(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Jan. 29, 2024 — Counterfeit detector pens use a starch-iodine reaction to identify fake bills. But could you fool them with chemistry? In today’s episode, we dive into the chemistry of iodine, its color and its clock reactions, all while making a little extra cash on the side. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xDaVCyOBSsY
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions and follow us on Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | Instagram
END
Can science beat counterfeit detector pens? (video)
2024-01-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How did humans learn to walk? New evolutionary study offers an earful
2024-01-29
Humans and our closest relatives, living apes, display a remarkable diversity of types of locomotion—from walking upright on two legs to climbing in trees and walking using all four limbs.
While scientists have long been intrigued by the question of how humans’ bipedal stance and movement evolved from a quadrupedal ancestor, neither past studies nor fossil records have permitted the reconstruction of a clear and definitive history of the early evolutionary stages that led to human bipedalism.
However, a new study, which centers on recently discovered evidence from skulls of a 6-million-year-old fossil ape, Lufengpithecus, ...
Alzheimer’s disease acquired from historic medical treatments
2024-01-29
Five cases of Alzheimer’s disease are believed to have arisen as a result of medical treatments decades earlier, reports a team of UCL and UCLH researchers.
Alzheimer’s disease is caused by the amyloid-beta protein, and is usually a sporadic condition of late adult life, or more rarely an inherited condition that occurs due to a faulty gene. The new Nature Medicine paper provides the first evidence of Alzheimer’s disease in living people that appears to have been medically acquired and due to transmission of the amyloid-beta protein.
The people described in the paper had all been treated as ...
Food insecurity and premature mortality and life expectancy in the us
2024-01-29
About The Study: Although the association of food security and life expectancy varied across sex and racial and ethnic groups, overall, lower levels of food security were associated with a higher risk of premature mortality and a shorter life expectancy in this study of 57,000 adults. The findings of this study highlight the potential importance of improving food security in promoting population health and health equity.
Authors: Lu Qi, M.D., of Tulane University in New Orleans, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Wealth redistribution to extend longevity in the U.S.
2024-01-29
About The Study: The findings of this study of 35,000 adults age 50 or older suggest that wealth inequality in the U.S. is associated with significant inequities in survival. Wealth redistribution policies may substantially reduce those inequities and increase population longevity.
Authors: Kathryn E. W. Himmelstein, M.D., M.S.Ed., of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.7975)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
Efficacy of electronic cigarettes vs varenicline and nicotine chewing gum as an aid to stop smoking
2024-01-29
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial including 1,068 smokers, electronic cigarettes were as effective as varenicline and more effective than nicotine chewing gum as a stop-smoking aid when all three treatments were provided with minimal behavioral support.
Authors: Zhao Liu, Ph.D., of the China-Japan Friendship Hospital in Beijing, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.7846)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
High school students who report using alcohol, cannabis or nicotine at higher risk for suicidal thoughts and other mental health disorders
2024-01-29
BOSTON –High school students who reported using cannabis, alcohol, or nicotine were more likely to have thoughts about suicide, feel depressed or anxious, have unusual experiences, and exhibit inattention or hyperactivity, according to recent survey-based study conducted by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the University of Minnesota.
The study, which is published in JAMA Pediatrics, included 2022–2023 survey results from more than 15,000 high school students across Massachusetts.
“We sought to determine ...
New evidence informs risk factors, diagnosis and care of patients with CVT stroke
2024-01-29
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Monday, Jan. 29, 2024
DALLAS, January 29, 2024 — A new scientific statement from the American Heart Association emphasizes the need to increase patients’ and physicians’ awareness of cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) to improve the recognition of this condition and initiate prompt medical treatment. The new statement, Diagnosis and Management of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis, published today in the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association’s peer-reviewed journal Stroke. ...
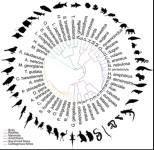
Researchers map genome for cats, dolphins, birds, and dozens of other animals
2024-01-29
Researchers mapped genetic blueprints for 51 species including cats, dolphins, kangaroos, penguins, sharks, and turtles, a discovery that deepens our understanding of evolution and the links between humans and animals.
“Being able to access that genetic information will have huge implications for understanding human health and evolution,” said lead author Michael Schatz, a Bloomberg Distinguished Professor of computer science and biology at Johns Hopkins University. “A lot of work ...
Overcoming the stigma: study recommends steps to move past barriers of brain health conversation
2024-01-29
INDIANAPOLIS -- Approximately four of five primary care clinicians consider themselves on the front lines of brain health. In the U.S., clinicians are the first point of contact for patients worried about memory loss and are most likely the first to detect and evaluate patients experiencing mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease or related dementias.
In a new study focused on understanding the barriers of clinician-patient conversations about brain health and cognitive concerns, Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine Research Scientist Malaz Boustani, M.D., MPH, found that early conversations about brain health between ...
PolyU develops high-efficiency carbon dioxide electroreduction system for reducing carbon footprint and progressing carbon neutrality goals
2024-01-29
Global warming continues to pose a threat to human society and the ecological systems, and carbon dioxide accounts for the largest proportion of the greenhouse gases that dominate climate warming. To combat climate change and move towards the goal of carbon neutrality, researchers from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) have developed a durable, highly selective and energy-efficient carbon dioxide (CO2) electroreduction system that can convert CO2 into ethylene for industrial purposes to provide an effective solution for ...