(Press-News.org) If life ever existed on Mars, the Perseverance rover’s verification of lake sediments at the base of the Jezero crater reinforces the hope that traces might be found in the crater.
In new research published in the journal Science Advances, a team led by UCLA and The University of Oslo shows that at some point, the crater filled with water, depositing layers of sediments on the crater floor. The lake subsequently shrank and sediments carried by the river that fed it formed an enormous delta. As the lake dissipated over time, the sediments in the crater were eroded, forming the geologic features visible on the surface today.
The periods of deposition and erosion took place over eons of environmental changes, the radar indicates, confirming that inferences about the Jezero crater’s geologic history based on Mars images obtained from space are accurate.
“From orbit we can see a bunch of different deposits, but we can’t tell for sure if what we’re seeing is their original state, or if we’re seeing the conclusion of a long geological story,” said David Paige, a UCLA professor of Earth, planetary and space sciences and first author of the paper. “To tell how these things formed, we need to see below the surface.”
The rover, which is about the size of a car and carries seven scientific instruments, has been exploring the 30-mile-wide crater, studying its geology and atmosphere and collecting samples since 2021. Perseverance’s soil and rock samples will be brought back to Earth by a future expedition and studied for evidence of past life.
Between May and December 2022, Perseverance drove from the crater floor onto the delta, a vast expanse of 3 billion-year-old sediments that, from orbit, resembles the river deltas on Earth.
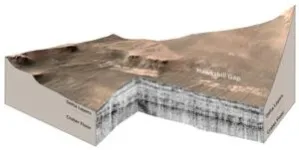
As the rover drove onto the delta, Perseverance’s Radar Imager for Mars’ Subsurface Experiment, or RIMFAX, instrument fired radar waves downward at 10-centimeter intervals and measured pulses reflected from depths of about 20 meters below the surface. With the radar, scientists can see down to the base of the sediments to reveal the top surface of the buried crater floor.
Years of research with ground-penetrating radar and testing of RIMFAX on Earth have taught scientists how to read the structure and composition of subsurface layers from their radar reflections. The resulting subsurface image shows rock layers that can be interpreted like a highway road cut.
“Some geologists say that the ability of radar to see under the surface is kind of like cheating,” said Paige, who is RIMFAX’s deputy principal investigator.
RIMFAX imaging revealed two distinct periods of sediment deposition sandwiched between two periods of erosion. UCLA and the University of Oslo report that the crater floor below the delta is not uniformly flat, suggesting that a period of erosion occurred prior to the deposition of lake sediments. The radar images show that the sediments are regular and horizontal - just like sediments deposited in lakes on Earth. The existence of lake sediments had been suspected in previous studies, but has been confirmed by this research.
A second period of deposition occurred when fluctuations in the lake level allowed the river to deposit a broad delta that once extended far out into the lake, but has now eroded back closer to the river’s mouth.
“The changes we see preserved in the rock record are driven by large-scale changes in the Martian environment,” Paige said. “It’s cool that we can see so much evidence of change in such a small geographic area, which allows us extend our findings to the scale of the entire crater.”
END
Confirmation of ancient lake on Mars builds excitement for Perseverance rover's samples
Findings reveal eons of environmental changes and offer hope that the rover’s soil and rock samples hold traces of life
2024-01-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
USC Stem Cell study shows how gene activity modulates the amount of immune cell production in mice
2024-01-26
As people age or become ill, their immune systems can become exhausted and less capable of fighting off viruses such as the flu or COVID-19. In a new mouse study funded in part by the National Institutes of Health and published in Science Advances, researchers from the USC Stem Cell lab of Rong Lu describe how specific gene activity could potentially enhance immune cell production.
“Hematopoietic stem cells, or HSCs, produce blood and immune cells, but not all HSCs are equally productive,” said the study’s corresponding author Rong Lu, PhD, ...
How waves and mixing drive coastal upwelling systems
2024-01-26
They are among the most productive and biodiverse areas of the world's oceans: coastal upwelling regions along the eastern boundaries of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. There, equatorward winds cause near-surface water to move away from the coast. This brings cold, nutrient-rich water from the depths to the surface, inducing the growth of phytoplankton and providing the basis for a rich marine ecosystem in these regions.
In some tropical regions, however, productivity is high even when the upwelling favourable winds are ...
How a timekeeping gene affects tumor growth depends entirely on context
2024-01-26
JANUARY 23, 2024, NEW YORK – A Ludwig Cancer Research study has found that the circadian clock—which synchronizes physiological and cellular activities with the day-night cycle and is generally thought to be tumor suppressive—in fact has a contextually variable role in cancer.
