(Press-News.org) The University of Manchester and SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics have announced the establishment of the SPIE-Manchester Postgraduate Scholarship in Photonics.
The $500k gift from the SPIE Endowment Matching Program will be matched 100% by the University and will be used to support both early-career and returning researchers from the University’s Photon Science Institute in partnership with the Royce Institute, the UK’s national institute for advanced materials research and innovation.
The partnership was announced today (29 January) during the SPIE Photonics West conference in San Francisco.
Photonics is the study of light and its interactions to develop technologies that impact our daily lives, from as fibre optics for communications, microscopy for medical applications, light sources for displays such as smartphones to next generation quantum applications.
With a goal of increasing diversity in the subject, the SPIE-Manchester Postgraduate Scholarship will have a particular focus on funding individuals returning to research following a career break or time in industry, and those pursuing unconventional career pathways or part-time study (situations often necessitated by caring responsibilities, for example).
Aligning current research and industrial needs for a robust training pipeline, an additional unique feature of the scholarship is an optional final-year placement of up to 12 months, during which students can develop industry-relevant skills in collaboration with local optics and photonics companies.
Dr Patrick Parkinson, Department Head of Research for Physics and Astronomy at The University of Manchester, said: “Today marks just the beginning of the partnership between The University of Manchester and SPIE.
“The establishment of the SPIE-Manchester Postgraduate Scholarship in Photonics is a testament to our shared values within skills training, fostering diversity in education and the vital role of photonics.
“This announcement holds special significance as it coincides with the University’s bicentenary year. We take great pride in using this generous donation to not only advance research and education but also to solidify our existing partnerships and forge new industrial collaborations to deliver a doctoral training program that will ensure a sustainable workforce for the North West of England.”
SPIE CEO Kent Rochford, added: “For many researchers and engineers, the traditional educational paths are barriers to their success.
“The SPIE-Manchester Postgraduate Scholarship in Photonics aims to remove those barriers and provide exciting opportunities for early-career researchers and those who may be pursuing unconventional career paths. Working internally at the University’s Photon Science Institute with the option of an industry-focused placement, promises to benefit young researchers as well as our future diverse workforce. I very much look forward to meeting the leaders in optics and photonics technologies who will emerge from this dynamic partnership between SPIE and The University of Manchester.”
The scholarship is the 11th major SPIE gift to universities and institutes as part of the Society's ongoing program to support the expansion of optical engineering teaching and research.
The SPIE Endowment Matching Program was established in 2019 to increase international capacity in the teaching and research of optics and photonics. With this latest gift, SPIE has provided more than $4 million in matching gifts, resulting in more than $11 million in dedicated funds. The SPIE Endowment Matching Program supports optics and photonics education and the future of the industry by contributing a match of up to $500,000 per award to college, institute, and university programs with optics and photonics degrees, or with other disciplines allied to the SPIE mission.
END
University of Manchester and SPIE announce $1 million endowment for postgraduate scholarships
2024-01-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Argonne scientists help scale up nanomaterials for sustainable manufacturing
2024-01-29
New material is self-assembling, long-lasting and recyclable.
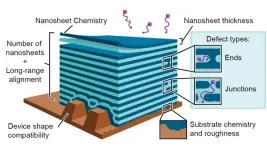
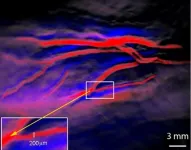
As electronic devices get smaller, the materials needed to create them get smaller as well. Nanoscience is the study of extremely small materials that find uses in energy storage, electronics, health and safety applications and more.
Now a team led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory has developed a new self-assembly method to fabricate multilayered 2D nanosheets. A nanosheet is an extremely small, lasagna-like material made of ultrathin layers of polymers and nanoparticles.
These nanosheets have significantly ...
OU scientists tests revolutionary imaging technique for pancreatic cancer
2024-01-29
Researchers at OU Health Stephenson Cancer Center at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences have embarked on a revolutionary new research study that could improve the detection of a deadly disease — pancreatic cancer — and give patients a chance to live longer, healthier lives.
The research focuses on an innovative combination of imaging techniques: a newly created contrast agent that recognizes pancreatic cancer cells, paired with Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography, or MSOT. Together, the approach can detect pancreatic cancer cells the width of an eyelash ...
