GIST researchers investigate strange transient responses of organic electrochemical transistors
Two novel 1,4-dithienylphenylene-based polymers were designed to explore peculiar transient behaviors of organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors
2024-01-22
(Press-News.org)
Organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors (OMIECs) are a highly sought-after class of materials for non-conventional applications, such as bioelectronics, neuromorphic computing, and bio-fuel cells, owing to their two-in-one electronic and ionic conduction properties. To ensure a much wider acceptance of these fascinating materials, there is a need to diversify their properties and develop techniques that allow application-specific tailoring of the features of OMIEC-based devices. A crucial aspect of this process is to develop strategies for evaluating the various properties of these materials. However, despite the increasing popularity of OMIECs, there is a severe lack of research on the molecular orientation-dependent transient behaviors of such conductors.
Now, however, an international team of researchers from Korea and UK, led by Professor Myung-Han Yoon from the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, set out to bridge this gap in our understanding of organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors. In their recent breakthrough study published in Nature Communications on 28 November 2023, the team explored peculiar transient behaviors of OMIECs governed by variations in molecular orientation with the help of an organic electrochemical transistor (OECT). In the past, several studies have already investigated OMIECs using the OECT platform, suggesting that various factors, such as direction, length, side chain symmetry, polymer backbone structure, and film crystallinity, modulate the properties of OECTs.
“OECTs are known to mimic the computing mechanisms of neurons and synapses in spiking neural networks (SNNs) and are thus considered promising,” explains Prof. Yoon, while talking about this study. “To aid the growing interest in exploring the dynamic behaviors of OECTs at the frequency domain, we focused on an aspect that is often overlooked. We decided to investigate the correlation between backbone planarity-dependent molecular orientation and transient OECT characteristics.”
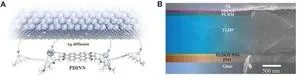
To this end, the researchers first synthesized two new 1,4-dithienylphenylene (DTP)-based OMEICs, DTP-2T and DTP-P, with co-monomer units, 2,2’-bithiophene and phenylene, respectively. The polymers comprised the same ionic and electronic properties, but by manipulating the polymer backbone planarity, the researchers were able to control the dominant molecular orientation of the mixed conductor system.
The DTP polymer was then used to fabricate OECT devices, which were subjected to electrochemical analysis. Initially, the team found that both polymers showed similar electrochemical properties despite having different molecular orientations. They then changed the ion injection direction when there was a certain current/voltage during the analysis. They observed that ion injection direction relative to the molecular orientation affected the length of the ion drift pathway, which, due to an indirect correlation with ion mobility within the polymers, resulted in peculiar transient responses in OECT devices.
The findings of this study provide a unique perspective into the world of molecular orientation-dependent characteristics of OECT devices. “OECT-based SNN architectures are anticipated to replace current computing systems in the future by increasing computation speed and reducing energy consumption. Our findings are expected to facilitate the realization of SNN-based computing systems soon,” concludes Prof. Yoon. Moreover, the team also believes that the insights from this study could facilitate the design and development of advanced organic mixed conductor materials for biomolecular and biosignal sensors.
Let us hope that this work paves the way for many exciting futuristic technologies!
***
Reference
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-42840-z
About the institute
The Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) was founded in 1993 by the Korean government as a research-oriented graduate school to help ensure Korea's continued economic growth and prosperity by developing advanced science and technology with an emphasis on collaboration with the international community. Since that time, GIST has pioneered a highly regarded undergraduate science curriculum in 2010 that has become a model for other science universities in Korea. To learn more about GIST and its exciting opportunities for researchers and students alike, please visit: http://www.gist.ac.kr/.
About the author
Prof. Myung-Han Yoon is a full Professor at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology). Yoon received his Ph.D. in Materials Chemistry from Northwestern University in 2006 and later went on to complete his postdoctoral training at Prof. Hongkun Park’s lab at Harvard University. His current areas of interest include the development of bio-interface integrated devices using organic and inorganic electronic materials for bioelectronic technology. His group is working on the fabrication of biodegradable composite materials for sustainable electronic devices.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-22
SPOKANE, Wash. – Researchers have identified a receptor protein known as CHRM1 as a key player in prostate cancer cells’ resistance to docetaxel, a commonly used chemotherapy drug to treat advanced cancer that has spread beyond the prostate. The discovery opens the door to new treatment strategies that could overcome this resistance. This could ultimately help extend the lives of those with prostate cancer, one of the leading causes of cancer deaths among men.
