system of simple multicellularity,” says Burnetti, referring to the long-running Multicellularity Long-Term Evolution Experiment (MuLTEE). “We want to give it phototrophy and see how it changes its evolution.”
Citation: Peterson et al., 2024, Current Biology 34, 1–7.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2023.12.044
END
Researchers create light-powered yeast, providing insights into evolution, biofuels, cellular aging
2024-01-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023: the warmest year on record globally
2024-01-12
Globally 2023 was the warmest year in a series stretching back to 1850, according to figures released today by the Met Office and the University of East Anglia.
2023 is the tenth year in succession that has equalled or exceeded 1.0 °C above the pre-industrial period (1850-1900).
The global average temperature for 2023 was 1.46 °C above the pre-industrial baseline; 0.17 °C warmer than the value for 2016, the previous warmest year on record in the HadCRUT5 global temperature dataset which runs from 1850.
Dr Colin Morice is a Climate ...
Researchers develop technique to synthesize water-soluble alloy nanoclusters
2024-01-12
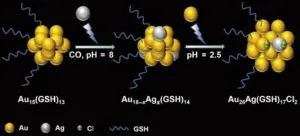
In recent years, ultrasmall metal nanoclusters have unlocked advances in fields ranging from bioimaging and biosensing to biotherapy thanks to their unique molecular-like properties. In a study published in the journal Polyoxometalates on December 11, 2023, a research team from Qingdao University of Science and Technology proposed a design to synthesize atomically precise, water-soluble alloy nanoclusters.
“The novelty of this study is in a new strategy for the synthesis of water-soluble alloy nanoclusters and a further contribution ...
Clinical predictive models created by AI are accurate but study-specific
2024-01-12
In a recent study, scientists have been investigating the accuracy of AI models that predict whether people with schizophrenia will respond to antipsychotic medication. Statistical models from the field of artificial intelligence (AI) have great potential to improve decision-making related to medical treatment. However, data from medical treatment that can be used for training these models are not only rare, but also expensive. Therefore, the predictive accuracy of statistical models has so far only been demonstrated in a few ...
$900,000 awarded to optimize graphene energy harvesting devices
2024-01-12
U of A physics professor Paul Thibado received a commitment of $904,000 from the WoodNext Foundation, administered by the Greater Houston Community Foundation. The five-year grant will support Thibado’s development of graphene energy harvesters.
“We have successfully developed a process for building graphene energy harvesting device structures,” Thibado said, “but current structures do not harvest enough power. This proposal will allow us to optimize these structures to harvest nanowatts of power, which is enough energy to run sensors.”
Thibado and his colleagues will develop graphene energy harvesting ...
Kessler Foundation scientist awarded prestigious federal grant for novel, mixed-method study on Latinos with multiple sclerosis
2024-01-12
East Hanover, NJ – January 12, 2024 – A research scientist at Kessler Foundation has been awarded a highly competitive Mentored Patient-Oriented Research Career Development Award (K23) from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities, a part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
This $704,054, five-year grant will support one of the first mixed-methods studies aimed at examining barriers to healthcare, cardiovascular risk factors, and accelerated brain aging in Latinos with multiple sclerosis (MS). The Principal Investigator and grant recipient, Cristina A. F. Román, PhD, is currently a research ...
Stress, via inflammation, is linked to metabolic syndrome
2024-01-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Lifestyle and genetics, and a range of other factors within and outside our control, are known to contribute to development of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that add up to increased risk for serious health problems.
A new study has found that stress, through its propensity to drive up inflammation in the body, is also linked to metabolic syndrome – leading researchers to suggest that cheap and relatively easy stress-management techniques may be one way to help improve biological health outcomes.
“We were specifically examining people in midlife – ...
NIH awards education grant for Weill Cornell Medicine’s first post-baccalaureate research program
2024-01-12
The National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health has awarded Weill Cornell Medicine a $1.8 million five-year grant to fund a new post-baccalaureate research education program that aims to cultivate scientists and physician-scientists who hail from groups traditionally underrepresented in science and medicine.
Advancing Success and Persistence in Research Education, or ASPiRE, will support college graduates who hope to attend professional and graduate school. The program will train four scholars each year for the first three years, and five scholars in years four and five. The program’s duration is designed to be flexible to the ...
Want safer prescribing? Provide doctors with a plan for helping patients in pain
2024-01-12
Physicians who are notified that a patient has died of a drug overdose are more judicious in issuing controlled substances if the notification includes a plan for what to do during subsequent patient visits, according to a study published today in Nature Communications.
Compared to a letter with demonstrated effectiveness at improving prescribing safety, physicians who received notifications with additional planning guidance reduced prescriptions of opioids by nearly 13%. They also reduced prescriptions of the anxiety medications benzodiazepines and by more than 8%. Together these drugs constitute the bulk of prescription drug overdoses.
The results suggest that the guidance, known ...
Study uncovers potential origins of life in ancient hot springs
2024-01-12
Newcastle University research turns to ancient hot springs to explore the origins of life on Earth.
The research team, funded by the UK’s Natural Environmental Research Council, investigated how the emergence of the first living systems from inert geological materials happened on the Earth, more than 3.5 billion years ago. Scientists at Newcastle University found that by mixing hydrogen, bicarbonate, and iron-rich magnetite under conditions mimicking relatively mild hydrothermal vent results in the formation of a spectrum of organic molecules, most notably including ...
Nutritional acquired immunodeficiency (N-AIDS) is the leading driver of the TB pandemic
2024-01-12
(Boston)—Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading infectious killer worldwide, with 10.6 million cases and 1.6 million deaths in 2021 alone. One in five incident TB cases were attributable to malnutrition, more than double the number attributed to HIV/AIDS. Like HIV/AIDS, malnutrition is a cause of secondary immunodeficiency, known as nutritionally acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (N-AIDS). However, N-AIDS remains the neglected cousin of HIV/AIDS in global TB elimination efforts.
In a review paper led by Madolyn Dauphinais, MPH, researchers at Boston University Chobanian ...