“A lot of evidence suggests that the biological clock is broken in cancer cells, so we expected its disruption would fuel tumor growth in mouse models of melanoma,” said Chi Van Dang, scientific director of the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, who led the study with Research Associate Xue Zhang. “But, contrary to our expectations, ...
UT Extension Consumer Economics Specialist named National Educator of the Year for 2023
2024-01-26
An assistant professor and consumer economics specialist with University of Tennessee Extension has been recognized by the Association for Financial Counseling and Planning Education (AFCPE) as the organization’s Educator of the Year for 2023. Christopher Sneed was among ten individuals, organizations, special projects and initiatives expanding access to personal finance resources and education across the country recognized as part of the 2023 AFCPE Awards late last year.
The AFCPE’s Mary Ellen Edmondson Educator of the Year Award honors ...
Female reproductive milestones may be risk factors for diabetes and high cholesterol later in life
2024-01-26
Boston, MA – A new review of available evidence led by researchers at the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute suggests that female reproductive characteristics may be overlooked as risk factors that contribute to later metabolic dysfunction.
The review, “Reproductive risk factors across the female lifecourse and later metabolic health,” was published in the January 26 edition of Cell Metabolism.
Metabolic health is characterized by optimal blood glucose, lipids, blood pressure, and body fat. Alterations in these characteristics may lead to the development of type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
“Our ...
Using fMRI, new vision study finds promising model for restoring cone function
2024-01-26
In the retinas of human eyes, the cones are photoreceptor cells responsible for color vision, daylight vision, and the perception of small details. As vision scientists from the Division of Experimental Retinal Therapies at the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine, Gustavo D. Aguirre and William A. Beltran have been working for decades to identify the basis of inherited retinal diseases. They previously showed they could recover missing cone function by reintroducing a copy of the normal gene in photoreceptor cells.
Both ...
Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine awarded $160 million 10-year US National Science Foundation Regional Innovation Engines grant
2024-01-26
WINSTON-SALEM, NC, January 26, 2024 – The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) is the recipient of an inaugural U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) Engines Program award. The NSF Engines: Piedmont Triad Regenerative Medicine Engine is a regional project that provides an innovation ecosystem to stimulate workforce development, job creation, and economic growth through the development of technologies that benefit the emerging industry. The Piedmont Triad Regenerative Medicine Engine team is led by WFIRM, and includes Forsyth Technical Community College (FTCC), North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University (N.C. A&T), the RegenMed Development ...
Powering the future: Unlocking the role of hydrogen in lithium-ion batteries
2024-01-26
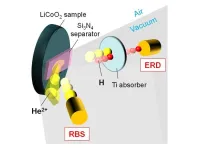
Lithium-ion batteries stand out as one of the most prevalent rechargeable battery technologies in the present era. Within these batteries, lithium-cobalt oxides (LiCoO2) are widely used as the materials for positive electrodes or cathodes (the conductors through which electric current either enters or exits a substance). The cathode plays a pivotal role in lithium-ion batteries and influences their capacity, performance over many charge-discharge cycles, and ability to manage heat.
One major issue leading to the deterioration of these batteries is the creation of hydrogen through the splitting of water. Therefore, gaining insights into how hydrogen builds ...
Scientists design a two-legged robot powered by muscle tissue
2024-01-26
Compared to robots, human bodies are flexible, capable of fine movements, and can convert energy efficiently into movement. Drawing inspiration from human gait, researchers from Japan crafted a two-legged biohybrid robot by combining muscle tissues and artificial materials. Publishing on January 26 in the journal Matter, this method allows the robot to walk and pivot.
“Research on biohybrid robots, which are a fusion of biology and mechanics, is recently attracting attention as a new field of robotics featuring biological function,” says corresponding author Shoji Takeuchi of the University of Tokyo, Japan. “Using muscle ...
Genomic “butterfly effect” explains risk for autism spectrum disorder
2024-01-26
Researchers in the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) examined the genetics of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by analyzing mutations in the genomes of individuals and their families. They discovered that a special kind of genetic mutation works differently from typical mutations in how it contributes to the condition. In essence, because of the three-dimensional structure of the genome, mutations are able to affect neighboring genes that are linked to ASD, thus explaining why ASD can occur even without direct mutations to ASD-related genes. This study appeared in the scientific journal Cell Genomics on January 26.
ASD is a group of conditions characterized in part ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
[Press-News.org] Confirmation of ancient lake on Mars builds excitement for Perseverance rover's samplesFindings reveal eons of environmental changes and offer hope that the rover’s soil and rock samples hold traces of life