Led by a team of scientists at Washington State University, ...
2024-01-22
About The Study: The findings of this study of 398,000 UK Biobank participants support the improvement of social isolation and loneliness in people with obesity to decrease obesity-related excess risk of mortality.
Authors: Lu Qi, M.D., Ph.D., of the Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine in New Orleans, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.52824)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
2024-01-22
About The Study: The results of this study including 2,261 and 1,940 infants ages 12 and 18 months, respectively, suggest that COVID-19 vaccination was safe during pregnancy from the perspective of infant neurodevelopment to 18 months of age. Additional longer-term research should be conducted to corroborate these findings and buttress clinical guidance with a strong evidence base.
Authors: Eleni G. Jaswa, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.5743)
Editor’s ...
2024-01-22
Key takeaways:
A new 3D-printable material called “supramolecular ink” replaces costly scarce metals with inexpensive, Earth-abundant materials.
The organic material requires far less energy to manufacture than conventional methods.
It could also enhance the sustainability of 3D-printable wearable devices, lighting technologies, and luminescent art and sculpture.
A research team led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has developed “supramolecular ink,” a new technology for use in OLED (organic light-emitting ...
2024-01-22
Commencing in January, the Urban Future Lab (UFL) at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering, in collaboration with Greentown Labs, will serve as the supportive entry point in the U.S. for the fourth cohort of Innovate UK’s Global Incubator Programme: Clean Growth edition. This initiative is specifically designed to foster and assist the establishment of innovative climate technology companies demonstrating significant potential for international scalability into new markets.
The annual program extends the opportunity to eight U.K.-based businesses, enabling them to explore the U.S. market and gain access to esteemed mentors over a six-month period.
"We’re ...
2024-01-22
The Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) promotes active collaborations with prominent European institutions, including leading 'Research & Technology Organisations (RTO), prestigious universities, and small & medium-sized enterprises (SME). KIER has consistently stressed the importance of international collaborations in developing evolving and advanced green technologies. As a consequence, the consortium entitled "Scalable High-power Output and Low-Cost MAde-to-measure Tandem Solar Modules Enabling Specialized PV Applications (SOLMATES)", in which KIER participated and worked as a partner with 13 other ...
2024-01-22
A breakthrough technology has been developed that enables the production of green hydrogen in a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly manner, bringing us closer to a carbon-neutral society by replacing expensive precious metal catalysts.
Led by Professor Jungki Ryu in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST and Professor Dong-Hwa Seo from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, a joint research team has successfully developed a bifunctional water electrolysis catalyst for the high-efficiency and stable production of high-purity green hydrogen.
The newly-developed catalyst exhibits exceptional durability even in highly corrosive acidic environments. ...
2024-01-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – No matter how well children are prepared for kindergarten, their transition to the classroom during the first few months plays a key role in their success, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that kids who made a more successful transition in the first 10-14 weeks of kindergarten scored higher than others on tests of academic and social-behavioral skills at the end of the school year.
Important parts of the transition – what the researchers called a “big little leap” – included making new friends, ...
2024-01-22
Bad to the Bone: UMass Amherst Engineer Aims to Prevent Fractures in Cancer Patients
National Cancer Institute funds research to assess if the treatment of cancer metastasis in patients is as damaging as the disease
AMHERST, Mass. – For some patients whose cancer has spread to their bones, the ensuing treatment can be more physically damaging than the original disease, leading to increased bone loss and fracture. Stacyann Bailey, assistant professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, has received a two-year grant from the National Cancer Institute to study the complex relationship between drugs used to treat metastatic cancer ...
2024-01-22
A team of researchers from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, jointly led by Professors Sung-Yeon Jang, Jungki Ryu, and Ji-Wook Jang, in collaboration with Professor Sang Kyu Kwak from Korea University, have achieved remarkable advancements in the stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells. Their groundbreaking work not only paves the way for the commercialization of perovskite solar cells (PSCs), but also offers significant potential in green hydrogen production technology, ensuring long-term operation with high efficiency.
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have garnered attention due to their reduced toxicity and broad light absorption ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] GIST researchers investigate strange transient responses of organic electrochemical transistors
Two novel 1,4-dithienylphenylene-based polymers were designed to explore peculiar transient behaviors of organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors