(Press-News.org) SPOKANE, Wash. – Researchers have identified a receptor protein known as CHRM1 as a key player in prostate cancer cells’ resistance to docetaxel, a commonly used chemotherapy drug to treat advanced cancer that has spread beyond the prostate. The discovery opens the door to new treatment strategies that could overcome this resistance. This could ultimately help extend the lives of those with prostate cancer, one of the leading causes of cancer deaths among men.
Led by a team of scientists at Washington State University, the study showed that blocking CHRM1 in resistant prostate cancer cell lines and an animal model based on patient-derived resistant tissue restored docetaxel’s ability to kill cells and stop tumor growth. The researchers did this by using dicyclomine, a drug that selectively inhibits CHRM1 activity. Dicyclomine is already on the market as a generic drug and is currently used to treat symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome.
“The effect was pretty dramatic in all the experimental models we tested,” said Boyang (Jason) Wu, an associate professor in the WSU College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences and co-senior author on the study. “And because dicyclomine already has a clinical use, this work has immediate translational potential.”
Published in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, the researchers’ findings support clinical testing to confirm whether combined use of docetaxel and dicyclomine could help overcome treatment resistance in prostate cancer patients. Docetaxel resistance can develop in prostate cancer after about six months of treatment. Chemotherapy drugs like docetaxel are among very few options available to patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer, a lethal form of the disease that no longer responds to hormone therapy.
Wu said this type of combination therapy could also potentially be used for other cancers that are currently being treated with docetaxel, such as breast and lung cancer. It may also be possible to use the same combination strategy with other similar chemotherapy drugs.
In addition to testing resistant cancer cell lines, the research team also tested cells that still responded to docetaxel treatment. They found that using dicyclomine to block CHRM1 in these cells made docetaxel more efficient at killing them. Wu said that this shows that prostate cancer patients could potentially benefit from a combination treatment strategy even before docetaxel resistance develops.
“What this suggests is that the lowest effective dose of docetaxel may be lower when the drug is combined with dicyclomine, compared to when docetaxel is used alone,” Wu said. “Being able to use a lower dose could help reduce unwanted side effects and make treatment more manageable for patients.”
Aside from Wu, co-authors on the study include co-senior author Tyler Bland—a former WSU postdoctoral fellow who is now a clinical assistant professor at the University of Idaho—as well as co-first authors Jing Wang, a recent WSU PhD graduate, and Jing Wei, a WSU postdoctoral fellow. The research team conducted the study in collaboration with scientists at the University of Washington, Medical University of Innsbruck in Austria and National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University in Taiwan.
Funding for this study came from a U.S. Department of Defense Prostate Cancer Research Program grant with additional support provided by the National Cancer Institute, a component of the National Institutes of Health, and WSU College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences startup funds.
END
Protein discovery could help solve prostate cancer drug resistance
2024-01-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Improvement of social isolation and loneliness and excess mortality risk in people with obesity
2024-01-22
About The Study: The findings of this study of 398,000 UK Biobank participants support the improvement of social isolation and loneliness in people with obesity to decrease obesity-related excess risk of mortality.
Authors: Lu Qi, M.D., Ph.D., of the Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine in New Orleans, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.52824)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
In utero exposure to maternal COVID-19 vaccination and offspring neurodevelopment at 12 and 18 months
2024-01-22
About The Study: The results of this study including 2,261 and 1,940 infants ages 12 and 18 months, respectively, suggest that COVID-19 vaccination was safe during pregnancy from the perspective of infant neurodevelopment to 18 months of age. Additional longer-term research should be conducted to corroborate these findings and buttress clinical guidance with a strong evidence base.
Authors: Eleni G. Jaswa, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.5743)
Editor’s ...
Scientists advance affordable, sustainable solution for flat-panel displays and wearable tech
2024-01-22
Key takeaways:
A new 3D-printable material called “supramolecular ink” replaces costly scarce metals with inexpensive, Earth-abundant materials.
The organic material requires far less energy to manufacture than conventional methods.
It could also enhance the sustainability of 3D-printable wearable devices, lighting technologies, and luminescent art and sculpture.
A research team led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has developed “supramolecular ink,” a new technology for use in OLED (organic light-emitting ...
