(Press-News.org) Considerable attention has focused on burnout and mental health of physicians and nurses on the frontline during the COVID-19 pandemic. First responders – law enforcement personnel, firefighters and emergency medical service (EMS) providers, also experienced increased levels of stress, anxiety and depression due to job-related pressures associated with the pandemic.
Given their exposure to work-related stress during this time, first responders may have been at considerable risk of developing problematic substance use. However, little is known about the factors associated with first responder drug and alcohol use during the pandemic.
A study by Florida Atlantic University and collaborators used a nationwide online survey to assess the experiences of 2,801 first responders serving in police departments, fire stations and EMS agencies during the early stages of COVID-19 (late 2020 to early 2021). Researchers examined the mediating impact of burnout on the associations between work pressure, workplace support strategies, COVID-related support strategies and problematic substance use.
Findings of the study, published in the International Journal of Drug Policy, showed:
Almost 61 percent of respondents reported no concerns with substance use.
Nearly 40 percent of respondents reported using substances to relieve emotional discomfort.
About 22 percent of respondents reported using more substances than they meant to use.
Twenty-one percent of respondents reported that they could not cut down on substance use.
Only 7.2 percent of respondents reported neglecting responsibilities because of substance use.
For problematic substance use, firefighters (12.7 percent) had a slightly higher score than EMTs (11.4 percent) and police officers (8.1 percent).
Results also revealed that although work pressures increased burnout and problematic substance use among first responders, general workplace support strategies such as decompression spaces reduced problematic substance use. Conversely, some COVID-related strategies such as compensation during quarantine increased problematic substance use. These results suggest a complex relationship between COVID-related support strategies and problematic substance use that may be influenced by stress associated with quarantine measures and greater availability of substances while off-duty.
“First responders represent a unique population as they have increased exposure to trauma and stress, which can be exacerbated by public health epidemics,” said Kaila Witkowski, Ph.D., senior author and an assistant professor, FAU School of Public Administration within the Dorothy F. Schmidt College of Arts and Letters. “Spaces to decompress at work that combine quiet and relaxing spaces with easily accessible mental health resources may be one way to overcome various barriers in this population such as the stigma associated with seeking help.”
Study findings also suggest that strategies aimed at reducing work-related burnout could focus on improving personal resiliency. Researchers highlight the resiliency training program that was provided for first responders involved with the 2012 Aurora, Colorado movie theater mass shooting as an example, which used problem-based learning techniques to teach resiliency skills, resulting in benefits to coping with stress.
“Although intended to reduce stress associated with the job, organizations should be mindful that not all support strategies will have their intended impact, and some may even unintentionally increase stress, burnout, and problematic substance use,” said Witkowski. “While we are not contending that compensation during quarantine is a negative workplace strategy, our study highlights the nuances of the COVID-19 quarantine measure, suggesting that additional stressors may have been placed on first responders throughout this process or that other beneficial workplace strategies were not easily accessible or used during this time.”
Study co-authors are Ryan J. Lofaro, Ph.D., an assistant professor of public administration, Georgia Southern University and recent FAU graduate; Andrea Headley, Ph.D., an assistant professor, McCourt School of Public Policy at Georgetown University; Santina Contreras, Ph.D., an assistant professor, Sol Price School of Public Policy, University of Southern California; Christa L. Remington, Ph.D., an assistant professor, School of Public Affairs, University of South Florida; and N. Emel Ganapati, Ph.D., an associate professor and director, Laboratory for Social Science Research, Florida International University.
This research was funded by the Drug Enforcement and Policy Center at The Ohio State University.
- FAU -
About Florida Atlantic University:
Florida Atlantic University, established in 1961, officially opened its doors in 1964 as the fifth public university in Florida. Today, the University serves more than 30,000 undergraduate and graduate students across six campuses located along the southeast Florida coast. In recent years, the University has doubled its research expenditures and outpaced its peers in student achievement rates. Through the coexistence of access and excellence, FAU embodies an innovative model where traditional achievement gaps vanish. FAU is designated a Hispanic-serving institution, ranked as a top public university by U.S. News & World Report and a High Research Activity institution by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. For more information, visit www.fau.edu.
END
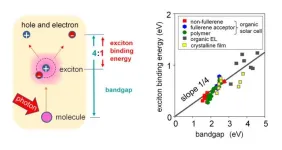
Organic semiconductors are a class of materials that find applications in various electronic devices owing to their unique properties. One attribute that influences the optoelectronic property of these organic semiconductors is their "exciton binding energy," which is the energy needed to divide an exciton into its negative and positive constituents. Since high binding energies can have a significant impact on the functioning of optoelectronic devices, low binding energies are desirable. This can help in reducing energy losses in devices like organic solar cells. While several methods for designing organic materials with low binding energies have ...
