(Press-News.org) Researchers from McGill University, led by Professor Alanna Watt of the Department of Biology, have identified previously unknown changes in brain cells affected by a neurological disease. Their research, published in eLife, could pave the way to future treatments for the disease.
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 6, known as SCA6, is a rare neurological disease that disrupts the function in a part of the brain called the cerebellum, causing difficulties with movement and coordination. The condition results from genetic mutations, with symptoms starting in adulthood and worsening over time, and currently has no cure.
While scientists have long known that SCA6 is characterized by changes in the cerebellum, the part of the brain that regulates motor movement and balance, the precise mechanisms of these changes and how they might contribute to the onset and progression of SCA6 are not fully understood.
The study looked at mouse models for SCA6, mice that were genetically modified with the same mutations as human SCA6 patients, and which exhibited movement problems consistent with the disease. Tissue samples from the SCA mice revealed striking and never-before-observed abnormalities in their cells’ endosomal systems.
“Cells are busy places, with lots of things going on, and it is therefore crucial for cells to transport proteins and molecules to the right place at the right time,” explained Anna Cook, a former McGill PhD researcher who is the first author of the study. “But in SCA6 this system goes wrong. Just like cars can get stuck in traffic, proteins and molecules can get held up in the transport machinery within certain cells.”
To see if the endosomal deficits could be corrected, the researchers tested a drug called 7,8-DHF and found that the compound corrected for the cellular abnormalities, enabling the misplaced proteins to get to where they needed to go. “This drug is effectively acting as a traffic cop,” Watt said. “It gets the traffic moving again, allowing key signaling molecules to get to the cellular locations where they are needed to work.”
“Since there is currently no cure for SCA6, new information about the pathological changes in the disease is vital to help develop new drugs and treatments,” Cook said. “This preclinical research is exciting not only because it sheds light on some of the fundamental mechanisms of this disease, but also because it points to an aspect of the disease that we have shown can be targeted therapeutically.”
The Watt lab continues to build on this work to identify disease mechanisms and potential treatments for SCA6 and other cerebellar diseases. Anna Cook is now a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Oxford, studying dopamine signaling in healthy and disease-affected brains.
About the study
Endosomal dysfunction contributes to cerebellar deficits in spinocerebellar ataxia type 6 was published in eLife.
END
Stuck in traffic: Researchers identify cellular traffic jams in a rare disease
Researchers zero in on spinocerebellar ataxia type 6, a disease that disrupts brain function
2024-01-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study examines substance use in first responders during the COVID-19 pandemic
2024-01-18
Considerable attention has focused on burnout and mental health of physicians and nurses on the frontline during the COVID-19 pandemic. First responders – law enforcement personnel, firefighters and emergency medical service (EMS) providers, also experienced increased levels of stress, anxiety and depression due to job-related pressures associated with the pandemic.
Given their exposure to work-related stress during this time, first responders may have been at considerable risk of developing problematic substance use. However, little is known about the factors associated with first responder drug and alcohol use during the pandemic.
A study by Florida ...
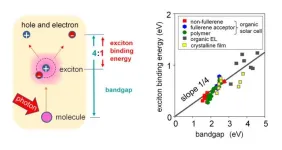
Lighting the path: Exploring exciton binding energies in organic semiconductors
2024-01-18
Organic semiconductors are a class of materials that find applications in various electronic devices owing to their unique properties. One attribute that influences the optoelectronic property of these organic semiconductors is their "exciton binding energy," which is the energy needed to divide an exciton into its negative and positive constituents. Since high binding energies can have a significant impact on the functioning of optoelectronic devices, low binding energies are desirable. This can help in reducing energy losses in devices like organic solar cells. While several methods for designing organic materials with low binding energies have ...
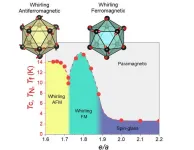
Unlocking the secrets of quasicrystal magnetism: revealing a novel magnetic phase diagram
2024-01-18
Quasicrystals are intermetallic materials that have garnered significant attention from researchers aiming to advance condensed matter physics understanding. Unlike normal crystals, in which atoms are arranged in an ordered repeating pattern, quasicrystals have non-repeating ordered patterns of atoms. Their unique structure leads to many exotic and interesting properties, which are particularly useful for practical applications in spintronics and magnetic refrigeration.
