(Press-News.org) By 2060, according to the Alzheimer’s Association, nearly one in four Americans will be in an age bracket at elevated risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease unless interventions can help preserve cognitive function before deficits begin. The COcoa Supplement and Multivitamin Outcomes Study (COSMOS) is a large-scale, nationwide, randomized trial rigorously testing cocoa extract and multivitamin supplements directed by researchers at Mass General Brigham. Two previously published studies of cognition in COSMOS suggested a positive effect for a daily multivitamin. COSMOS researchers now report the results of a third study of cognition in COSMOS, which focused on participants who underwent in-person assessments, together with the results of a combined analysis from the three separate studies. The results from this latest report confirm consistent and statistically significant benefits of a daily multivitamin versus placebo for both memory and global cognition. Results are published today in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
“Cognitive decline is among the top health concerns for most older adults, and a daily supplement of multivitamins has the potential as an appealing and accessible approach to slow cognitive aging,” said first author Chirag Vyas, MBBS, MPH, instructor in investigation at the Department of Psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system.
In the in-clinic study the researchers administered detailed, in-person cognitive assessments among 573 participants in the subset of COSMOS known as COSMOS-Clinic. Within COSMOS, two previous studies had tested multivitamin supplementation on cognition using telephone-based cognitive assessments (COSMOS-MIND) and online web-based cognitive assessments (COSMOS-Web). In their prespecified analyses of data from COSMOS-Clinic, investigators observed a modest benefit for the multivitamin, compared to placebo, on global cognition over two years. There was a statistically significant benefit of multivitamin supplementation for change in episodic memory, but not in executive function/attention.
The team also conducted a meta-analysis based on the three separate studies, with non-overlapping COSMOS participants (ranging 2-3 years in treatment duration), which showed strong evidence of benefits for both global cognition and episodic memory. The authors estimate that the daily multivitamin slowed global cognitive aging by the equivalent of two years compared to placebo.
Vyas said, “The meta-analysis of three separate cognition studies provides strong and consistent evidence that taking a daily multivitamin, containing more than 20 essential micronutrients, helps prevent memory loss and slow down cognitive aging.” Olivia Okereke, MD SM, senior author of the report and director of Geriatric Psychiatry at MGH, added “These findings will garner attention among many older adults who are, understandably, very interested in ways to preserve brain health, as they provide evidence for the role of a daily multivitamin in supporting better cognitive aging.”
The overall COSMOS trial is led by JoAnn Manson, MD, DrPH, and Howard Sesso, ScD, MPH, both of Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), also a founding member of Mass General Brigham. Manson, co-author of the report and Chief of the Division of Preventive Medicine at BWH, commented: “The finding that a daily multivitamin improved memory and slowed cognitive aging in three separate placebo-controlled studies in COSMOS is exciting and further supports the promise of multivitamins as a safe, accessible and affordable approach to protecting cognitive health in older adults.”
The COSMOS consortium of cognitive studies represents a collaboration between MGH, BWH, Columbia University, and Wake Forest University, using both traditional and innovative approaches to assessing cognitive outcomes. These approaches allow large numbers of participants (>5,000 in total) to be included in cognitive studies in a high-quality and cost-efficient manner. COSMOS participants are aged 60 and older and reside throughout the U.S.
Sesso, also a co-author and the associate director of the BWH Division of Preventive Medicine, added: “With these three studies using different approaches for assessing cognition in COSMOS, each providing support for a daily multivitamin, it is now critical to understand the mechanisms by which a daily multivitamin may protect against memory loss and cognitive decline with a focus on nutritional status and other aging-related factors. For example, the modifying role of baseline nutritional status on protecting against cognitive decline has been shown for the COSMOS cocoa extract intervention. A typical multivitamin such as that tested in COSMOS contains many essential vitamins and minerals that could explain its potential benefits.”
COSMOS Cognition Coauthors:
Chirag M. Vyas (MGH), JoAnn E. Manson (BWH); Howard D. Sesso (BWH); Nancy R. Cook (BWH); Pamela M. Rist (BWH); Alison Weinberg (BWH); M Vinayaga Moorthy (BWH); Laura D. Baker (Wake Forest University); Mark A. Espeland (Wake Forest University); Lok-Kin Yeung (Columbia University); Adam M. Brickman (Columbia University); Olivia I. Okereke (MGH).
Disclosures: Sesso additionally reported receiving investigator-initiated grants from Pure Encapsulations and Pfizer Inc. and honoraria and/or travel for lectures from the Council for Responsible Nutrition, BASF, NIH, and the American Society of Nutrition during the conduct of the study.
Funding: COSMOS-Clinic and the cognition studies in the meta-analysis were supported in-part by investigator-initiated grants from Mars Edge, a segment of Mars Inc., and the National Institutes of Health. Multivitamin and placebo tablets and packaging were donated by Pfizer, Inc Consumer Healthcare (now Haleon).
Paper cited: Vyas CM, Manson, JE, Sesso HD, et al. “Effect of multivitamin-mineral supplementation versus placebo on cognitive function: Results from the clinic sub-cohort of the COSMOS randomized clinical trial and meta-analysis of three cognition studies within COSMOS” AJCN D0I: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.12.011
END
Third major study finds evidence that daily multivitamin supplements improve memory and slow cognitive aging in older adults
In a meta-analysis of 5,000 participants, including more than 500 who underwent in-person assessments over two years, multivitamins showed benefits for memory and global cognition
2024-01-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nurse home visits have a lasting impact for disadvantaged mothers and daughters
2024-01-18
Nurse home visits to disadvantaged mothers can significantly reduce their rates of hypertension and their daughters’ likelihood of obesity, finds a new reanalysis of health data by a team led by a UCL researcher.