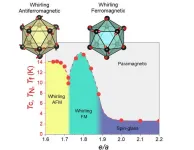
Quasicrystals are intermetallic materials that have garnered significant attention from researchers aiming to advance condensed matter physics understanding. Unlike normal crystals, in which atoms are arranged in an ordered repeating pattern, quasicrystals have non-repeating ordered patterns of atoms. Their unique structure leads to many exotic and interesting properties, which are particularly useful for practical applications in spintronics and magnetic refrigeration.
A unique quasicrystal variant, known as the Tsai-type icosahedral quasicrystal (iQC) and their cubic approximant crystals (ACs), display intriguing characteristics. These include long-range ferromagnetic (FM) ...
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have used DNA origami, the art of folding DNA into desired structures, to show how an important cell receptor can be activated in a previously unknown way. The result opens new avenues for understanding how the Notch signalling pathway works and how it is involved in several serious diseases. The study is published in Nature Communications.
Notch is a cell receptor that is of great importance to a wide range of organisms and plays a crucial role in many different processes, including early embryonic development in both flies and humans. Notch ...
The mystery behind why Alaskan horses, cryptodiran turtles and island lizards shrunk over time may have been solved in a new study.
The new theoretical research proposes that animal size over time depends on two key ecological factors: the intensity of direct competition for resources between species, and the risk of extinction from the environment.
Using computer models simulating evolution, the study, published today (Thursday, 18 January) in communications biology, identifies why some species gradually get smaller, as indicated by fossil records.
Dr Shovonlal Roy, an ecosystem modeller from the University of Reading who led the research, ...
Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center reported promising results in a Phase I/II trial of 37 patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies who were treated with cord blood-derived chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) natural killer (NK) cell therapy targeting CD19.
Published today in Nature Medicine, the findings reveal an overall response (OR) rate of 48.6% at 100 days post treatment, with one-year progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) rates of 32% & 68%, respectively. The trial reported an excellent safety profile with no cases of severe cytokine release syndrome (CRS), neurotoxicity, ...
· New finding to understand brain cell loss in neurodegenerative disease
· Increasing protective short RNAs may be new approach to halt or delay Alzheimer’s
· SuperAgers with superior memories have more protective short RNAs in their brains
CHICAGO --- Alzheimer’s disease, which is expected to have affected about 6.7 million patients in the U.S. in 2023, results in a substantial loss of brain cells. But the events that cause neuron death are poorly understood.
A new Northwestern Medicine study shows that RNA interference may play a key role in Alzheimer’s. For the first time, ...
The way science is funded is hampering Earth System Models and may be skewing important climate predictions, according to a new comment published in Nature Climate Change by Woodwell Climate Research Center and an international team of model experts.
Emissions from thawing permafrost, frozen ground in the North that contains twice as much carbon as the atmosphere does and is thawing due to human-caused climate warming, are one of the largest uncertainties in future climate projections. But accurate representation of permafrost dynamics is missing from ...
A team of researchers from China, Australia, France, Spain, and Germany has revealed advanced material culture in East Asia by 45,000 years ago.
The new study was published in Nature Ecology & Evolution on Jan. 18.
The researchers examined a previously excavated archaeological collection from the Shiyu site, located in Shanxi Province.
"Our new study identified an Initial Upper Palaeolithic archaeological assemblage from the Shiyu site of North China dating to 45,000 years ago that includes blade technology, tanged and hafted projectile points, long-distance obsidian transfer, and the use of a perforated ...
Throughout the brain’s cortex, neurons are arranged in six distinctive layers, which can be readily seen with a microscope. A team of MIT neuroscientists has now found that these layers also show distinct patterns of electrical activity, which are consistent over many brain regions and across several animal species, including humans.
The researchers found that in the topmost layers, neuron activity is dominated by rapid oscillations known as gamma waves. In the deeper layers, slower oscillations called alpha and beta waves ...
200 US communities will fail to transition to 100% renewable energy by 2050 despite their pledges to do so, according to a new study published in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research: Infrastructure and Sustainability.
The study shows that by 2050 gas will firmly remain the primary source of energy in the US given that the current infrastructure plans for implementing renewable energy cannot provide sufficient energy output. Recent projections suggest that renewable energy generation will need to triple to meet even a 45% share of energy production. The results indicate that in many instances renewable energy ...