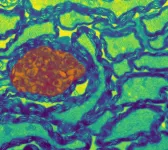
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON—Coronary artery calcification is increasing in prevalence, leading to greater risks both during procedures such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and adverse events in the short and long term. Along with these challenges, treatment options are expanding, increasingly including calcium modification prior to stent implantation. A newly published SCAI Expert Consensus Statement on the Management of Calcified Coronary Lesions outlines methods for interventional cardiologists to identify various types of calcified coronary lesions and presents an algorithm to help them guide the use of these various calcium modification strategies.
“This expert consensus statement incorporates detailed tips for the use of each treatment modality and the latest in emerging trials and therapies to help interventional cardiologists rise to these challenges,” said SCAI President George D. Dangas, MD, PhD, MSCAI.
In addition to outlining methods for identifying various types of calcified lesions and reviewing the different calcium modifying tools, “the document provides images using two different types of intravascular imaging technology and a consensus of practical tips when using the different treatment strategies, including in the use of different types of calcified lesion subsets,” said Binita Shah, MD, MS, FSCAI, Chair of the document’s writing committee, associate professor of medicine at NYU School of Medicine and associate director of interventional cardiology for VA NY Harbor Healthcare System. “We bring the data and our experience all together with an algorithm designed to identify and address the various calcified CAD phenotypes. Our group is proud of this document and the uniqueness of it.”
Among the consensus document’s many takeaways, highlights include:
Calcified coronary lesions are becoming commonplace in the cardiac catheterization lab, and their treatment is associated with increased short- and long-term risks compared to noncalcified lesions.
The use of intravascular imaging and the proper use of calcium modification devices can help decrease these risks.
The authors propose an algorithm for how to identify and treat these lesions with the various currently available calcium modification devices, along with tips and tricks for using these devices.
“This consensus statement is meant to increase awareness about the prevalence of calcified coronary lesions, the ramifications of testing these lesions when indicated, the various treatment options available including tips for using them, and offer an algorithm for choosing between these treatment options,” said Robert F. Riley, MD, MS, FSCAI, director of the complex coronary therapeutics program at Overlake Medical Center & Clinics.
For the interventional cardiologist community, “our hope is that this document aids in improving outcomes for some of our most challenging patients,” said Mitul Patel, MD, FSCAI, interventional cardiologist, VA San Diego Health System.
About SCAI: The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions is a professional organization representing more than 4,000 invasive and interventional cardiology professionals in approximately 75 nations. SCAI's mission is to promote excellence in invasive/interventional cardiovascular medicine through physician education and representation, and advancement of quality standards to enhance patient care.
END
SCAI publishes expert consensus statement on management of calcified coronary lesions requiring intervention
Outlines methods for interventional cardiologists to identify types of calcified coronary lesions and presents an algorithm to guide the use of calcium modification strategies
2024-01-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Firing nerve fibers in the brain are supplied with energy on demand
2024-01-31
Brain function depends on the swift movement of electrical signals along axons, the long extensions of nerve cells that connect billions of brain cells. The nerve fibers are insulated by a fatty layer called myelin, which is produced by specialized cells called oligodendrocytes. These cells wrap around and insulate nerve fibers ensuring the rapid and efficient transmission of signals that is essential for brain function.
Oligodendrocytes sense and respond to the electrical signals
Now, a team of neuroscientists led by Aiman Saab at the Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology at the University ...
Engineering viruses to kill deadly pathogens
2024-01-31
Northwestern University researchers have successfully coaxed a deadly pathogen to destroy itself from the inside out.
In the new study, researchers modified DNA from a bacteriophage or “phage,” a type of virus that infects and replicates inside of bacteria. Then, the research team put the DNA inside Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa), a deadly bacterium that is also highly resistant to antibiotics. Once inside the bacterium, the DNA bypassed the pathogen’s defense mechanisms ...
NIH study shows higher mortality rates for patients on respiratory support in rural intermediate care units
2024-01-31
NIH study shows higher mortality rates for patients on respiratory support in rural intermediate care units
Findings highlight the importance of providing ICU-level care to rural patients with respiratory failure
A new National Institutes of Health-supported study finds that patients receiving ventilator life support in the intermediate care units – a potentially less costly alternative for people not sick enough for the intensive care units (ICUs) but too ill for the general ward – of rural hospitals had significantly higher death rates than patients in the same type of ...
Perspective paper explores the debate over sentient machines
2024-01-31
A researcher from the New Jersey Institute of Technology has published a perspective paper that examines sentience and its application to artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics. Sentience describes the ability to sense and feel, drawing its meaning from the Latin word sentire which means “to feel.” The paper addresses a set of ideological commitments at stake in debates over sentient machines. The author proposes that artificial sentience is both necessary and impossible.
The perspective paper is published in the Journal of Social Computing on December 31, 2023.
“I argue ...