The study, published in the journal JAMA Network Open, reanalysed data taken as part of a Nurse-Family Partnership trial started more than 30 years ago – The Memphis New Mothers Study (1990-1994). The researchers found that prenatal and infancy nurse home visits decreased the likelihood of daughters being obese by 55% and being severely obese by 81% in adolescence. Similarly, mothers of girls showed a decrease ...
Cannabis and driving in older adults
2024-01-18
About The Study: The findings of this study that included 31 participants ages 65 to 79 suggest that older drivers, even if they regularly use cannabis, show evidence of impaired driving performance after smoking cannabis. Weaving was increased and speed was decreased at 30 minutes after smoking, which was not correlated with blood tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) concentrations; subjective experience and self-reports of impaired driving persisted for three hours.
Authors: Patricia Di Ciano, Ph.D., of the Centre for Addiction ...
Neurostimulation for advanced Parkinson disease and quality of life at 5 years
2024-01-18
About The Study: This nonrandomized controlled trial of 108 patients with advanced Parkinson disease found that at 5-year follow-up quality of life remained stable in the deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus (STN-DBS) group and worsened in the standard-of-care medication group, mainly driven by the favorable effect of STN-DBS on mobility. These findings may provide helpful information when counseling patients on the efficacy of STN-DBS for Parkinson disease and monitoring patients postoperatively in long-term follow-up.
Authors: Stefanie T. Jost, Ph.D., and Haidar S. Dafsari, M.D., of the University of Cologne, Germany, are the corresponding ...
Monell Center study: New gut-brain circuits found for sugar and fat cravings
2024-01-18
Philadelphia, PA (January 18, 2024) – Understanding why we overeat unhealthy foods has been a long-standing mystery. While we know food's strong power influences our choices, the precise circuitry in our brains behind this is unclear. The vagus nerve sends internal sensory information from the gut to the brain about the nutritional value of food. But, the molecular basis of the reward in the brain associated with what we eat has been incompletely understood.
Now, a new study published in Cell Metabolism by a team from the ...
Ancient chewing gum reveals stone age diet
2024-01-18
What did people eat on the west coast of Scandinavia 10 000 years ago? A new study of the DNA in a chewing gum shows that deer, trout and hazelnuts were on the diet. It also shows that one of the individuals had severe problems with her teeth.
Some 9 700 years ago, a group of people were camping on the west coast of Scandinavia, north of what is today Göteborg. They had been fishing, hunting and collecting resources for food. And some teenagers, both boys and girls, were chewing resin to produce glue, just after ...
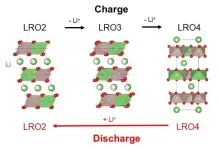
Hidden cause of lithium-rich cathode materials’ low energy efficiency revealed
2024-01-18
1. A research team consisting of the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) and Softbank Corp. has found that voltage hysteresis in Li2RuO3—a high-energy-density rechargeable battery cathode material—is caused by differences in the intermediate crystalline phases formed during charge and discharge processes. Voltage hysteresis is a phenomenon detrimental to lithium (Li)-ion batteries in which discharge voltage becomes significantly lower than charge voltage. These results revealed a voltage-hysteresis-causing mechanism inconsistent with conventional theory.
2. ...
Next-generation batteries could go organic, cobalt-free for long-lasting power
2024-01-18
In the switch to “greener” energy sources, the demand for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries is surging. However, their cathodes typically contain cobalt — a metal whose extraction has high environmental and societal costs. Now, researchers in ACS Central Science report evaluating an earth-abundant, carbon-based cathode material that could replace cobalt and other scarce and toxic metals without sacrificing lithium-ion battery performance.
Today, lithium-ion batteries power everything from cell phones to laptops to electric vehicles. One of the limiting factors for realizing a global shift to energy produced by renewable sources — particularly for the transition ...
FAU Engineering receives $2.6 million NSF grant for CyberCorps student scholarship program
2024-01-18
The College of Engineering and Computer Science of Florida Atlantic University received a $2.6 million grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to establish a scholarship program in the burgeoning and critical field of cybersecurity. The NSF’s CyberCorps® Scholarship for Service program seeks to increase the number of qualified cybersecurity professionals working for federal, state, local, territorial and tribal governments.
The program is managed by the NSF in collaboration with the United States Office of Personnel Management and the U.S. Department of Homeland Security. FAU is one of only six universities ...
AI harnesses tumor genetics to predict treatment response
2024-01-18
In a groundbreaking study published on January 18, 2024, in Cancer Discovery, scientists at University of California San Diego School of Medicine leveraged a machine learning algorithm to tackle one of the biggest challenges facing cancer researchers: predicting when cancer will resist chemotherapy.
All cells, including cancer cells, rely on complex molecular machinery to replicate DNA as part of normal cell division. Most chemotherapies work by disrupting this DNA replication machinery in rapidly dividing tumor ...
AMS 2024 Annual Meeting highlights climate challenges and solutions
2024-01-18
[Boston, MA—January 18, 2023] The American Meteorological Society’s (AMS) 104th Annual Meeting will gather thousands of people at the Baltimore Convention Center 28 January–1 February to attend the world’s largest annual meeting focused on weather, water, and climate. The AMS is the professional society for everyone in the atmospheric and hydrologic sciences and services, including meteorologists, research scientists, emergency managers, academics, weather broadcasters, and more.
“The theme of our 104th Annual Meeting is ‘Living in a Changing Environment,’” says AMS President Brad Colman. “It’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Third major study finds evidence that daily multivitamin supplements improve memory and slow cognitive aging in older adultsIn a meta-analysis of 5,000 participants, including more than 500 who underwent in-person assessments over two years, multivitamins showed benefits for memory and global cognition