(Press-News.org)
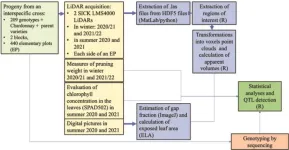
In response to the pressing need to reduce pesticide usage and adapt grapevine varieties to climate change, there's an unprecedented effort to phenotype new genotypes using high-throughput methods. Teams globally are developing advanced systems, employing technologies like multispectral cameras and LiDAR, to assess growth traits, photosynthetic capability, and other architectural parameters. However, traditional methods remain time-consuming and less efficient for large-scale studies. The current research gap lies in effectively employing LiDAR technology to explore genetic factors affecting grapevine vigor for sustainable viticulture.
In November 2023, Plant Phenomics published a research article entitled by “LiDAR Is Effective in Characterizing Vine Growth and Detecting Associated Genetic Loci ”.
The study assessed growth traits in 209 grapevine genotypes using methods such as fresh pruning wood weight, exposed leaf area from digital images, leaf chlorophyll concentration, and LiDAR-derived volumes. It found 6 genomic regions associated with trait variations, validating LiDAR as an effective tool for characterizing grapevine growth. LiDAR-derived canopy volumes showed strong correlations with traditional methods, and pruning wood volume from LiDAR positively correlated with actual pruning weight. However, some relationships varied between seasons, indicating that LiDAR provided more consistent measurements overall. Traits except exposed leaf area (ELA) in certain years met normality criteria, and parents displayed significant differences for most traits. LiDAR-derived traits exhibited high, stable heritability, outperforming traditional methods. These traits also led to effective genetic models explaining substantial phenotypic variance. The study generated high-density genetic maps and identified quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with growth traits. It found stable QTLs across seasons and validated the genetic determinism of grapevine vigor using LiDAR. The study also noted that LiDAR-derived volumes at véraison and winter were more reliable and heritable than traditional methods, and powerful QTL detection confirmed their efficacy.
In summary, this research underscores the potential of LiDAR technology for high-throughput phenotyping and genetic studies of grapevine growth, providing a more efficient alternative to conventional methods. It opens avenues for understanding environmental effects, management techniques, and training systems on grapevine growth, moving towards more detailed genetic insights into grapevine vigor and architecture.
###
References
Authors
Elsa Chedid1, Komlan Avia1, Vincent Dumas1, Lionel Ley2, Nicolas Reibel2, Gisèle Butterlin1, Maxime Soma3, Raul Lopez-Lozano4, Frédéric Baret4, Didier Merdinoglu1, and Éric Duchêne1*
Affiliations
1INRAE, University of Strasbourg, UMR SVQV, 28, rue de Herrlisheim, 68000 Colmar, France.
2INRAE, UEAV, 28, rue de Herrlisheim, 68000 Colmar, France.
3INRAE, Aix-Marseille Université, UMR RECOVER, 3275 Route de Cézanne, 13182 Aix-en-Provence, France.
4INRAE, Avignon Université, UMR EMMAH, UMT CAPTE, 228, route de l’aérodrome, 84914 Avignon, France.
About Éric Duchêne
He is currently the Deputy Director of the Joint INRAE-UNISTRA Research Unit on Vine Health and Wine Quality (SVQV). His research revolves around two main lines: on the one hand, plant-(vector)-pathogen interactions to reduce the use of pesticides and the impact of diseases; on the other hand, to maintain the productivity of vineyards and the quality of wines in the context of vine decline and climate change.
END
Cultivating seed mixtures for local pastures is an age-old method to produce cost-effective and balanced animal feed, enhancing agricultural autonomy and environmental friendliness in line with evolving European regulations and organic consumer demands. Despite its benefits, farmers face adoption challenges due to the asynchronous ripening of cereals and legumes and the difficulty in assessing the nutritional value of heterogeneous seeds. Current practices rely on informal, empirical methods, and a proposed solution is to develop a mobile app or online service, similar to Pl@ntNet, for automated nutritional evaluation of seed mixtures, ...
