(Press-News.org) Combining testosterone-blocking drugs in patients with prostate cancer relapse prevents the spread of cancer better than treatment with a single drug, a multi-institution, Phase 3 clinical trial led by UC San Francisco researchers has found.
The approach can extend the time between debilitating drug treatments without prolonging the time it takes to recover from each treatment.
Prostate cancer affects 1 in 8 men and causes 34,000 deaths each year in the United States. It is usually treated with one of several testosterone-lowering drugs for a set period of time.
“This adds to a growing body of evidence in favor of more intensive testosterone-blocking therapy in patients with higher-risk prostate cancer,” said Rahul Aggarwal, MD, professor in the UCSF School of Medicine and lead author of the paper.
The researchers’ findings were published on Jan. 23, 2024, in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. They were first announced in September 2022 at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
A case for intensifying prostate cancer treatment
The new study focused on patients who had surgery for prostate cancer, and yet the cancer relapsed and was detected through a sudden jump in the blood levels of a protein called prostate-specific antigen (PSA).
“We looked at patients who had a fast rise in their PSA – an indicator of a higher-risk form of relapsed prostate cancer,” Aggarwal said. “Our goal was to test several different hormone therapy strategies to find the best approach in terms of delaying the cancer’s progression.”
Between 2017 and 2022, 503 patients were randomly assigned to take a single testosterone-lowering therapy chosen by their oncologist, or to combine it with one or two other testosterone-lowering drugs. The additional drugs were already FDA-approved for other cancers but hadn’t been tested in this way with prostate cancer.
The patients stayed on the assigned therapy for a year. Whether given singly or in combination, the drugs caused their testosterone to plummet. That put the brakes on their cancer but also caused fatigue, hot flashes, decreased libido and other problems for patients, according to Aggarwal.
Compared to the prostate cancer patients who only received a single drug therapy during their year of treatment, patients who received either one or two additional drugs stayed cancer-free, with low PSA levels, for longer.
Once off the treatment, patients who took the combination therapies saw their testosterone levels recover just as fast as others who took the single drug.
The researchers are following up with a more detailed analysis of how patients fared on the different treatments – which side effects they experienced and for how long, and how they felt overall as they recovered.
“New cancer therapies must clear a high bar to make their way to patients,” Aggarwal said. “With the evidence in this study and others, combination hormone therapy should be considered a standard of care in prostate cancer patients with high-risk relapse after prior treatment.”
About UCSF: The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is exclusively focused on the health sciences and is dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. UCSF Health, which serves as UCSF's primary academic medical center, includes top-ranked specialty hospitals and other clinical programs, and has affiliations throughout the Bay Area. UCSF School of Medicine also has a regional campus in Fresno. Learn more at https://ucsf.edu, or see our Fact Sheet.
###
Follow UCSF
ucsf.edu | Facebook.com/ucsf | YouTube.com/ucsf
END
Could two drugs be better than one for treating prostate cancer?
2024-01-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Predicting and controlling bad-actor AI activity in a year of global elections
2024-01-23
MEDIA CONTACT:
Cate Douglass; cdouglass@gwu.edu
More than 50 countries are set to hold national elections this year and analysts have long sounded the alarm on the threat of bad actors using artificial intelligence (AI) to disseminate and amplify disinformation during the election season across the globe.
Now, a new study led by researchers at the George Washington University predicts that daily, bad-actor AI activity is going to escalate by mid-2024, increasing the threat that it could affect election results. The research, published today in the journal PNAS Nexus, is the first quantitative scientific ...
When lab-trained AI meets the real world, ‘mistakes can happen’
2024-01-23
First study to examine the impact of tissue contamination on AI models
‘If it’s paying attention to the tissue contaminants, it’s paying less attention to the patient’s tissue that is being examined’
‘Pathologists fear — and AI companies hope — that the computers are coming for our jobs. Not yet.’
Human pathologists are extensively trained to detect when tissue samples from one patient mistakenly end up on another patient’s microscope slides ...
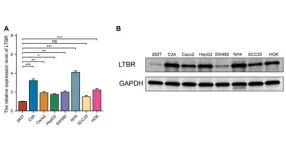
Systematic analysis of the prognostic value and immunological function of LTBR in cancer
2024-01-23
“[...] we identified LTBR as a potential target for cancer immunotherapy and a marker of immune infiltration and poor prognosis.”
