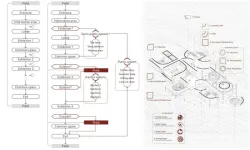
A building rising from the hilltop—Three topographical approaches to building in a landscape
2024-01-25
(Press-News.org)
This essay writes on a building project in the remote southwestern China that is built in uninhabited and is inspired and informed by its landscape context. The essay discusses how an extraordinary building project reacts to three different dimensions about landscape–architecture—a natural terrain being manipulated and recast. A small building needs to find its precise connecting point to a much larger historical and environmental context. A practical project needs to reach a balance between architectural pursuits and engineering concerns. Initially, artificial works might be isolated from and in conflict with the terrain, which requires architectural approaches to reconciling the demands at different scales and of functions. Finally, people who use the building will move forward to an effective and open dialogue between architecture and its landscape settings.
The work entitled “A Building Rising From the Hilltop—Three Topographical Approaches to Building in a Landscape” was published on the journal of Landscape Architecture Frontiers (December 7, 2023).
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-25
Flinders University researchers say that cohesive and collaborative action from preventive health communicators and organisations is needed to inform young people about the devastating harms of vaping.
“Despite awareness of the potential harms, recreational vaping is increasing among younger people with our South Australian participants seeing vaping as ‘cleaner’ and less harmful than cigarettes,” says Flinders University’s Dr Joshua Trigg.
“We know that nicotine vapes are highly addictive and expose people to harmful chemicals, respiratory irritants, and toxic substances. In order to discourage ...
2024-01-25
Kyoto, Japan -- Our understanding of the world relies greatly on our knowledge of its constituent materials and their interactions. Recent advances in materials science technologies have ratcheted up our ability to identify chemical substances and expanded possible applications.
One such technology is infrared spectroscopy, used for molecular identification in various fields, such as in medicine, environmental monitoring, and industrial production. However, even the best existing tool -- the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer or FTIR -- utilizes a heating element as its light source. Resulting detector noise in the infrared region limits the devices' ...
2024-01-25
According to a new analysis, almost a quarter of Australians with disabilities smoke when compared to just 12.6% of the wider population.
While the number of Australians smoking is declining, the barriers for people with disabilities mean targeted support is needed to develop healthier habits.
Flinders University and Cancer Council NSW health experts are recommending new strategies to tackle the alarming smoking rate through targeted government policies, data collection on smoking and training for disability support workers on tobacco prevention ...
2024-01-25
A Rutgers Health analysis of millions of Medicare records has laid the groundwork for improving end-of-life care by demonstrating that nearly all older Americans follow one of nine trajectories in their last three years of life.
“Identifying which paths people actually take is a necessary precursor to identifying which factors send different people down different paths and designing interventions that send more people down whatever path is right for them,” said Olga Jarrín, the Hunterdon Professor of Nursing Research at Rutgers and corresponding author of the study published in BMC Geriatrics.
The team pulled the final three years of clinical records ...
2024-01-25
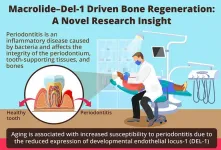
Niigata, Japan - Scientists from Niigata University discover macrolide-based molecules that increase the expression of DEL-1 protein and help in bone regeneration
Periodontitis is characterized by the loss of teeth resulting from inflammation of gums due to bacterial infections. The susceptibility to such bone loss disorders increases with age. The expression of the developmental endothelial locus-1 protein, crucial for bone regeneration, declines with age. Recently, researchers from Niigata University, University of Pennsylvania team identified ...
2024-01-25
Menopausal women who regularly swim in cold water report significant improvements to their physical and mental symptoms, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The research, published in Post Reproductive Health, surveyed 1114 women, 785 of which were going through the menopause, to examine the effects of cold water swimming on their health and wellbeing.
The findings showed that menopausal women experienced a significant improvement in anxiety (as reported by 46.9% of the women), mood swings (34.5%), ...
2024-01-25
Kiwifruit has proven itself as a powerful mood booster and new research from the University of Otago has shown just how fast its effects can be.
In a study, published in The British Journal of Nutrition, researchers found the furry fruit improved vitality and mood in as little as four days.
Co-author Professor Tamlin Conner, of the Department of Psychology, says the findings provide a tangible and accessible way for people to support their mental well-being.
“It’s great for people ...
2024-01-24
Women and people of colour remain invisible to many people in Britain and the USA as people pick white men as their heroes instead, a study shows. Their achievements are often forgotten or not recognised when people are choosing who inspires them, researchers have found.
Most people said their family and friends, people closest to them, were their heroes. These ‘everyday’ heroes accounted for one in three choices in Britian and 41 per cent in the US.
In both countries, politicians were popular as heroes, with more common choices including Ronald Reagan, Abraham Lincoln, ...
2024-01-24
In findings that have implications for potential new HIV therapies, researchers from Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed) used genetic sequencing techniques on the nonhuman primate version of the virus to identify that lymph nodes in the abdomen are the leading source of rebound infection after the first week of stopping antiretroviral treatment.
The study regarding simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) was reported in the journal Science Translational Medicine. SIV is very closely related to HIV and is commonly used as a proxy to study HIV in animal models.
“Lymphoid tissues are known to be large ...
2024-01-24
Microplastics, with a size from 1 micron to < 5 millimeters, are pervasive pollutants that have been found in all parts of the global ocean, and have made their way into the marine food webs. Researchers, led by University of British Columbia UBC’s Institute for the Oceans and Fisheries scientists and Ecuadorian researchers from Galápagos and the ESPOL Polytechnic School (Guayaquil, Ecuador), looked closely at how microplastic bioaccumulation was affecting the endangered Galápagos penguin (Spheniscus mendiculus) as an indicator species to trace how deeply microplastic bioaccumulation has entered the food web in the isolated Galápagos Islands.
An ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A building rising from the hilltop—Three topographical approaches to building in a landscape