(Press-News.org)
As people age or become ill, their immune systems can become exhausted and less capable of fighting off viruses such as the flu or COVID-19. In a new mouse study funded in part by the National Institutes of Health and published in Science Advances, researchers from the USC Stem Cell lab of Rong Lu describe how specific gene activity could potentially enhance immune cell production.
“Hematopoietic stem cells, or HSCs, produce blood and immune cells, but not all HSCs are equally productive,” said the study’s corresponding author Rong Lu, PhD, who is an associate professor of stem cell biology and regenerative medicine, biomedical engineering, medicine, and gerontology at USC, and a Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Scholar. “We wanted to understand the mechanism of why some stem cells produce more immune cells, while other stem cells produce fewer.”
With this goal in mind, first author Du Jiang, PhD, and his colleagues in the in the Lu Lab at the Keck School of Medicine of USC pioneered new techniques for understanding the quantitative association between immune cell production and gene expression in lab mice. The scientists labeled individual stem cells with genetic “barcodes” to track their immune cell production. They then correlated the barcode tracking with measurements of gene expression activity. They also developed innovative bioinformatics approaches to characterize their quantitative association.
By leveraging these technical advances, the scientists identified nearly 40 genes—including genes associated with diseases such as myelodysplastic syndrome, a type of cancer caused by abnormal blood-forming cells—that are related to immune cell production. They discovered associations between the activity of these genes and both the quantity and variety of immune cells produced. For example, certain genes are associated with the production of lymphoid cells, others with myeloid cells, and still others with a healthy balance of various immune cell types.
A few of the genes showed what the scientists described as a “constant association” with the production of lymphocytes only. In other words, at any level of lymphocyte output, gene expression was always associated with lymphocyte production.
A few other genes had a “discrete association” with the production of lymphocytes only. This means that gene activity was associated with lymphocyte production within a specific range of lymphocyte output levels.
Most commonly, genes would have either a “unimodal or multimodal” association with immune cell production. In these instances, which involved both lymphoid and myeloid cells, gene activity was only associated with immune cell production at either one or multiple specific levels of immune cell production.
“In this study, we show that most genes associated with immune cell production are associated only at specific levels of immune cell production,” said Jiang, who earned his PhD in the Lu Lab. “Our findings can inform strategies to optimize bone marrow transplantation—for example, by selecting donor bone marrow cells with gene activity associated with high and balanced levels of immune cell production.”
Additional authors include Adnan Y. Chowdhury, Anna Nogalska, Jorge Contreras, Yeachan Lee, Mary Vergel-Rodriguez, and Melissa Valenzuela from the Lu Lab.
The project was supported by federal funding from the National Institutes of Health (grants R00HL113104, R01HL138225, R01HL135292, R01HL135292-S1, R35HL150826, and R01AG080982) and the National Cancer Institute (grant P30CA014089). Additional support came from the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society (grant LLS-1370-20), California Institute for Regenerative Medicine, and the Hearst Foundations.
END
They are among the most productive and biodiverse areas of the world's oceans: coastal upwelling regions along the eastern boundaries of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. There, equatorward winds cause near-surface water to move away from the coast. This brings cold, nutrient-rich water from the depths to the surface, inducing the growth of phytoplankton and providing the basis for a rich marine ecosystem in these regions.
In some tropical regions, however, productivity is high even when the upwelling favourable winds are ...
JANUARY 23, 2024, NEW YORK – A Ludwig Cancer Research study has found that the circadian clock—which synchronizes physiological and cellular activities with the day-night cycle and is generally thought to be tumor suppressive—in fact has a contextually variable role in cancer.
“A lot of evidence suggests that the biological clock is broken in cancer cells, so we expected its disruption would fuel tumor growth in mouse models of melanoma,” said Chi Van Dang, scientific director of the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, who led the study with Research Associate Xue Zhang. “But, contrary to our expectations, ...