A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 1, entitled, “Systematic analysis of the prognostic value and immunological function of LTBR in human cancer.”
Lymphotoxin beta receptor (LTBR) is a positive T cell proliferation regulator gene. It is closely associated with the tumor immune microenvironment. However, its role in cancer and ...
CUNY SPH Foundation expands Molina Health Equity Scholarship Fund with endowment
2024-01-23
The CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy (CUNY SPH) has announced an expansion and endowment of the Molina Health Equity Scholarship Fund as a groundbreaking and permanent source of support for students dedicated to advancing health equity in underserved Hispanic and Latino communities.
Established by Dr. Marilyn Aguirre-Molina, CUNY SPH professor emerita and CUNY SPH Foundation Board member, and distinguished academician Dr. Carlos W. Molina, the Molina Health Equity Scholarship Fund now becomes the first named and endowed master’s degree scholarship in the school’s ...
Study reveals disparities in use of evidence-based integrative pain management modalities among adults with chronic pain
2024-01-23
A recent study from researchers at University Hospitals (UH) Connor Whole Health examined variables associated with engagement in (1) integrative health and medicine (IHM) and (2) nonpharmacologic modalities rather than opioids among United States adults with chronic pain. The study, published in the Journal of Pain Research, uncovered disparities in access to these modalities, particularly among older adults, Black/African American individuals, and those with higher depressive symptoms and lower education and income levels, who are more likely to have chronic pain.
The researchers used data ...
Ageism, mistaken beliefs complicate acceptance of older adults’ sexuality
2024-01-23
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — More than 25% of the young adults surveyed in a recent study mistakenly believed that sexual activity increases older adults’ risk of heart attack and that disinterest in sex is a normal and inevitable part of aging. While most of those in the study had permissive views about sexual activity in later life, the findings also shed light on the misconceptions and ageist views that can infringe on older adults’ rights to sexual expression.
More than 270 young adults ages 18-35 participated in the study, which assessed their level of knowledge about sexuality in older adulthood, their general attitudes toward ...
Marine heat waves trigger shift in hatch dates and early growth of Pacific cod
2024-01-23
Marine heat waves appear to trigger earlier reproduction, high mortality in early life stages and fewer surviving juvenile Pacific cod in the Gulf of Alaska, a new study shows. These changes in the hatch cycle and early growth patterns persisted in years following the marine heat waves, which could have implications for the future of Gulf of Alaska Pacific cod, an economically and culturally significant species,
END ...
Norman A. Abrahamson earns top honor in seismology
2024-01-23
The Seismological Society of America (SSA) will present its highest honor, the 2024 Harry Fielding Reid Medal, to Norman A. Abrahamson, adjunct professor of civil and environmental engineering at the University of California, Berkeley and University of California, Davis, and former engineering seismologist at Pacific Gas & Electric Co.
Abrahamson, who will receive the Reid Medal at the 2024 SSA Annual Meeting, is recognized as a global leader in the field of probabilistic seismic hazard assessment (PSHA). Within the seismic hazard community, he is known for developing new methodologies as well as refining state-of-the-art practices ...
Doyeon Kim honored with Charles F. Richter Early Career Award
2024-01-23
Doyeon Kim (DK) has been honored with the Seismological Society of America’s (SSA) 2024 Charles F. Richter Early Career Award for his scientific productivity across a variety of topics, including recent work on Martian seismology and his pioneering approaches to seismic imaging.
Kim, a lecturer in planetary science in the Faculty of Engineering at Imperial College London, will receive the Richter Award at the 2024 SSA Annual Meeting.
“I am sincerely grateful for this award, which I humbly attribute to the collective efforts of those who have played a pivotal role in shaping my academic career. This recognition fuels my dedication to furthering ...
Harley M. Benz honored by SSA for Advances in Communicating Earthquake Science
2024-01-23
For his work leading to profound improvements in how earthquake science is communicated to students, the media and decision makers, the Seismological Society of America (SSA) honors Harley M. Benz with the 2024 Frank Press Public Service Award.
Benz, a former U.S. Geological Survey technical coordinator for the Advanced National Seismic System (ANSS) and the director of the USGS National Earthquake Information Center (NEIC), will receive the Press Award at the 2024 SSA Annual Meeting.
In his nomination of Benz for the award, Gavin Hayes, senior science advisor for earthquake ...