(Press-News.org) Earth’s moon shrank more than 150 feet in circumference as its core gradually cooled over the last few hundred million years. In much the same way a grape wrinkles when it shrinks down to a raisin, the moon also develops creases as it shrinks. But unlike the flexible skin on a grape, the moon’s surface is brittle, causing faults to form where sections of crust push against one another.
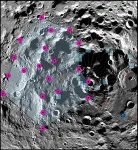
A team of scientists discovered evidence that this continuing shrinkage of the moon led to notable surface warping in its south polar region—including areas that NASA proposed for crewed Artemis III landings. Because fault formation caused by the moon’s shrinking is often accompanied by seismic activity like moonquakes, locations near or within such fault zones could pose dangers to future human exploration efforts.
In a new paper published in The Planetary Science Journal, the team linked a group of faults located in the moon’s south polar region to one of the most powerful moonquakes recorded by Apollo seismometers over 50 years ago. Using models to simulate the stability of surface slopes in the region, the team found that some areas were particularly vulnerable to landslides from seismic shaking.
“Our modeling suggests that shallow moonquakes capable of producing strong ground shaking in the south polar region are possible from slip events on existing faults or the formation of new thrust faults,” said the study’s lead author Thomas R. Watters, a senior scientist emeritus in the National Air and Space Museum’s Center for Earth and Planetary Studies. “The global distribution of young thrust faults, their potential to be active and the potential to form new thrust faults from ongoing global contraction should be considered when planning the location and stability of permanent outposts on the moon.”
Shallow moonquakes occur near the surface of the moon, just a hundred or so miles deep into the crust. Similar to earthquakes, shallow moonquakes are caused by faults in the moon’s interior and can be strong enough to damage buildings, equipment and other human-made structures. But unlike earthquakes, which tend to last only a few seconds or minutes, shallow moonquakes can last for hours and even a whole afternoon—like the magnitude 5 moonquake recorded by the Apollo Passive Seismic Network in the 1970s, which the research team connected to a group of faults detected by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter more recently.
According to Nicholas Schmerr, a co-author of the paper and an associate professor of geology at the University of Maryland, this means that shallow moonquakes can devastate hypothetical human settlements on the moon.
“You can think of the moon’s surface as being dry, grounded gravel and dust. Over billions of years, the surface has been hit by asteroids and comets, with the resulting angular fragments constantly getting ejected from the impacts,” Schmerr explained. “As a result, the reworked surface material can be micron-sized to boulder-sized, but all very loosely consolidated. Loose sediments make it very possible for shaking and landslides to occur.”
The researchers continue to map out the moon and its seismic activity, hoping to identify more locations that may be dangerous for human exploration. NASA’s Artemis missions, which are set to launch their first crewed flight in late 2024, ultimately hope to establish a long-term presence on the moon and eventually learn to live and work on another world through moon-based observatories, outposts and settlements.
“As we get closer to the crewed Artemis mission’s launch date, it’s important to keep our astronauts, our equipment and infrastructure as safe as possible,” Schmerr said. “This work is helping us prepare for what awaits us on the moon—whether that’s engineering structures that can better withstand lunar seismic activity or protecting people from really dangerous zones.”
END
The moon is shrinking, causing landslides and instability in lunar south pole
New paper identifies potential landing sites for Artemis mission that are particularly vulnerable to quakes and landslides.
2024-01-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Icahn Mount Sinai School of Medicine receives Helmsley Charitable Trust grant for Crohn's disease research
2024-01-25
New York, NY [January 25, 2024]—The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has been awarded a grant of more than $4 million from The Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust to support an innovative research project aimed at understanding the early stages of Crohn’s disease before noticeable symptoms develop.
Led by the Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences along with the Dr. Henry D. Janowitz Division of Gastroenterology in the Department of Medicine at the Icahn School of ...
Sika deer overpopulation endangers beech forests in Southern Kyushu, Japan
2024-01-25
Fukuoka, Japan—Kyushu University researchers have found that Japanese beech (Fagus crenata) in the forests of southern Kyushu have seen reduced growth, due to soil erosion caused by the overpopulation of sika deer (Cervus nippon). Their findings, which were published in the journal Catena, could help in the development of new strategies for forest conservation.
Conservation is more than just preserving forests; it's about protecting the diverse web of life. One area where conservation has become critical is a beech forest in Shiiba Village, in the remote mountains of Southern Kyushu. The Japanese beech is a prominent and iconic species in ...
UTSA researchers reveal faint features in galaxy NGC 5728 though JWST image techniques
2024-01-25
(SAN ANTONIO, TEXAS) — Mason Leist is working remotely—127 million light-years from Earth—on images of a supermassive black hole in his office at the UTSA Department of Physics and Astronomy.