An assistant professor and consumer economics specialist with University of Tennessee Extension has been recognized by the Association for Financial Counseling and Planning Education (AFCPE) as the organization’s Educator of the Year for 2023. Christopher Sneed was among ten individuals, organizations, special projects and initiatives expanding access to personal finance resources and education across the country recognized as part of the 2023 AFCPE Awards late last year.
The AFCPE’s Mary Ellen Edmondson Educator of the Year Award honors ...
Boston, MA – A new review of available evidence led by researchers at the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute suggests that female reproductive characteristics may be overlooked as risk factors that contribute to later metabolic dysfunction.
The review, “Reproductive risk factors across the female lifecourse and later metabolic health,” was published in the January 26 edition of Cell Metabolism.
Metabolic health is characterized by optimal blood glucose, lipids, blood pressure, and body fat. Alterations in these characteristics may lead to the development of type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
“Our ...
In the retinas of human eyes, the cones are photoreceptor cells responsible for color vision, daylight vision, and the perception of small details. As vision scientists from the Division of Experimental Retinal Therapies at the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine, Gustavo D. Aguirre and William A. Beltran have been working for decades to identify the basis of inherited retinal diseases. They previously showed they could recover missing cone function by reintroducing a copy of the normal gene in photoreceptor cells.
Both ...
WINSTON-SALEM, NC, January 26, 2024 – The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) is the recipient of an inaugural U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) Engines Program award. The NSF Engines: Piedmont Triad Regenerative Medicine Engine is a regional project that provides an innovation ecosystem to stimulate workforce development, job creation, and economic growth through the development of technologies that benefit the emerging industry. The Piedmont Triad Regenerative Medicine Engine team is led by WFIRM, and includes Forsyth Technical Community College (FTCC), North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University (N.C. A&T), the RegenMed Development ...
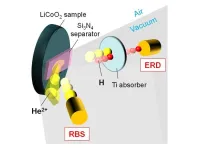
Lithium-ion batteries stand out as one of the most prevalent rechargeable battery technologies in the present era. Within these batteries, lithium-cobalt oxides (LiCoO2) are widely used as the materials for positive electrodes or cathodes (the conductors through which electric current either enters or exits a substance). The cathode plays a pivotal role in lithium-ion batteries and influences their capacity, performance over many charge-discharge cycles, and ability to manage heat.
One major issue leading to the deterioration of these batteries is the creation of hydrogen through the splitting of water. Therefore, gaining insights into how hydrogen builds ...
Compared to robots, human bodies are flexible, capable of fine movements, and can convert energy efficiently into movement. Drawing inspiration from human gait, researchers from Japan crafted a two-legged biohybrid robot by combining muscle tissues and artificial materials. Publishing on January 26 in the journal Matter, this method allows the robot to walk and pivot.
“Research on biohybrid robots, which are a fusion of biology and mechanics, is recently attracting attention as a new field of robotics featuring biological function,” says corresponding author Shoji Takeuchi of the University of Tokyo, Japan. “Using muscle ...
Researchers in the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) examined the genetics of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by analyzing mutations in the genomes of individuals and their families. They discovered that a special kind of genetic mutation works differently from typical mutations in how it contributes to the condition. In essence, because of the three-dimensional structure of the genome, mutations are able to affect neighboring genes that are linked to ASD, thus explaining why ASD can occur even without direct mutations to ASD-related genes. This study appeared in the scientific journal Cell Genomics on January 26.
ASD is a group of conditions characterized in part ...
Cellular agriculture – the production of meat from cells grown in bioreactors rather than harvested from farm animals – is taking leaps in technology that are making it a more viable option for the food industry. One such leap has now been made at the Tufts University Center for Cellular Agriculture (TUCCA), led by David Kaplan, Stern Family Professor of Engineering, in which researchers have created bovine (beef) muscle cells that produce their own growth factors, a step that can significantly cut costs of production.
Growth factors, whether ...