A unique quasicrystal variant, known as the Tsai-type icosahedral quasicrystal (iQC) and their cubic approximant crystals (ACs), display intriguing characteristics. These include long-range ferromagnetic (FM) ...
DNA construction led to unexpected discovery of important cell function
2024-01-18
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have used DNA origami, the art of folding DNA into desired structures, to show how an important cell receptor can be activated in a previously unknown way. The result opens new avenues for understanding how the Notch signalling pathway works and how it is involved in several serious diseases. The study is published in Nature Communications.
Notch is a cell receptor that is of great importance to a wide range of organisms and plays a crucial role in many different processes, including early embryonic development in both flies and humans. Notch ...
Why animals shrink over time explained with new evolution theory
2024-01-18
The mystery behind why Alaskan horses, cryptodiran turtles and island lizards shrunk over time may have been solved in a new study.
The new theoretical research proposes that animal size over time depends on two key ecological factors: the intensity of direct competition for resources between species, and the risk of extinction from the environment.
Using computer models simulating evolution, the study, published today (Thursday, 18 January) in communications biology, identifies why some species gradually get smaller, as indicated by fossil records.
Dr Shovonlal Roy, an ecosystem modeller from the University of Reading who led the research, ...
CD19-targeted CAR NK cell therapy achieves promising one-year results in patients with B-cell malignancies
2024-01-18
Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center reported promising results in a Phase I/II trial of 37 patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies who were treated with cord blood-derived chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) natural killer (NK) cell therapy targeting CD19.
Published today in Nature Medicine, the findings reveal an overall response (OR) rate of 48.6% at 100 days post treatment, with one-year progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) rates of 32% & 68%, respectively. The trial reported an excellent safety profile with no cases of severe cytokine release syndrome (CRS), neurotoxicity, ...
New cause of neuron death in Alzheimer's discovered
2024-01-18
· New finding to understand brain cell loss in neurodegenerative disease
· Increasing protective short RNAs may be new approach to halt or delay Alzheimer’s
· SuperAgers with superior memories have more protective short RNAs in their brains
CHICAGO --- Alzheimer’s disease, which is expected to have affected about 6.7 million patients in the U.S. in 2023, results in a substantial loss of brain cells. But the events that cause neuron death are poorly understood.
A new Northwestern Medicine study shows that RNA interference may play a key role in Alzheimer’s. For the first time, ...
Most Earth System Models are missing key piece of future climate puzzle
2024-01-18
The way science is funded is hampering Earth System Models and may be skewing important climate predictions, according to a new comment published in Nature Climate Change by Woodwell Climate Research Center and an international team of model experts.
Emissions from thawing permafrost, frozen ground in the North that contains twice as much carbon as the atmosphere does and is thawing due to human-caused climate warming, are one of the largest uncertainties in future climate projections. But accurate representation of permafrost dynamics is missing from ...
Shiyu discovery reveals East Asia’s advanced material culture by 45,000 years ago
2024-01-18
A team of researchers from China, Australia, France, Spain, and Germany has revealed advanced material culture in East Asia by 45,000 years ago.
The new study was published in Nature Ecology & Evolution on Jan. 18.
The researchers examined a previously excavated archaeological collection from the Shiyu site, located in Shanxi Province.
"Our new study identified an Initial Upper Palaeolithic archaeological assemblage from the Shiyu site of North China dating to 45,000 years ago that includes blade technology, tanged and hafted projectile points, long-distance obsidian transfer, and the use of a perforated ...
Study reveals a universal pattern of brain wave frequencies
2024-01-18
Throughout the brain’s cortex, neurons are arranged in six distinctive layers, which can be readily seen with a microscope. A team of MIT neuroscientists has now found that these layers also show distinct patterns of electrical activity, which are consistent over many brain regions and across several animal species, including humans.
The researchers found that in the topmost layers, neuron activity is dominated by rapid oscillations known as gamma waves. In the deeper layers, slower oscillations called alpha and beta waves ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Stuck in traffic: Researchers identify cellular traffic jams in a rare diseaseResearchers zero in on spinocerebellar ataxia type 6, a disease that disrupts brain function