The UTSA Graduate Research Assistant led a study, published in The Astronomical Journal, on the best method to improve images obtained by the James Webb Science Telescope (JWST) using a mathematical approach called deconvolution. He was tasked by the Galactic Activity, Torus, and Outflow Survey (GATOS), an international team of scientists, to enhance JWST observations of the galaxy NGC 5728.
The GATOS team, co-led by UTSA Professor and Leist’s doctoral ...
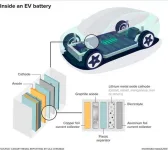
Polymer power: Incheon National University researchers enhance the safety of lithium batteries
2024-01-25
Lithium-ion batteries are a widely used class of rechargeable batteries in today’s world. One of the processes that can hamper the functioning of these batteries is an internal short circuit caused by direct contact between the cathode and anode (the conductors that complete the circuit within a battery). To avoid this, separators composed of polyolefins—a type of polymer— can be employed to maintain separation. However, these separators can melt at higher temperatures, and the inadequate absorption of electrolytes (essential for conveying ...
Suicide and race: Uncovering patterns underlying increasing suicide rates in the USA
2024-01-25
Are there specific communities that bear the brunt of suicide mortality? Certain studies have revealed that historically marginalized and economically deprived indigenous populations are linked with higher rates of cluster suicides—especially in Canada, the United States, and Australia. Public health officials need to consider that the risk of suicide contagion—social transmission due to insufficient interventions and resources—is real and must be countered. Now, a consortium of public health experts from Japan, Australia, and China have analyzed trends in suicide mortality in American Indian or Alaskan Native (AIAN) populations, while exploring ...
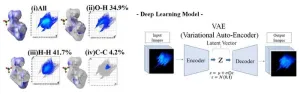
Deep learning reveals molecular secrets of explosive perchlorate salts
2024-01-25
Perchlorates are a class of compounds that are notorious for their explosive nature. This raises safety concerns during experiments involving complex compounds that contain perchlorate ions, since explosions can be triggered even by the slightest shock or heat. It is, therefore, important to study their molecular structure and understand the reason behind their explosive nature.
In this context, a method called the Hirschfield surface analysis has been extensively used for visualizing and quantifying the crystal structure and molecular interactions of crystal compounds. Moreover, a two-dimensional fingerprint plot derived from the Hirschfield ...
National retailers support heart and stroke health through annual Life is Why™ campaign
2024-01-25
DALLAS, Jan. 25, 2024 — This February, during American Heart Month and the American Heart Association’s Centennial year, the Association is devoted to a world of healthier lives for all by teaming up with retailers and brands around the country for Life is Why™, a cause marketing campaign supporting the Association’s life-saving heart and brain health mission. Life is Why inspires consumers to celebrate their reasons to live healthier, longer lives and participate personally in the mission of the Association by donating at the point-of-sale or by purchasing a product ...
Permeable pavements could reduce coho-killing tire pollutants
2024-01-25
PUYALLUP, Wash. — The pore-like structure of permeable pavements may help protect coho salmon by preventing tire wear particles and related contaminants from entering stormwater runoff, according to a Washington State University study.
Researchers demonstrated that four types of permeable pavements can act as giant filters, retaining more than 96% of applied tire particle mass. They also captured several tire-associated chemicals, resulting in a 68% average reduction of 6PPD-quinone, a contaminant shown to kill coho salmon in urban streams. The study findings were published in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
“The pressure on existing stormwater management technologies ...
Study: UAB researchers establish optimal immunosuppression regimen for pig-to-human kidney transplants
2024-01-25
Read all news releases on UAB’s peer-reviewed, published xenotransplant research and find media kits with video, photos, graphics and more at go.uab.edu/xenotransplant
The UAB News Studio is available for live or taped interviews with UAB experts.
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Currently used Food and Drug Administration-approved transplant drugs — with the addition of an also already FDA-approved complement inhibitor — are the optimal immunosuppression regimen for pig-to-human kidney transplants, according to a landmark discovery by University of Alabama at Birmingham investigators. The peer-reviewed research is published today in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“These ...
Potassium-enriched salt is the missing ingredient in hypertension guidelines
2024-01-25
A call to include recommendations on low-sodium potassium-enriched salt in hypertension treatment guidelines has been made by an international group of experts today in the American Heart Association’s scientific journal Hypertension.
High levels of sodium intake and low levels of potassium intake are widespread, and both are linked to high blood pressure (hypertension) and greater risk of stroke, heart disease and premature death. Using a salt substitute where part of the sodium chloride is replaced with potassium chloride ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] The moon is shrinking, causing landslides and instability in lunar south poleNew paper identifies potential landing sites for Artemis mission that are particularly vulnerable to quakes and landslides.