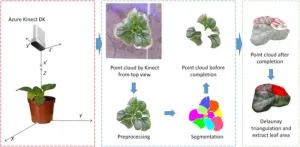
The 3-dimensional point cloud technology revolutionizes non-invasive measurement of plant phenotypic parameters, offering vital data for agriculture and research. Current research focuses on overcoming the limitations of 2.5D imaging and occlusions. Methods such as structure from motion, multi-view stereo, and advanced active 3D reconstruction techniques are being explored for this purpose. However, issues persist with incomplete data acquisition and the inaccuracy of phenotypic parameter extraction due ...
To improve grape yield predictions, automated berry counting has emerged as a crucial yet challenging task due to the dense distribution and occlusion of berries. While grape cultivation is a significant global economic activity, traditional manual counting methods are inaccurate and inefficient. Recent research has shifted towards deep learning and computer vision, employing detection and density estimation techniques for more precise counts. However, these methods grapple with the variability of farmland and high occlusion rates, leading to significant counting errors. Additionally, creating high-performance ...
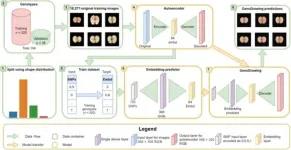
Advancements in whole-genome sequencing have revolutionized plant species characterization, providing a wealth of genotypic data for analysis. The combination of genomic selection and neural networks, especially deep learning and autoencoders, has emerged as a promising method for predicting complex traits from this data. Despite the success in applications like plant phenotyping, challenges remain in accurately translating visual information from images into measurable data for genomic studies.
In November 2023, Plant ...
Erin Overstreet has been selected as the new executive director of the USC Stevens Center for Innovation where she will oversee the university’s commercialization of USC-driven intellectual property.
Overstreet’s expertise and experience embody technology transfer and innovation across the academic, educational, and venture capital sectors; such experience is critical for bridging USC research to a broadened, national technology transfer ecosystem, said Ishwar Puri, senior vice president of the Office of Research and Innovation.
“The university has the utmost confidence in Dr. Overstreet’s ability to ...
In the field of Landscape Architecture, Topography aims to study the complex and ongoing changing relationship between humans and the land through continuously updated and iterative tools and media. It maintains a balance between abstract concepts and concrete perceptions, which can both drive the development of science and technology in this field and hold on to openness to artistic expression. Thus, topographical design may be an effective way to help facilitate refining landscape design methods.
The work entitled “Can Topography ...
Associate Professor Andrew Baker from QUT School of Biology and Environmental Science said antechinuses are carnivorous marsupials well-known for suicidal sex sessions where all males die after the 1 to 3 week breeding period.
“During the breeding season, male and females mate promiscuously in frenzied bouts lasting as long as 14 hours. Certain stress-induced death follows for all males as surging testosterone causes cortisol to flood uncontrolled through the body, reaching pathological levels,” Professor Baker said.
“The males drop dead, which provides an opportunity ...
Protecting the world’s oceans against accelerating damage from human activities could be cheaper and take up less space than previously thought, new research has found.
The University of Queensland’s Professor Anthony Richardson collaborated on the study, which looks to halt the rapid decline of marine biodiversity from expanding industrial activities in marine areas beyond national jurisdictions (ABNJ).
“This ‘blue acceleration’ as we call it, has seen a greater diversity of stakeholders interested in ABNJs, such as the high seas and the international seabed beyond exclusive economic zones,” ...
Frequently using more than three strategies to stay alert while driving could be a sign of excessive sleepiness due to obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), according to a study published today (Thursday) in ERJ Open Research [1].
People with OSA often snore loudly, their breathing starts and stops during the night, and they may wake up several times. Around one in five people are estimated to have OSA but the majority of sufferers do not realise they have a problem. OSA causes excessive sleepiness and people with untreated OSA are at higher risk of collisions on the road.
Researchers say that asking people ...
Globally, non-point source pollution is an important source of water quality deterioration in rivers and lakes. A ditch-pond system, consisting of ditches and ponds, is considered to be similar to free-surface wetlands, linking pollution sources to the receiving water bodies. The ditch-pond system includes vegetation, microorganisms and sediment, which can slow down the flow velocity and promote the precipitation of particulate matter carried by running water. At the same time, ditch and pond systems reduces nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations, and those of other nutrients entering the downstream water by means of plant absorption, sediment adsorption and microbial degradation, ...