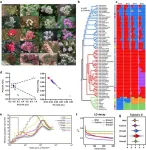
(Press-News.org) Social systems where influence is focused around one or a few individuals may create environments where new ideas are ignored, and innovation is hindered.
This is according to a study published today in People and Nature by researchers at the University of Sydney and Stockholm University. It looked at the social networks and fertiliser use of 30 rural, cocoa-producing villages in Sulawesi, to examine how innovative and sustainable farming practices are adopted among communities.
It found that when one or two farmers hold a disproportionate level of influence (often due to their roles as "model farmers" in official sustainability programs) most other farmers tend to adopt similar practices, in this case decisions around how to fertilise their crops.
This type of social hierarchy – referred to by the researchers as “hub and spoke” networks – risks hindering innovation and could be detrimental to the adoption of practices which promote sustainability and food security, said Associate Professor Matous from the University of Sydney’s School of Project Management.
“If you’ve ever watched a group of kindergarteners play soccer, you’ll know that they run after the one kid who has the ball all at the same time. It’s a bit like that – to foster innovation what you really need is people playing a range of roles and exploring a problem from different angles,” said Associate Professor Matous.
“Centralising influence risks locking in the wrong approach as the status quo – from there it can create a culture of homogeneity, reinforcing pack mentality and group think. When combined with power hierarchies in which those who are less central are not listened to, it can crowd out innovative voices, sometimes swaying entire communities one way or another. In the case of fertilisers, this is a problem because too much can threaten the environment and too little can impact food security,” he said.
According to a UN study, smallholder farms support the livelihoods of 2.5 billion people worldwide, with farmers’ decisions on how to manage their land having profound consequences for the environment and global food security. The research was published in collaboration with Swisscontact, an NGO that works to promote sustainable agricultural practices.
“As we advocate for a nuanced approach to sustainable farming initiatives, we caution against programs that elevate a select group of farmers based merely on the fact that these farmers have been the conduit for outside interventions in the past. This can simply reinforce traditionalists and therefore, the status quo,” says Ross Jaax, Swisscontact’s Senior Technical Advisor for Sustainable Agriculture.
The study’s co-author from the University of Stockholm, Professor Örjan Bodin said: “While these individuals may hold sway in the short term, our findings suggest that top-down interventions risk undermining the social fabric of communities, potentially hindering adaptive capacities in the face of evolving agricultural and environmental challenges.
Associate Professor Matous said the results extend beyond the agricultural context and may also hold some truth in corporate and other leadership settings, areas which the School of Project Management explores.
“In contrast to the popular idea of a strong leader, we are interested in understanding socialised forms of leadership where decisions and influence are broadly shared, so we can find more effective ways of engaging communities in projects and programs".
INFORMATION:
The researchers have no conflicts of interest to declare. The research was financially supported by Swisscontact.
END
Centralized social networks potentially hinder innovation by making decision-making too similar
Study examines how communities adopt innovative and sustainable farming practices
2024-01-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tunnelling of electrons via the neighboring atom
2024-01-24
Tunnelling is one of most fundamental processes in quantum mechanics, where the wave packet could traverse a classically insurmountable energy barrier with a certain probability. Within the atomic scale, tunnelling effects play an important role in molecular biology, such as accelerating enzyme catalysis, prompting spontaneous mutations in DNA and triggering olfactory signaling cascades. Photoelectron tunnelling is a key process in light-induced chemical reactions, charge and energy transfer and radiation emission. The size of optoelectronic chips ...
Space-based landscape site perception: Teaching principles and methods for the basic course of landscape architecture
2024-01-24
Replacing abstract form-making training with the perception of landscape site has been an important trend in the basic course of landscape architecture. Based on theoretical research and the authors’ teaching practice, this article aims to explore the significance, objects, and methods of site perception training. The authors argue that because landscape design is stemmed from the perception and interpretation of site characteristics, experiencing landscape sites must precede form-making training to become the foundation of design learning. Human-scale spaces that concern elements, structure, processes, and feelings for perception, representation, ...
Suppression of deep-level traps for lead-free perovskite solar cells
2024-01-24
Tin perovskites have gained tremendous attention in lead-free perovskite solar cells. However, Sn vacancies and undercoordinated Sn ions on the tin perovskite surfaces can create deep-level traps, leading to non-radiative recombination and absorption nucleophilic O2 molecules, impeding further device efficiency and stability.