Rising sea levels could lead to more methane emitted from wetlands
2024-01-29
As sea levels rise due to global warming, ecosystems are being altered. One small silver lining, scientists believed, was that the tidal wetlands found in estuaries might produce less methane – a potent greenhouse gas – as the increasing influx of seawater makes these habitats less hospitable to methane-producing microbes.
However, research from biologists at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley indicates that these assumptions aren’t always true. After examining the microbial, chemical, and geological features of 11 wetland zones, the team found that a wetland region exposed ...
Study urges people to think twice before going on a diet
2024-01-29
A new qualitative study highlights the negative interpersonal and psychological consequences associated with “yo-yo dieting,” also known as weight cycling. The work underscores how toxic yo-yo dieting can be and how difficult it can be for people to break the cycle.
“Yo-yo dieting – unintentionally gaining weight and dieting to lose weight only to gain it back and restart the cycle – is a prevalent part of American culture, with fad diets and lose-weight-quick plans or drugs normalized as people pursue beauty ...
Astronomers spot 18 black holes gobbling up nearby stars
2024-01-29
Star-shredding black holes are everywhere in the sky if you just know how to look for them. That’s one message from a new study by MIT scientists, appearing today in the Astrophysical Journal.
The study’s authors are reporting the discovery of 18 new tidal disruption events (TDEs) — extreme instances when a nearby star is tidally drawn into a black hole and ripped to shreds. As the black hole feasts, it gives off an enormous burst of energy across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Astronomers have detected previous tidal disruption events by looking for characteristic bursts in the optical and X-ray bands. To date, these searches have ...
The DiAL-Health study will help determine how intermittent fasting and calorie counting can improve a person’s “healthspan”
2024-01-29
January is a time when many people are looking for new diet routines, and intermittent fasting is trending, as are traditional calorie cutting programs.
Research conducted with animal models suggests that intermittent fasting slows aging, and those animals live longer. Researchers at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center and the University of Alabama at Birmingham are conducting the DiAL-Health study to see if eating for 8 hours and fasting for 16 each day shows similar results in people. These researchers ...
From simulation to reality: Making social media a safer space for kids through AI
2024-01-29
Like it or not, social media has become the new mall for kids. It’s where they want to be, and it’s a place they can easily go—often with no guidance, no oversight, and no guardrails. And when the content gets ugly or confusing or weird, it can be tough for them to know what to do.
Dominic DiFranzo, an assistant professor of computer science and engineering in Lehigh University’s P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science, has devoted his research to helping kids better navigate the perils of social media. He and his team have recently received two grants from the National Science Foundation to develop artificial intelligence tools ...
Shah studying fingerprinting technology for enhancing 5G/NextG O-RAN supply chain risk management
2024-01-29
Vijay Shah, Assistant Professor, Cybersecurity Engineering, received funding for the project: "Fingerprinting Technology for Enhancing 5G/NextG O-RAN Supply Chain Risk Management."
In this project, Shah is focusing on distinctive power signatures and electromagnetic emanations to fortify supply chain risk management of 5G/Next G networks.
This technology has the potential to create a robust framework for comprehensive validation and testing across the entire lifespan of deployed Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) systems. This, in turn, could ...
From Baby Boomers to Gen Alpha – Is it time to stop talking about generations?
2024-01-29
'Millennials don't really want to work. They're far too focused on avocado toast and chai lattes!' Just one of the many clichés expressed by workers over the age of fifty. And those being criticized? Well, they often reply with a bored 'OK, Boomer' followed by an eye roll and some ironic remark about the excessively performance-driven worldview of those born between the mid 1950s and the mid 1960s. Work, it seems, just isn't as important to the young as it is to older generations. But it's not just about baby boomers and millennials. Parked between them is Generation X, ...
Destroying tumor cells with calcium
2024-01-29
Calcium ions are essential for cells, but can be toxic in higher concentrations. A team of researchers has now designed and prepared a combination drug that kills tumor cells by modulating the calcium influx into the cell. An external calcium source is not necessary because only the calcium ions already present in the tumor tissue are used, according to the study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Biological cells need calcium ions, among other things, for the proper functioning of the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cells. However, ...