(Press-News.org) Consider the faba bean, also known as the fava bean or broad bean.
The bright-green legume has been enjoyed as a diet staple for thousands of years in Africa, Asia, and the Mediterranean. Just one cup of faba beans has 13 grams of protein — making it a better protein source than most other legumes — along with plenty of fiber, potassium, and iron. Plus, it’s a good cover crop that helps improve soil health, slow erosion, and control pests, disease, and weeds.
But you don’t often see it in the fields or on the menus in Virginia.
That’s why College of Agriculture and Life Sciences Professor and Virginia Cooperative Extension Specialist Maria Balota is piloting a $2.7 million multistate project funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture's National Institute of Food and Agriculture Specialty Crops Research Initiative to introduce the faba bean as a sustainable fall and winter crop in the mid-Atlantic region.
“Growing resilient crops to climate change is one way to achieve agricultural sustainability in an evolving environment,” Balota said. “We can improve traditional plant varieties’ tolerance of more extreme temperatures and rainfall through breeding. But in addition to this strategy, we can scavenge for crops that fit this new environment naturally. Faba beans are a cool-season legume that fit well into the winter production systems of the mid-Atlantic.”
Balota is teaming up with School of Plant and Environmental Sciences Associate Professor David Haak, food science and technology Professor Sean O’Keefe, and other researchers from Virginia Tech, Virginia State University, University of Maryland, North Carolina State University, and the University of Delaware to conduct on-farm field studies of the faba bean in each state.
In addition to cultivating hardy faba beans that can thrive in the mid-Atlantic’s fall and winter climate, researchers plan to develop the most nutritious and flavorful beans to appeal to consumers.
They will also create Extension programs for farmers and industry partners and convene a Faba Bean Advisory Committee. The committee, composed of researchers, growers, processors, seed producers, Extension agents, and farmers market representatives, will meet annually to evaluate the program and the faba bean’s potential for broader production.
“The faba is gaining popularity in Europe and United States because of an increased trend in veganism,” said Balota, who is based at the Tidewater Agricultural Research and Extension Center. “Among the pulses, the faba bean has the highest protein content – 50 percent over that of lima beans based on our preliminary data – which makes it a fabulous choice for plant-derived protein products for vegan diets. Of course, fresh and dry faba seed consumption is perfectly reasonable in hummus, soups, and sautéed and puréed dishes. Or, if you like, in salads along with young, fresh leaves. Stems and old leaves can go into the ground to improve the soil. Everything is useable from it.”
Federal and state incentive programs reward the planting of cover crops as a climate-smart practice that reduces erosion and runoff, improves soil health, and supports bees and other pollinators. Virginia farmers grow over 430,000 acres of cover crops, predominantly as a means of enhancing soil nutrients before planting cash crops in the spring.
The researchers hope that the faba bean will prove to be a sustainable cover crop and cash crop that brings nutritional, environmental, and economic benefits to the region.
“Why not attempt to grow a legume – either as a green faba bean or dry fava seed – as a major crop that can bring farmers soil benefits along with some cash?” Balota said. “It’s a win for Virginia’s farmers, the state’s economy, and the climate.”
Other Virginia Tech researchers on this project include
Abhilash Chandel, assistant professor of precision agriculture technologies and data management at the Tidewater Agricultural and Research Extension Center
Joseph Oakes, superintendent of the Eastern Virginia Agricultural and Research Extension Center
Renata Carneiro, research assistant professor in the Department of Food Science and Technology
Alejandro Del-Pozo, assistant professor of entomology at the Hampton Roads Agricultural and Research Extension Center
Douglas Higgins, assistant professor of plant pathology and Extension specialist at the Eastern Shore Agriculture Research and Extension Center END
Researchers awarded $2.7 million grant to develop the faba bean as a sustainable mid-Atlantic crop
Because of its high nutrition and cool-weather hardiness, the faba bean poses great agricultural promise for feeding a changing world
2024-01-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cobalt-free batteries could power cars of the future
2024-01-18
CAMBRIDGE, MA – Many electric vehicles are powered by batteries that contain cobalt — a metal that carries high financial, environmental, and social costs.
MIT researchers have now designed a battery material that could offer a more sustainable way to power electric cars. The new lithium-ion battery includes a cathode based on organic materials, instead of cobalt or nickel (another metal often used in lithium-ion batteries).
In a new study, the researchers showed that this material, which could be produced at much lower cost than cobalt-containing batteries, can conduct electricity at similar rates as cobalt batteries. The new battery also has comparable storage ...
New study reveals the impact of skin microorganisms on earthworm toxicity in polluted environments
2024-01-18
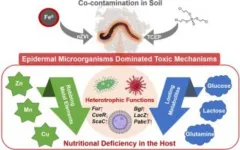
Epidermal microorganisms, vital in nutrient exchange between hosts and environments, have now been shown to play a key role in host toxicity through community changes. This research highlights how changes in the community of skin-based microbes correlate more significantly with earthworm toxicity than those in intestinal microorganisms, especially under combined soil contaminations.
