(Press-News.org)
The use of dual metal sulfides, specifically ZnS/CuS, shows marked improvement in electrochemical stability and performance when included in the design of flexible lithium-ion capacitors over the use of transition metal sulfides and carbon fiber materials.
Technology is becoming more and more integrated with daily life, especially wearable, flexible tech and smart devices. Transition metal sulfide (TMS) materials are popular among choices for anodes in developing flexible lithium-ion capacitors (FLICs) but do not live up to their theoretical capabilities when put into practice. Researchers are looking to change that by developing zinc-sulfide nanoparticles that can be embedded in multichannel carbon fibers (CFs) to enhance the performance of FLICs.
The results were published in Energy Materials and Devices on December 13.
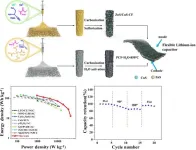
Researchers went about navigating the challenges of traditional powder electrodes by utilizing a solution blow spinning method, a method that produces fiber sheets with a high porosity and large surface area. This was followed by sulfidation, which adds sulfide ions to the material. The resulting material is multichannel carbon fibers with embedded ZnS/CuS nanoparticles. This material showed lower resistance to charge transfer and ion diffusion, as well as improved high specific capacity and rate capacity. By combining mixed metal sulfides with a FLIC, energy and power densities were improved.
“An effective strategy to enhance the energy and power densities of CF-based anode materials involves coupling them with highly active materials,” said Bohan Li, researcher and author of the study.
Metals like zinc, when combined with sulfides, appear to have a good track record in conjunction with carbon fibers to yield a high-capacity anode. Their high activity level can make for a faster reaction, which is a significant area of improvement in FLICs.
In addition to the material’s improved performance, the structure of the carbon fiber network reduces the chance of the nanoparticles bunching up, which helps maintain consistency in cycling and stability.
“Carbon fibers function as a conductive network and 3D matrix, accommodating volume expansion and maximizing the high-capacity feature of ZnS and CuS nanoparticles. This enhances the specific capacity and cycle stability of CF-based anode materials,” said Li.
The carbon fibers’ three-dimensional matrix also reduces how much the ZnS and CuS can expand. Expansion of the components inside the battery can at the very least reduce function and at worst, cause a complete failure of the battery.
When it comes to testing how usable the tech is under pressure (bending), a pouch cell was used. Pouch cells essentially are an enclosed anode and cathode with a separator and conducting material; these are often used in cars, laptops or cell phones. The results show how flexible the technology is with various angles of bend being used to light up an LED, which was successful at all angles. Not only did the tech hold up to bending initially, but it was able to return to its original shape with no issue, an integral part of the function of flexible technology.
The goal of this material is to improve upon existing technology to improve the variety of smart, flexible devices that are flooding into the mainstream. Improvements in these types of electronics can lead to more sustainable tech that is widely available for consumers and companies to take advantage of. Production of the ZnS/CuS nanoparticles on a continuous carbon fiber network would need to be scaled up to be a technology available for use in portable and wearable devices over the typical TMSs used in FLICs.
Bohan Li, Chong Wang, Zhouyang Qin, Changzhen Zhan, Liangliang Li, Wanci Shen and Zheng-Hong Huang of the Key Laboratory of Advanced Materials at Tsinghua University with Ruitao Lv and Zheng-Hong Huang also of the State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics and Fine Processing at Tsinghua University, and Chenhui Luan of the School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering at China University of Mining and Technology contributed to this research.
The National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Major Science and Technology Project made this research possible.
About Energy Materials and Devices
Energy Materials and Devices is launched by Tsinghua University, published quarterly by Tsinghua University Press, aiming at being an international, single-blind peer-reviewed, open-access and interdisciplinary journal in the cutting-edge field of energy materials and devices. It focuses on the innovation research of the whole chain of basic research, technological innovation, achievement transformation and industrialization in the field of energy materials and devices, and publishes original, leading and forward-looking research results, including but not limited to the materials design, synthesis, integration, assembly and characterization of devices for energy storage and conversion etc.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is a professional open access resource for discovery of scientific and technical content published by the Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners, providing the scholarly publishing community with innovative technology and market-leading capabilities. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, and identity management and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development by offering a range of options across all functions as Journal Layout, Production Services, Editorial Services, Marketing and Promotions, Online Functionality, etc. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
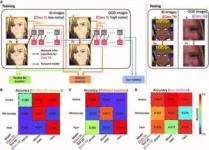
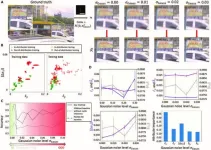
Uncertainty estimation is critical to improving the reliability of deep neural networks. A research team led by Aydogan Ozcan at the University of California, Los Angeles, has introduced an uncertainty quantification method that uses cycle consistency to enhance the reliability of deep neural networks in solving inverse imaging problems.