Researchers led by Prof. Ligang Xu at Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, China, are interested in lead-free perovskite solar cells, where the deep-level traps lead to inferior efficiency and stability. The work first introduced semicarbazide hydrochloride (SEM-HCl) into ...
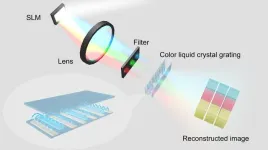
Color liquid crystal grating based color holographic 3D display system with large viewing angle
2024-01-24
Holographic display technology provides an ultimate solution for real 3D display and has great potential in augmented reality and virtual reality. However, the color and viewing angle of holographic 3D display mainly depend on the wavelength of the laser and the pixel size of the current spatial light modulator. Inevitable color differences and narrow viewing angle in conventional systems seriously affect the holographic display effect and hinder the application of holographic 3D display in many fields.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Qiong-Hua Wang from Beihang ...
Walking fitness can predict fracture risk in older adults
2024-01-24
The ability to walk one kilometre comfortably can help predict fracture risk, according to researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research. The findings, published today in JAMA Network Open, suggest that simply asking a patient about walking limitation could allow clinicians to identify those in need of further bone health screening and prescribe interventions that could prevent fractures from occurring.
“We’ve discovered that trouble walking even short distances appears closely tied to higher fracture risk over the following five years,” says lead author of the study, Professor ...
Genome assembly and resequencing analyses provide new insights into the evolution, domestication and ornamental traits of crape myrtle
2024-01-24
Crape myrtle (Lagerstroemia indica), a widely cherished ornamental plant, boasts a rich history, originating in Southeast Asia to Oceania and flourishing in cultivation centers like China for over 1600 years. Renowned for its unique blooming during the summer peak, it has evolved through extensive hybridization, and now includes more than 200 species. Current research has made strides in understanding the determinants of plant architecture, flower, leaf color, and dwarfism traits through transcriptomics and QTL mapping. However, the absence of a reference genome for L. indica severely limits comprehensive ...
Learning for life: The higher the level of education, the lower the risk of dying
2024-01-24
Education saves lives regardless of age, sex, location, and social and demographic backgrounds. That’s according to the latest and largest study of its kind published today in The Lancet Public Health.
Researchers have known that those who reach higher levels of schooling live longer than others, but they didn’t know to what extent until now. What they found was that the risk of death drops by two per cent with every additional year of education. That means those who completed six years of primary school had a lower risk of death by an average of 13 per cent. After graduating from secondary school, the risk ...
Community perinatal mental health teams reduce risk of mental health relapse after childbirth
2024-01-24
New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London, and in partnership with the University of Exeter and the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, has found that women with a history of severe mental illness face a lower risk of relapse after giving birth in regions where they have access to a community perinatal mental health team (CPMHT).
The research, published in Lancet Psychiatry, is the first of its kind to evaluate the effectiveness of CPMHTs, and suggests that women with access to specialist support have a reduced risk of acute relapse after birth, but also highlights the importance of the need for ...
Non-COVID-19 deaths among people with diabetes jumped during pandemic
2024-01-24
Non-COVID-19-related deaths among people with diabetes increased during the pandemic, as did the diabetes complication of sight loss, according to a global study review led by a University of Massachusetts Amherst public health researcher that examined the impacts of pandemic-related disruptions on this vulnerable population.
The review, commissioned by the World Health Organization (WHO) and published Jan. 23 in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, looked at 138 studies comparing pre-pandemic to during pandemic periods in North America (39), Western Europe (39), Asia (17), Eastern Europe (14), South America (four), Egypt (one), Australia ...
World's largest database of weeds lets scientists peer into the past, and future, of global agriculture
2024-01-24
New database of 928 species of weeds from Universities of Sheffield and Oxford published to provide free, global resource for plant ecologists and archaeologists
The data changes our understanding of the history of agriculture as well as ability to understand the future of our farming practices in a time of climate change
The project, based on 30 years of research partnerships, is a testament to how academics of different disciplines can collaborate on globally significant research
A new database of weeds that can help scientists understand how ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
[Press-News.org] Centralized social networks potentially hinder innovation by making decision-making too similarStudy examines how communities adopt innovative and sustainable farming practices