(Press-News.org) To prevent aircraft stalls, engineers have long studied the flow of air over airfoils such as airplane wings to detect the angles when flow separation occurs. Recently, a team of researchers at Shanghai Jiao Tong University including Xi-Jun Yuan and Zi-Qiao Chen investigated the use of quantum computing in connection with machine learning as a more accurate way of solving such problems. Their research was published Nov. 21 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The use of a quantum support vector machine rather than a classical support vector machine increased the accuracy of classification of flow separation from 81.8% to 90.9% and increased the accuracy of classification of the angle of attack from 67.0% to 79.0%. These results help show that using quantum computing methods for fluid dynamics problems could be faster and more accurate than using classical computing methods, especially because the datasets in such contexts are large. Potential applications of quantum support vector machines in addition to aircraft design include underwater navigation and target tracking.
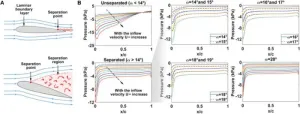
The researchers performed two classification tasks. The first was a binary classification on a small dataset to detect whether or not flow separation had occurred. A small dataset was chosen because it is difficult to achieve high-accuracy classification for small datasets. Data for this task were collected from pressure sensors on an airfoil in a wind tunnel with different airspeeds and angles of attack. The dataset consists of 45 multidimensional points: 27 cases without flow separation and 18 cases with flow separation. This dataset was divided into 34 points for training and 11 points for testing.
The second task was more complex. It classified the angle of attack of the airfoil after flow separation into one of four classes. To achieve this, the problem was broken into four one-against-all classification problems, with a binary in-or-out classifier for each of the four classes. Data for this task were created by simulation. The dataset consists of 63 multidimensional points obtained by sampling. This dataset was divided into 43 points for training and 20 for testing. The training and testing process was repeated 10 times with different combinations of training and test data, and the average accuracy of 10 tests was obtained.
The particular type of classification algorithm chosen by the researchers is a quantum-annealing-based supervised machine learning algorithm called a support vector machine. The quantum annealer they used was the D-Wave Advantage 4.1 system, a physical quantum computing device.
Quantum annealing implementations of support vector machines have demonstrated better performance than their classical counterparts, which are structurally simple and robust, but have high storage and computation costs and thus do not scale up easily.
Quantum annealing is an optimization process that uses quantum fluctuations to look for a global minimum among a set of solutions. Because the process generates multiple good candidates for the global minimum, it can achieve more accurate results than other optimization algorithms, which are more likely to get stuck at a local minimum.
END
Quantum computing and machine learning are effective tools in fluid dynamics
Quantum support vector machines classify flow separation better than classical counterparts
2024-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Modified soft material promises better bioelectronics
2024-01-16
The scientific community has long been enamored of the potential for soft bioelectronic devices, but has faced hurdles in identifying materials that are biocompatible and have all of the necessary characteristics to operate effectively. Researchers have now taken a step in the right direction, modifying an existing biocompatible material so that it conducts electricity efficiently in wet environments and can send and receive ionic signals from biological media.
“We’re talking about ...
Study reveals key factors in surgeons' opioid prescribing patterns
2024-01-16
Key takeaways
Decreasing trend in opioid prescriptions: There was a notable nationwide reduction in opioid prescriptions after surgery from 2013 to 2017, reflecting a shift in the medical community's approach to pain management.
Social determinants affect opioid prescription rates: At the county level, lower median population age, higher education levels, insufficient sleep, higher health care costs, fewer mental health providers, and higher uninsured rates are linked to higher opioid prescription rates.
No ...
We need a staph vaccine: here’s why we don’t have one
2024-01-16
Staphylococcus aureus (SA) is an extremely common bacterial infection; about 30% of people have colonies of SA living in their nose. SA is often harmless, but it is also a leading cause of hospital-acquired and community-associated infections. A vaccine for SA would be a game-changer for public health, but for decades, all vaccine candidates for SA have failed in clinical trials despite successful preclinical studies in mice. Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have finally explained why.
In a new study, published January ...
Analysis of breast cancer mortality in the US
2024-01-16
About The Study: Based on four simulation models, breast cancer screening, treatment of stage I to III breast cancer, and treatment of metastatic breast cancer were each associated with reduced breast cancer mortality between 1975 and 2019 in the U.S.
Authors: Sylvia K. Plevritis, Ph.D., of the Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.25881)
Editor’s ...
Consumption of 100% fruit juice and body weight in children and adults
2024-01-16
About The Study: This systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 eligible studies, including 17 among children (n = 45,851) and 25 among adults (n = 268,095), found a positive association between intake of 100% fruit juice and weight gain in children. Analysis of cohort studies in adults found a significant positive association among studies unadjusted for total energy, suggesting potential mediation by calories; an analysis of trials in adults found no significant association between 100% fruit juice consumption and body weight. The findings ...
Employer-sponsored health insurance premium cost growth and its association with earnings inequality among families
2024-01-16
About The Study: The findings of this study of U.S. families receiving employer-sponsored health insurance suggest that three decades of increasing health care premiums were likely associated with reduced annual earnings and increased earnings inequality by race and ethnicity and wage level and were meaningfully associated with wage stagnation.
Authors: Kurt Hager, Ph.D., M.S., of the UMass Chan Medical School in Worcester, Massachusetts, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Experiences of interpersonal violence in sport and perceived coaching style among college athletes
2024-01-16
About The Study: The results of this survey study involving 4,119 currently competing U.S. college athletes suggest that interpersonal violence is associated with marked changes in the psychosocial health and emotional well-being of college athletes, particularly those who identify as female and with non-heterosexual sexual orientations. Variations in coaching style have the potential to alter these associations. Ongoing efforts are needed to leverage the unique position that coaches hold to help reduce interpersonal violence and create safe places where all college athletes can thrive.
Authors: Yetsa A. Tuakli-Wosornu, M.D., ...
Largest-ever study of palliative care demonstrates scalable strategy to increase support for seriously ill patients in the hospital
2024-01-16
PHILADELPHIA – Ordering a palliative care consultation by “default” – via an automatic order programmed into the electronic medical record that doctors may cancel if they choose – is an effective strategy to give more hospitalized patients the opportunity to benefit from palliative care, and sooner, according to a new study led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Palliative care is specialized medical care focused on relieving the symptoms and stress of a serious illness and improving quality of life, in alignment with a patient’s ...
Cost of employer-sponsored health insurance is flattening worker wages, contributing to income inequality
2024-01-16
The rising cost of health insurance is an ongoing concern in the United States. New research shows that increasing health insurance costs are eating up a growing proportion of worker’s compensation, and have been a major factor in both flattening wages and increasing income inequality over the past 30 years.
In a study from the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University, researchers found that the cost of employer-sponsored insurance (ESI) health care benefits increased much faster than workers’ wages since the late 1980s, ...
Palliative telecare significantly improves quality of life for those with chronic illnesses, and results last for months
2024-01-16
AURORA, Colo. (January 16, 2024) – Researchers from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have found that a team intervention, provided by phone, leads to persistent improvements in depression, anxiety, and quality of life for people managing chronic illnesses. Additionally, researchers found that the improvement in quality of life results last months after intervention concludes.
In a study, published today in JAMA, researchers observe the impact a telecare intervention program, called ADAPT, has on veterans suffering from poor quality of life as a result ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Quantum computing and machine learning are effective tools in fluid dynamicsQuantum support vector machines classify flow separation better than classical counterparts