Neurostimulation for advanced Parkinson disease and quality of life at 5 years
JAMA Network Open
2024-01-18
(Press-News.org)
About The Study: This nonrandomized controlled trial of 108 patients with advanced Parkinson disease found that at 5-year follow-up quality of life remained stable in the deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus (STN-DBS) group and worsened in the standard-of-care medication group, mainly driven by the favorable effect of STN-DBS on mobility. These findings may provide helpful information when counseling patients on the efficacy of STN-DBS for Parkinson disease and monitoring patients postoperatively in long-term follow-up.
Authors: Stefanie T. Jost, Ph.D., and Haidar S. Dafsari, M.D., of the University of Cologne, Germany, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.52177)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.52177?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=011824
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-18
Philadelphia, PA (January 18, 2024) – Understanding why we overeat unhealthy foods has been a long-standing mystery. While we know food's strong power influences our choices, the precise circuitry in our brains behind this is unclear. The vagus nerve sends internal sensory information from the gut to the brain about the nutritional value of food. But, the molecular basis of the reward in the brain associated with what we eat has been incompletely understood.
Now, a new study published in Cell Metabolism by a team from the ...
2024-01-18
What did people eat on the west coast of Scandinavia 10 000 years ago? A new study of the DNA in a chewing gum shows that deer, trout and hazelnuts were on the diet. It also shows that one of the individuals had severe problems with her teeth.
Some 9 700 years ago, a group of people were camping on the west coast of Scandinavia, north of what is today Göteborg. They had been fishing, hunting and collecting resources for food. And some teenagers, both boys and girls, were chewing resin to produce glue, just after ...
2024-01-18
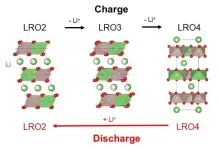
1. A research team consisting of the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) and Softbank Corp. has found that voltage hysteresis in Li2RuO3—a high-energy-density rechargeable battery cathode material—is caused by differences in the intermediate crystalline phases formed during charge and discharge processes. Voltage hysteresis is a phenomenon detrimental to lithium (Li)-ion batteries in which discharge voltage becomes significantly lower than charge voltage. These results revealed a voltage-hysteresis-causing mechanism inconsistent with conventional theory.
2. ...
2024-01-18
In the switch to “greener” energy sources, the demand for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries is surging. However, their cathodes typically contain cobalt — a metal whose extraction has high environmental and societal costs. Now, researchers in ACS Central Science report evaluating an earth-abundant, carbon-based cathode material that could replace cobalt and other scarce and toxic metals without sacrificing lithium-ion battery performance.
Today, lithium-ion batteries power everything from cell phones to laptops to electric vehicles. One of the limiting factors for realizing a global shift to energy produced by renewable sources — particularly for the transition ...
2024-01-18
The College of Engineering and Computer Science of Florida Atlantic University received a $2.6 million grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to establish a scholarship program in the burgeoning and critical field of cybersecurity. The NSF’s CyberCorps® Scholarship for Service program seeks to increase the number of qualified cybersecurity professionals working for federal, state, local, territorial and tribal governments.
The program is managed by the NSF in collaboration with the United States Office of Personnel Management and the U.S. Department of Homeland Security. FAU is one of only six universities ...
2024-01-18
In a groundbreaking study published on January 18, 2024, in Cancer Discovery, scientists at University of California San Diego School of Medicine leveraged a machine learning algorithm to tackle one of the biggest challenges facing cancer researchers: predicting when cancer will resist chemotherapy.
All cells, including cancer cells, rely on complex molecular machinery to replicate DNA as part of normal cell division. Most chemotherapies work by disrupting this DNA replication machinery in rapidly dividing tumor ...
2024-01-18
[Boston, MA—January 18, 2023] The American Meteorological Society’s (AMS) 104th Annual Meeting will gather thousands of people at the Baltimore Convention Center 28 January–1 February to attend the world’s largest annual meeting focused on weather, water, and climate. The AMS is the professional society for everyone in the atmospheric and hydrologic sciences and services, including meteorologists, research scientists, emergency managers, academics, weather broadcasters, and more.
“The theme of our 104th Annual Meeting is ‘Living in a Changing Environment,’” says AMS President Brad Colman. “It’s ...
2024-01-18
New research has been published that identifies positive steps towards a better understanding of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), specifically in hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP).
Antimicrobial, or antibiotic resistance, is a growing global issue, yet little is known about how to dose antibiotics to minimise bacteria developing resistance in patients. However, the University of Liverpool is playing a key role in contributing to international efforts to better understand AMR.
In a paper published today (Thursday 18 January), ...
2024-01-18
Researchers from McGill University, led by Professor Alanna Watt of the Department of Biology, have identified previously unknown changes in brain cells affected by a neurological disease. Their research, published in eLife, could pave the way to future treatments for the disease.
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 6, known as SCA6, is a rare neurological disease that disrupts the function in a part of the brain called the cerebellum, causing difficulties with movement and coordination. The condition results from genetic mutations, ...
2024-01-18
Considerable attention has focused on burnout and mental health of physicians and nurses on the frontline during the COVID-19 pandemic. First responders – law enforcement personnel, firefighters and emergency medical service (EMS) providers, also experienced increased levels of stress, anxiety and depression due to job-related pressures associated with the pandemic.
Given their exposure to work-related stress during this time, first responders may have been at considerable risk of developing problematic substance use. However, little is known about the factors associated with first responder drug and alcohol use during the pandemic.
A study by Florida ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Neurostimulation for advanced Parkinson disease and quality of life at 5 years
JAMA Network Open