(Press-News.org) JMIR Publications is pleased to announce a new theme issue titled “Perioperative Blood Management” in JMIR Perioperative Medicine. The premier, peer-reviewed journal is indexed in PubMed and focuses on how technology and data science can improve care delivery and surgical patient outcomes. The new theme issue aims to explore the latest advancements, challenges, and patient-centered innovative approaches in optimizing blood-related practices before, during, and after surgical procedures.
JMIR Perioperative Medicine welcomes contributions from global researchers, clinicians, and experts in the field of perioperative medicine. We encourage submissions exploring diverse aspects related to blood management in perioperative care such as:
Digital and technological innovations and the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) in perioperative blood management
Preoperative anemia management
Perioperative blood transfusion thresholds
Perioperative blood management protocols and programs
Advances in blood conservation techniques
Strategies for minimizing perioperative blood loss
Transfusion-related complications
Economic and ethical considerations in perioperative blood management
Global and regional inequities in blood availability during the perioperative phase
Contributors are encouraged to submit their work by June 30, 2024. All submissions will undergo rigorous peer review, and accepted articles will be published as part of the “Perioperative Blood Management” theme issue.
To learn more please visit: https://periop.jmir.org/announcements/440
About JMIR Publications:
JMIR Publications is a renowned publisher with a long-standing commitment to advancing digital health research and progressing open science. Our portfolio includes a wide array of prestigious open access, peer-reviewed journals dedicated to the dissemination of high-quality research in the field of digital health. JMIR Publications is celebrating its 25th anniversary in 2024 as the leading open access, digital health publisher.
To learn more about JMIR Publications, please visit https://www.JMIRPublications.com or connect with us via X, LinkedIn, YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram.
Head office: 130 Queens Quay East, Unit 1100, Toronto, ON, M5A 0P6 Canada
Media contact: communications@JMIR.or
END
JMIR Perioperative Medicine invites submissions on perioperative blood management
2024-01-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Structural color ink: Printable, non-iridescent and lightweight
2024-01-30
A new way of creating color uses the scattering of light of specific wavelengths around tiny, almost perfectly round silicon crystals. This Kobe University development enables non-fading structural colors that do not depend on the viewing angle and can be printed. The material has a low environmental and biological impact and can be applied extremely thinly, promising significant weight improvements over conventional paints.
An object has color when light of a specific wavelength is reflected. With traditional pigments, this happens by molecules absorbing other colors from white light, but over time this interaction makes the molecules degrade and the color fades. ...
A faster, more efficient imaging system for nanoparticles
2024-01-30
Teams led by professors Jinyang Liang and Fiorenzo Vetrone from the Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications Research Centre at the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) have developed a new system for imaging nanoparticles. It consists of a high-precision, short-wave infrared imaging technique capable of capturing the photoluminescence lifetimes of rare-earth doped nanoparticles in the micro- to millisecond range.
This groundbreaking discovery, which was published in the journal Advanced Science, paves the way for promising applications, particularly in the biomedical and information security fields.
Rare-earth ...
Lifetime of ‘biodegradable’ straws in the ocean is 8-20 months, study finds
2024-01-30
Plastic drinking straws that get into marine ecosystems make beaches unsightly and pose problems for turtles and seabirds. So, people increasingly favor alternatives marketed as biodegradable or compostable. But do marine microorganisms break apart those straws? Researchers conducted experiments with seawater and report in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering that some commercial bioplastic or paper straws might disintegrate within eight to 20 months in coastal ocean systems and switching to ...
Tomato juice’s antimicrobial properties can kill salmonella
2024-01-30
Washington, D.C.—Tomato juice can kill Salmonella Typhi and other bacteria that can harm people's digestive and urinary tract health, according to research published this week in Microbiology Spectrum, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology. Salmonella Typhi is a deadly human-specific pathogen that causes typhoid fever.
“Our main goal in this study was to find out if tomato and tomato juice can kill enteric pathogens, including Salmonella Typhi, and if so, what qualities they ...
Joint efforts to ensure the sustainability of our one and only Earth
2024-01-30
The 37th International Geological Congress (IGC 2024) in August 2024, Busan, Korea, will highlight a growing concern amid urgent threats posed by accelerated climate and environmental changes. This will prompt collaborative efforts towards ensuring the sustainability of our planet.
Abnormally high temperatures across the globe during the past year were expected to make 2023 the hottest year in Earth's history. This realization underscores the concept of climate change, which was once confined to academic desks but has since permeated into our daily existence.
Geologists now assert that the rapid climate and environmental changes necessitate ...
KIMM develops technology for detecting injection of medication to prevent medical accidents related to analgesic drug infusion pump in hospitals
2024-01-30
Excessive administration of analgesic drugs frequently results in medical accidents. To prevent the occurrence of these accidents, a drug infusion pump featuring a technology for safely detecting medication administration has been developed for the first time in the world.
The research team led by Senior Researcher Dong-kyu Lee of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (President Seog-hyun Ryu, hereinafter referred to as KIMM), an institute under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Science and ICT, has succeeded in developing the technology for customized sensor modules capable of measuring the extremely low flow rate of analgesic drug infusion pumps as well as the existence ...
Machine sentience and you: what happens when machine learning goes too far
2024-01-30
There’s always some truth in fiction, and now is about the time to get a step ahead of sci-fi dystopias and determine what the risk in machine sentience can be for humans.
Although people have long pondered the future of intelligent machinery, such questions have become all the more pressing with the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learningT. These machines resemble human interactions: they can help problem solve, create content, and even carry on conversations. For fans ...
Drexel researchers propose AI-guided system for robotic inspection of buildings, roads and bridges
2024-01-30
Our built environment is aging and failing faster than we can maintain it. Recent building collapses and structural failures of roads and bridges are indicators of a problem that’s likely to get worse, according to experts, because it’s just not possible to inspect every crack, creak and crumble to parse dangerous signs of failure from normal wear and tear. In hopes of playing catch-up, researchers in Drexel University’s College of Engineering are trying to give robotic assistants the tools to help inspectors with the job.
Augmenting visual ...
Residents of rural ‘glades’ take a ‘leap of faith’ to combat dementia
2024-01-30
The prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) is disproportionately high among rural, racially/ethnically diverse older residents. In fact, they face up to an 80 percent greater risk of cognitive impairment in older age, and 2.5 times potentially preventable ADRD-related hospitalizations compared to urban dwellers. It is estimated that early and accurate diagnosis in the mild cognitive impairment stage could save up to $7 trillion in patients’ health and long-term care costs by 2050.
To address these health disparities in rural underserved populations, researchers from Florida ...
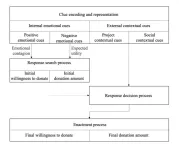
Emotions drive donation behavior in disease relief projects on a fundraising platform
2024-01-30
The digital age has profoundly changed how we communicate as humans. Today, we can regularly interact with people we are unrelated to and unacquainted with in real time across the world. Because of this, individuals can now engage in prosocial behaviors, including cooperating, sympathizing, helping and donating, with complete strangers, but the motivating factors behind these behaviors are poorly understood. Analysis of data generated from a fundraising website suggests that positive emotions elicit higher total donation amounts while negative emotions result in higher individual donation amounts.
Fundraising ...