New AI technique significantly boosts Medicare fraud detection
2024-01-31
Medicare is sporadically compromised by fraudulent insurance claims. These illicit activities often go undetected, allowing full-time criminals and unscrupulous health providers to exploit weaknesses in the system. Last year, the estimated annual fraud topped $100 billion according to the National Health Care Anti-Fraud Association, but it is likely much higher.
Traditionally, to detect Medicare fraud, a limited number of auditors, or investigators, are responsible for manually inspecting thousands of claims, but only have enough time to look for very specific patterns indicating suspicious behaviors. Moreover, there are not enough ...
Fungal-rich soil may improve green roofs
2024-01-31
Green roofs have become increasingly popular thanks to their benefits related to climate adaptation, mitigation, and urban biodiversity management.
These vegetated surfaces on the rooftops of buildings absorb excess storm water, reduce energy use by insulating buildings, and cool neighborhoods, tempering urban heat islands, while also creating urban habitats for plants, pollinators, and wildlife.
But, in the U.S., green roofs are typically planted with non-native plants in sterile soils, and their effectiveness declines over time.
A Dartmouth-led research team set out to determine ...
Autoimmune disease and pregnancy
2024-01-31
SEATTLE – For many aspiring mothers with autoimmune disease, pregnancy can be daunting and full of unknowns. In some cases, those suffering from specific autoimmune conditions have chosen to forego pregnancy altogether due to concerns about their disease treatments and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
In a just-published study in the journal Lancet eClinical Health, researchers at the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) and Providence showed nuanced pregnancy outcomes for pregnant individuals with autoimmune disease. The ...
Looking for love? Try finding purpose as well
2024-01-31
The world of online dating can be overwhelming with the dizzying array of options for attracting a partner but new research from Washington University in St. Louis shows that those looking for love may have more success if they also seek a sense of purpose in life.
Researcher Isabella D’Ottone, in the lab of Patrick Hill, associate professor of psychological and brain sciences in Arts & Sciences, published a study about how that sense of purpose can affect how others may rate dating app profiles. Those whose profiles show a sense of purpose were rated higher on various scales for attractiveness compared ...
Brain changes behind pain sensitivity may affect older women more
2024-01-31
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study has found that the brain system enabling us to inhibit our own pain changes with age, and that gender-based differences in those changes may lead females to be more sensitive to moderate pain than males as older adults.
Researchers used fMRI scans to examine brain responses in men and women who had rated the intensity and unpleasantness of pain during exposure to increasing levels of heat. The results suggested that established gender differences in pain perception could likely be traced at least ...
Enhancing solid-state phosphorescence in π-electronic molecules
2024-01-31
Photoluminescent molecules, capable of absorbing and re-emitting light, play an important role in the development of technologies such as light-emitting diodes, sensors, and displays. Among them, ordered arrangements of π-electronic molecules such as crystals of organoplatinum(II) complexes, where a platinum(II) ion is coordinated by organic ligands in a square-planar arrangement, stand out for their applications in energy-efficient flexible displays. However, their luminescence in the solid state is short-lived due to the interaction between excitons (bound electron-hole pairs) of neighboring molecules. To address this ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
Cost of copper must rise double to meet basic copper needs
A gel for wounds that won’t heal
Iron, carbon, and the art of toxic cleanup
Organic soil amendments work together to help sandy soils hold water longer, study finds
Hidden carbon in mangrove soils may play a larger role in climate regulation than previously thought
Weight-loss wonder pills prompt scrutiny of key ingredient
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
Combining AI with OCT shows potential for detecting lipid-rich plaques in coronary arteries
SeaCast revolutionizes Mediterranean Sea forecasting with AI-powered speed and accuracy
JMIR Publications’ JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology invites submissions on Bridging Data, AI, and Innovation to Transform Health
Honey bees navigate more precisely than previously thought
Air pollution may directly contribute to Alzheimer’s disease
Study finds early imaging after pediatric UTIs may do more harm than good
UC San Diego Health joins national research for maternal-fetal care
New biomarker predicts chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer
Treatment algorithms featured in Brain Trauma Foundation’s update of guidelines for care of patients with penetrating traumatic brain injury
Over 40% of musicians experience tinnitus; hearing loss and hyperacusis also significantly elevated
Artificial intelligence predicts colorectal cancer risk in ulcerative colitis patients
Mayo Clinic installs first magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia system for cancer research in the US
Calibr-Skaggs and Kainomyx launch collaboration to pioneer novel malaria treatments
JAX-NYSCF Collaborative and GSK announce collaboration to advance translational models for neurodegenerative disease research
[Press-News.org] SCAI publishes expert consensus statement on management of calcified coronary lesions requiring interventionOutlines methods for interventional cardiologists to identify types of calcified coronary lesions and presents an algorithm to guide the use of calcium modification strategies