New AEM study evaluates potential disparities in restraint use in the emergency department at a minority-serving safety-net hospital
2024-01-19
(Press-News.org) Des Plaines, IL — A new study that contributes additional data to a growing body of evidence demonstrating disparities in restraint use in the emergency department (ED) has been published in the January issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), the peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM). The study, titled Disparities in use of physical restraints at an urban, minority-serving hospital emergency department evaluates the association between race/ethnicity and the use of restraints in an ED population at a minority-serving, safety-net institution.
Using chart review methodology, Pino et al. observed a decrease in the odds of restraint use among Black and Hispanic patients compared to White patients in their ED among all adults. However, among patients with a documented history of mental illness or substance use disorder, the investigators found an increase in the use of restraints among female Black and Hispanic patients and among male Black patients (but not male Hispanic patients).
The lead author of this article is Elizabeth C. Pino, PhD, Department of Emergency Medicine, Boston Medical Center and Boston University School of Medicine. Pino et al. conclude that further studies are needed to evaluate the drivers of increased restraint use in patients of color with substance use disorder and mental health diagnoses and whether there are effective strategies to minimize the use of restraints and, when restraints are necessary, assure an equitable application of this intervention.
###
ABOUT ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE
Academic Emergency Medicine, the monthly journal of Society for Academic Emergency Medicine, features the best in peer-reviewed, cutting-edge original research relevant to the practice and investigation of emergency care. The above study is published open access and can be downloaded by following https://doi.org/10.1111/acem.14792. Journalists wishing to interview the authors may contact Laura Giblin at lgiblin@saem.org.
ABOUT THE SOCIETY FOR ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE
SAEM is a 501(c)(3) not-for-profit organization dedicated to the improvement of care of the acutely ill and injured patient by leading the advancement of academic emergency medicine through education and research, advocacy, and professional development. To learn more, visit saem.org.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-19
Using CRISPR, an immune system bacteria use to protect themselves from viruses, scientists have harnessed the power to edit genetic information within cells. In fact, the first CRISPR-based therapeutic was recently approved by the FDA to treat sickle cell disease in December 2023. That therapy is based on a highly studied system known as the CRISPR-Cas9 genetic scissor.
However, a newer and unique platform with the potential to make large-sized DNA removals, called Type I CRISPR or CRISPR-Cas3, waits in the wings for potential therapeutic use.
A new study from Yan Zhang, ...
2024-01-19
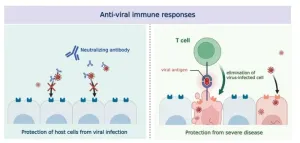
It has been 4 years since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 has yet to be eradicated and new variants are continuously emerging. Despite the extensive immunization programs, breakthrough infections (infection after vaccination) by new variants are common. New research suggests that human immune responses are also changing in order to combat the never-ending emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants. Specifically, it has been discovered the immune system that encountered breakthrough infection by the Omicron variant acquires enhanced immunity against future versions of the Omicron.
A team of South Korean scientists ...
2024-01-19
A team led by Dr. Guadalupe Sabio at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) in Madrid has discovered a possible therapeutic target for pulmonary hypertension.
The study, published in the journal Science Advances, identifies the first therapeutic target that can be modulated to preserve cardiac function in pulmonary hypertension, providing hope in the fight against this rare but fatal disease for which there is currently no cure.
Pulmonary hypertension is a condition of elevated blood pressure in the arteries that carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs. This increased pulmonary blood pressure puts the heart under continuous strain ...
2024-01-19
Scientists working on biological design should focus on the idiosyncrasies of biological systems over optimisation, according to new research.
In a study, published today in Science Advances, researchers from the Universities of Bristol and Ghent have shown how exploring the unknown may be the crucial step needed to realise the continual innovation needed for the biotechnologies of the future.
Recognising the role of open-endedness in achieving this goal and its growing importance in fields like computer science and evolutionary biology, the team mapped out how open-endedness is linked to bioengineering practice today and what would be required to achieve it in ...
2024-01-19
In the study led by the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) and published in Science Immunology, the researchers found that CD4+ T cells, traditionally called ‘helper T cells’ for their role in aiding the activation of other immune cells, are remarkably effective in controlling melanoma.
University of Melbourne’s Dr Emma Bawden, Postdoctoral Researcher at the Doherty Institute and lead author of the study, said this discovery challenges the conventional understanding of the role of CD4+ T cells in cancer immunity.
“Our ...
2024-01-19
A team of scientists led by a Tulane University oceanographer has found that deposits deep under the ocean floor reveal a way to measure the ocean oxygen level and its connections with carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere during the last ice age, which ended more than 11,000 years ago.
The findings, published in Science Advances, help explain the role oceans played in past glacial melting cycles and could improve predictions of how ocean carbon cycles will respond to global warming.
Oceans adjust atmospheric CO2 as ice ages transition to warmer climates by releasing the greenhouse ...
2024-01-19
URBANA, Ill. — In a few years, popcorn could become a standard element in science classrooms across Illinois and the nation. With funding from a new USDA grant, a University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign crop scientist and collaborating educators are developing a popcorn-based curriculum to reinforce concepts around agricultural science, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, computer science, genomics, research methods, and more for 4-H and high school students.
The funding may be new, but Tony Studer has proselytized ...
2024-01-19
Hepatitis C and B viruses are one of the causes of this type of cancer –a most frequent on in blood–, and the pathologies that precede it, known as gammopathies.
Early identification of an infection with these viruses can help doctors to prescribe appropriate treatment and prevent it from leading to malignant pathologies.
The research has been discussed in an editorial article in the journal Haematologica
A few years ago, a patient was cured of multiple myeloma after being treated for hepatitis C, astounding researchers from the group led by Joaquín ...
2024-01-19
Family businesses account for more than 70 percent of global GDP, and survey data shows that they are much friendlier to female leadership: up to 55 percent have at least one woman on their board and 70 percent are considering a woman for their next CEO. Experts have attributed this outlier gender parity to an emphasis on long-term strategies or family values. But a new study, published in the Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, suggests that women’s success as leaders in family businesses is deeply rooted in how employees interpret their leadership style.
“Family firms tend to focus on being inclusive ...
2024-01-19
The atmosphere contains many tiny solid particles. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPI-DS) and the University of Göttingen in collaboration with the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS) in France and the university of Gothenburg, Sweden, now studied how such non-spherical particles settle in air. For this, they used a new precision apparatus equipped with high-speed cameras and a novel particle injection mechanism. Using a 3D-printer, they created particles of different shapes resembling discs of thickness as low as 50 micrometer and rods of length as high as 880 micrometers. Thanks to this setup, they could observe that particles ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New AEM study evaluates potential disparities in restraint use in the emergency department at a minority-serving safety-net hospital