Under strict embargo: 19:00hrs GMT 24 January 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
Gene behind heart defects in Down syndrome identified
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and UCL have identified a gene that causes heart defects in Down syndrome, a condition that results from an additional copy of chromosome 21.
Reducing the overactivity of this gene partially reversed these defects in mice, setting the scene for potential future therapies for heart conditions in people with Down syndrome.
Down syndrome affects around 1 in 800 new births and is caused by an extra third copy of chromosome 21. About half of babies born with Down syndrome have heart defects, such as a failure of the heart to separate into four chambers, leaving a ‘hole in the heart’.
If the heart defects are very serious, high-risk surgery might be needed soon after birth and people often require ongoing monitoring of the heart for the rest of their life. Therefore, better treatment options are needed and this must be guided by knowledge of which of the extra 230 genes on chromosome 21 are responsible for the heart defects. But before this study the identity of these causative genes was not known.
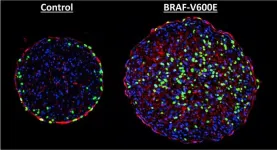
In research published today in Science Translational Medicine, the team at the Crick and UCL studied human Down syndrome fetal hearts as well as embryonic hearts from a mouse model of Down syndrome.
Using genetic mapping, the researchers identified a gene on human chromosome 21 called Dyrk1a, which causes heart defects when present in three copies in the mouse model of Down syndrome. This gene has previously been linked to cognitive impairment and facial changes in Down syndrome, but its role in heart development was not known.
An extra copy of Dyrk1a turned down the activity of genes required for cell division in the developing heart and the function of the mitochondria, which produce energy for the cells. These changes correlated with a failure to correctly separate the chambers of the heart.
The team found that while Dyrk1a is required in three copies to cause heart defects in mice, it was not sufficient alone. Thus, another unknown gene must also be involved in the origin of heart defects in Down syndrome. The team is currently searching for this second gene.
Dyrk1a codes for an enzyme called DYRK1A. The researchers tested a DYRK1A inhibitor on mice pregnant with pups that model the hearts defects in Down syndrome, as their hearts were forming. When DYRK1A was inhibited, the genetic changes were partially reversed and the heart defects in the pups were less severe.
Victor Tybulewicz, Group Leader of the Immune Cell Biology Laboratory & Down Syndrome Laboratory, said: “Our research shows that inhibiting DYRK1A can partially reverse changes in mouse hearts, suggesting that this may be a useful therapeutic approach.
“However, in humans the heart forms in the first 8 weeks of pregnancy, likely before a baby could be screened for Down syndrome, so this would be too early for treatment. The hope is that a DYRK1A inhibitor could have an effect on the heart later in pregnancy, or even better after birth. These are possibilities we are currently investigating.”
This research forms part of the lab’s overall goal to understand the genetics behind all aspects of Down syndrome.
Eva Lana-Elola, Principal Laboratory Research Scientist at the Crick, and co-first author, said: “It was remarkable that just restoring the copy number of one gene from 3 to 2 reversed the heart defects in the mouse model for Down syndrome. We’re now aiming to understand which of the other genes on this extra chromosome are involved. Even though Dyrk1a isn’t the only gene involved, it’s clearly a major player in many different aspects of Down syndrome.”
Rifdat Aoidi, Postdoctoral Project Research Scientist at the Crick, and co-first author, said: “We don’t yet know why the changes in cell division and mitochondria mean the heart can’t correctly form chambers. Dysfunction in the mitochondria has also been linked to cognitive impairment in Down syndrome, so boosting mitochondrial function could be another promising avenue for therapy.”
The researchers worked with Perha Pharmaceuticals to test the DYRK1A inhibitor. The company is now testing the drug in a clinical trial for cognitive disorders associated with Down syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease.
-ENDS-
For further information, contact: press@crick.ac.uk or +44 (0)20 3796 5252
Notes to Editors
Reference: Lana-Elola, E and Aoidi, R. et al. (2024). Increased dosage of DYRK1A leads to congenital heart defects in a mouse model of Down syndrome. Science Translational Medicine.10.1126/scitranslmed.add6883.
The Francis Crick Institute is a biomedical discovery institute dedicated to understanding the fundamental biology underlying health and disease. Its work is helping to understand why disease develops and to translate discoveries into new ways to prevent, diagnose and treat illnesses such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, infections, and neurodegenerative diseases.
An independent organisation, its founding partners are the Medical Research Council (MRC), Cancer Research UK, Wellcome, UCL (University College London), Imperial College London and King’s College London.
The Crick was formed in 2015, and in 2016 it moved into a brand new state-of-the-art building in central London which brings together 1500 scientists and support staff working collaboratively across disciplines, making it the biggest biomedical research facility under a single roof in Europe.
http://crick.ac.uk/
About UCL – London’s Global University
UCL is a diverse global community of world-class academics, students, industry links, external partners, and alumni. Our powerful collective of individuals and institutions work together to explore new possibilities.
Since 1826, we have championed independent thought by attracting and nurturing the world's best minds. Our community of more than 50,000 students from 150 countries and over 16,000 staff pursues academic excellence, breaks boundaries and makes a positive impact on real world problems.
The Times and Sunday Times University of the Year 2024, we are consistently ranked among the top 10 universities in the world and are one of only a handful of institutions rated as having the strongest academic reputation and the broadest research impact.
We have a progressive and integrated approach to our teaching and research – championing innovation, creativity and cross-disciplinary working. We teach our students how to think, not what to think, and see them as partners, collaborators and contributors.
For almost 200 years, we are proud to have opened higher education to students from a wide range of backgrounds and to change the way we create and share knowledge.
We were the first in England to welcome women to university education and that courageous attitude and disruptive spirit is still alive today. We are UCL.
www.ucl.ac.uk | Follow @uclnews on Twitter | Read news at www.ucl.ac.uk/news/ | Listen to UCL podcasts on SoundCloud | View images on Flickr | Find out what’s on at UCL Minds.
END