A new study (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eehl.2023.11.001) published in the journal Eco-Environment & Health, researchers from Zhejiang University revealed the crucial role of epidermal microorganisms in influencing earthworm toxicity under environmental stress, notably in conditions ...
Scientists, farmers and managers work together to avoid the decline of the little bustard, an endangered steppe bird
2024-01-18
The collaboration between scientists, farmers and managers is crucial to improve the protection of the little bustard, an endangered steppe-land bird in Spain due to human activity. The reduction of natural habitats, the increase in irrigation and the urbanization of the land have led to having less surface areas that guarantee the survival of this vulnerable species. An article published in the journal Biological Conservation reveals how cooperation between different actors is key to finding answers and avoiding the decline of the most threatened populations of the little bustard.
The study, a pioneer example of adaptative conservation, ...
Better wireless communication made possible through machine learning
2024-01-18
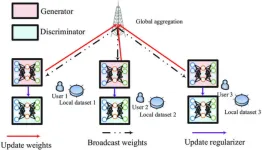
In today's increasingly interconnected world, high-quality communication has become more vital than ever. Accurately estimating the dynamic status of communication channels is a key factor in achieving this. Recently, a joint research team designed a new algorithm that offers high-level estimation accuracy and privacy protection with low computational and communication costs. This research was published Jan. 5 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
This new algorithm uses a specially designed deep learning model for precise estimation and a federated learning framework ...
Study with over 11,000 individuals of African descent finds genetic variants linked to glaucoma
2024-01-18
Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness around the globe, affecting up to 44 million people. Although people of African ancestry are most frequently and severely affected by this hereditary disease, its genetic underpinnings in this population have rarely been studied. Now, a team of investigators has published findings revealing previously unknown inherited genetic variants that contribute to primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), the most common form of the disease. The study was based on the analysis of 11,275 individuals of African descent and is being published January 18, 2024, in Cell.
“Individuals with African ancestry are five times more likely to be affected ...
Economics: Sea level rises could cost EU and UK economies up to 872 billion Euros by 2100
2024-01-18
Damage caused by sea level rises could cost the EU and UK economies up to 872 billion Euros in total by the end of the century, according to a modelling study published in Scientific Reports.
Ignasi Cortés Arbués, Theodoros Chatzivasileiadis, Tatiana Filatova and colleagues modelled the potential economic impacts of sea level rises for 271 European regions by 2100 under a high emissions scenario (SSP5-RCP8.5) with no new coastal protection measures implemented after 2015. They combined ...
Genetics: Chewing over poor Mesolithic oral health
2024-01-18
Members of a hunter-gatherer group that lived in south-western Scandinavia during the Mesolithic era — approximately 10,000 years ago — may have been affected by tooth decay and gum disease, according to a study published in Scientific Reports.
Emrah Kırdök, Anders Götherström and colleagues sequenced the DNA found on three pieces of birch tar — a substance made from heated birch bark — that were excavated in the 1990s from Huseby Klev, Sweden and have been dated to between 9,890 ...
Mega-analysis identifies gene variants associated with glaucoma in people of African ancestry
2024-01-18
PHILADELPHIA— A new analysis focusing specifically on people of African ancestry identified three gene variants that may be contributing to this population’s susceptibility to developing and being blinded by glaucoma. People of African ancestry are five times as likely as others to develop glaucoma and up to 15 times as likely to be blinded by the condition, but the vast majority of research has used data from people of European ancestry. Led by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University ...
Third major study finds evidence that daily multivitamin supplements improve memory and slow cognitive aging in older adults
2024-01-18
By 2060, according to the Alzheimer’s Association, nearly one in four Americans will be in an age bracket at elevated risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease unless interventions can help preserve cognitive function before deficits begin. The COcoa Supplement and Multivitamin Outcomes Study (COSMOS) is a large-scale, nationwide, randomized trial rigorously testing cocoa extract and multivitamin supplements directed by researchers at Mass General Brigham. Two previously published studies of cognition in COSMOS suggested a positive effect for a daily multivitamin. ...
Nurse home visits have a lasting impact for disadvantaged mothers and daughters
2024-01-18
Nurse home visits to disadvantaged mothers can significantly reduce their rates of hypertension and their daughters’ likelihood of obesity, finds a new reanalysis of health data by a team led by a UCL researcher.
The study, published in the journal JAMA Network Open, reanalysed data taken as part of a Nurse-Family Partnership trial started more than 30 years ago – The Memphis New Mothers Study (1990-1994). The researchers found that prenatal and infancy nurse home visits decreased the likelihood of daughters being obese by 55% and being severely obese by 81% in adolescence. Similarly, mothers of girls showed a decrease ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Researchers awarded $2.7 million grant to develop the faba bean as a sustainable mid-Atlantic cropBecause of its high nutrition and cool-weather hardiness, the faba bean poses great agricultural promise for feeding a changing world