Innovate UK, the Urban Future Lab, and Greentown Labs announce the Year 4 cohort for their Global Incubator Programme
2024-01-22
Commencing in January, the Urban Future Lab (UFL) at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering, in collaboration with Greentown Labs, will serve as the supportive entry point in the U.S. for the fourth cohort of Innovate UK’s Global Incubator Programme: Clean Growth edition. This initiative is specifically designed to foster and assist the establishment of innovative climate technology companies demonstrating significant potential for international scalability into new markets.
The annual program extends the opportunity to eight U.K.-based businesses, enabling them to explore the U.S. market and gain access to esteemed mentors over a six-month period.
"We’re ...
KIER Accelerates Carbon-Neutral Technological Innovation through International Collaboration with Horizon Europe
2024-01-22
The Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) promotes active collaborations with prominent European institutions, including leading 'Research & Technology Organisations (RTO), prestigious universities, and small & medium-sized enterprises (SME). KIER has consistently stressed the importance of international collaborations in developing evolving and advanced green technologies. As a consequence, the consortium entitled "Scalable High-power Output and Low-Cost MAde-to-measure Tandem Solar Modules Enabling Specialized PV Applications (SOLMATES)", in which KIER participated and worked as a partner with 13 other ...
Groundbreaking discovery enables cost-effective and eco-friendly green hydrogen production
2024-01-22
A breakthrough technology has been developed that enables the production of green hydrogen in a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly manner, bringing us closer to a carbon-neutral society by replacing expensive precious metal catalysts.
Led by Professor Jungki Ryu in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST and Professor Dong-Hwa Seo from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, a joint research team has successfully developed a bifunctional water electrolysis catalyst for the high-efficiency and stable production of high-purity green hydrogen.
The newly-developed catalyst exhibits exceptional durability even in highly corrosive acidic environments. ...
Navigating the ‘big little leap’ to kindergarten
2024-01-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – No matter how well children are prepared for kindergarten, their transition to the classroom during the first few months plays a key role in their success, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that kids who made a more successful transition in the first 10-14 weeks of kindergarten scored higher than others on tests of academic and social-behavioral skills at the end of the school year.
Important parts of the transition – what the researchers called a “big little leap” – included making new friends, ...
Bad to the bone: UMass Amherst engineer aims to prevent fractures in cancer patients
2024-01-22
Bad to the Bone: UMass Amherst Engineer Aims to Prevent Fractures in Cancer Patients
National Cancer Institute funds research to assess if the treatment of cancer metastasis in patients is as damaging as the disease
AMHERST, Mass. – For some patients whose cancer has spread to their bones, the ensuing treatment can be more physically damaging than the original disease, leading to increased bone loss and fracture. Stacyann Bailey, assistant professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, has received a two-year grant from the National Cancer Institute to study the complex relationship between drugs used to treat metastatic cancer ...
Breakthrough research enhances stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells
2024-01-22
A team of researchers from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, jointly led by Professors Sung-Yeon Jang, Jungki Ryu, and Ji-Wook Jang, in collaboration with Professor Sang Kyu Kwak from Korea University, have achieved remarkable advancements in the stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells. Their groundbreaking work not only paves the way for the commercialization of perovskite solar cells (PSCs), but also offers significant potential in green hydrogen production technology, ensuring long-term operation with high efficiency.
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have garnered attention due to their reduced toxicity and broad light absorption ...
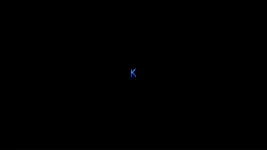
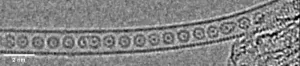
Scientists trap krypton atoms to form one-dimensional gas
2024-01-22
For the first time, scientists have successfully trapped atoms of krypton (Kr), a noble gas, inside a carbon nanotube to form a one-dimensional gas.
Scientists from the University of Nottingham’s School of Chemistry used advanced transmission electron microscopy (TEM) methods to capture the moment when Kr atoms joined together, one by one, inside a “nano test tube” container with diameter half a million times smaller than the width of a human hair. The research has been published in the journal of the American Chemical Society.
The behaviour of atoms has been studied by scientists ever since it was hypothesized that ...