This research was published Dec. 21 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Deep neural networks have been used to solve inverse imaging problems, such as image denoising, ...
The Aston Institute for Membrane Excellence (AIME) will be set up with a £10m grant from Research England
AIME will be led by Professor Roslyn Bill from Biosciences and Professor Paul Topham from Chemical Engineering and Applied Chemistry
The globally unique institute will use biomimetic polymer membranes for applications such as water purification and drug development
Aston University will establish the Aston Institute for Membrane Excellence (AIME), a globally unique, cross-disciplinary institute to develop novel biomimetic membranes, after receiving a major grant of £10m from Research England.
AIME will be led by Professor Roslyn Bill, from the School ...
In early 2020, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), a highly contagious and pathogenic virus, made its alarming debut and quickly spread worldwide, causing the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic that threatened human health and public safety. While the world was brought to a standstill, hospitals and health care systems entered unchartered territory and quickly adapted to the evolving health crisis to care for their community and keep potentially sick patients and health care workers from spreading the virus.
The magnitude of response involved the reinforced universal masking of health care ...
Cambridge, Mass., Jan. 16, 2024 - A team of researchers from the ADA Forsyth Institute and University of North Carolina (UNC), Chapel Hill used single-cell transcriptomic analysis to successfully map dental pulp stem cells (DPSC) and periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSC) and found remarkable differences between them. The study, which appeared in the Journal of Dental Research, provides the most detailed analysis of these stem cells to date, identifying the entire genome of the stem cells and their potential differentiation trajectories.
“Dental pulp and periodontal ligament stem cells both have the potential to develop into any type of cell in the body,” ...
Neuroscientists from the University of Vienna and the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm have investigated whether playing violent video games leads to a reduction in human empathy. To do this, they had adult test subjects play a violent video game repeatedly over the course of an experiment lasting several weeks. Before and after, their empathic responses to the pain of another person were measured. It was found that the violent video game had no discernible effect on empathy and underlying brain activity. These results have now been published in the renowned journal eLife.
Video games have become an integral part of the everyday life of many ...
WASHINGTON (Jan. 16, 2024) – Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to detect rheumatic heart disease (RHD) with the same accuracy as a cardiologist, according to new research demonstrating how sophisticated deep learning technology can be applied to this disease of inequity. The work could prevent hundreds of thousands of unnecessary deaths around the world annually.
Developed at Children’s National Hospital and detailed in the latest edition of the Journal of the American Heart Association, the new AI system combines the power of novel ultrasound probes with portable electronic ...
Knowing a patient’s weight is necessary for many weight-based medications such as thrombolytics, anticoagulants and numerous cardiovascular medications. Scaling drugs to a patient’s weight prevents adverse events from overtreatment and treatment failure due to underdosing. Inaccurate weight estimations may lead to inaccurate drug doses, which could cause patient harm.
However, in the emergency department (ED) during resuscitative care, measuring weight is often impossible. Moreover, little is known about the relative accuracy of different methods currently used to weigh patients during emergency care. For example, ...
TORONTO (16 January 2024) – As part of its pioneering approach to drug discovery, the Canadian nonprofit Conscience announced today that its first open science competition has resulted in the identification of seven promising molecules, or “hits,” that show potential for new, more effective drugs for familial Parkinson’s disease.
This first competition in Conscience’s CACHE (Critical Assessment of Computational Hit-Finding Experiments) Challenge series was funded by The ...
From inside an operating room in Barquisimeto, Venezuela, electrophysiologist Maria Milagros Arends, M.D., threads wires from a pacemaker through the veins and into the heart muscle of a patient.
This pacemaker, which regulates the heartbeat and can be lifesaving, was once in the body of another person. It has been recycled, or “reconditioned”— donated, tested, sterilized and shipped from the United States to the South American country for implantation.
“We have a waiting list of around 300 people who could potentially lose their lives in less than a month,” ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new study links increased use of acetaminophen during pregnancy – particularly in the second trimester – to modest but noticeable increases in problems with attention and behavior in 2-, 3- and 4-year-olds. The study adds to a growing body of evidence linking the frequent use of acetaminophen in pregnancy to developmental problems in offspring.
The findings are detailed in the journal Neurotoxicology and Teratology.
The research is part of the Illinois Kids Development Study at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, which explores how environmental ...