(Press-News.org) Among the most difficult types of pain to alleviate is neuropathic pain, pain that is usually caused by damage to nerves in various body tissues, including skin, muscle and joints. It can cause patients to suffer feelings like electric shocks, tingling, burning or stabbing. Diabetes, multiple sclerosis, chemotherapy drugs, injuries and amputations have all been associated with neuropathic pain, which is often chronic, sometimes unrelenting and affects millions of people worldwide. Many of the available pain medications are only moderately effective at treating this type of pain and often come with serious side effects, as well as risk of addiction.
Now researchers at UT Austin, The University of Texas at Dallas and the University of Miami have identified a molecule that reduces hypersensitivity in trials in mice by binding to a protein they have shown is involved in neuropathic pain.
The findings appear in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“We found it to be an effective painkiller, and the effects were rather long-lived,” said Stephen Martin, the June and J. Virgil Waggoner Regents Chair in Chemistry at The University of Texas at Austin and co-corresponding author of the paper. “When we tested it on different models, diabetic neuropathy and chemotherapy-induced neuropathy, for example, we found this compound has an incredible beneficial effect.”
The new compound, dubbed FEM-1689, does not engage opioid receptors in the body, making it a possible alternative to existing pain medications linked to addiction. In addition to reducing sensitivity, the compound can help regulate the integrated stress response (ISR), a network of cellular signaling that helps the body respond to injuries and diseases. When well regulated, the ISR restores balance and promotes healing. When it goes awry, the ISR can contribute to diseases such as cancer, diabetes and metabolic disorders.
“It’s our goal to make this compound into a drug that can be used to treat chronic pain without the dangers of opioids,” Martin said. “Neuropathic pain is often a debilitating condition that can affect people their entire lives, and we need a treatment that is well tolerated and effective.”
NuvoNuro Inc., a company co-founded by Martin and other authors on the paper, was recently awarded a grant from the National Institutes of Health HEAL Initiative, which funds research to find scientific solutions to the national opioid crisis, to create a drug based on their findings.
“This work is the culmination of a wonderful five-year collaboration with our colleagues at UT Austin and is a great example of academic drug discovery pushing the field of non-opioid pain therapeutics forward,” said Theodore Price, a professor of neuroscience at The University of Texas at Dallas and co-corresponding author of the paper. “Our funding from NIH on this continuing project through our spin-out company, NuvoNuro, has the potential to take us toward clinical development in the next few years, which is extraordinarily exciting.”
Muhammad Saad Yousuf, Eric T. David, Stephanie Shiers, Marisol Mancilla Moreno, Jonathan Iketem, Danielle M. Royer, Chelsea D. Garcia, Jennifer Zhang, Veronica M. Hong, Subhaan M. Mian, Ayesha Ahmad and Benedict J. Kolber of The University of Texas at Dallas; James J. Sahn and Hongfen Yang of UT Austin; and Daniel J. Liebl of University of Miami Miller School of Medicine were also authors on the paper.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and the Robert A. Welch Foundation.
The University of Texas at Austin is committed to transparency and disclosure of all potential conflicts of interest. University investigators involved in this research have submitted required financial disclosure forms with the University. As co-founders of NuvoNuro Inc., Stephen Martin and James Sahn also are co-inventors on patents and pending patent applications related to work described in this article.
END
Researchers uncover potential non-opioid treatment for chronic pain
A new approach to treating neuropathic pain is making a key step forward thanks to researchers at The University of Texas at Austin
2024-01-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
John Theurer Cancer Center (JTCC) physician co-authors clinical research on innovative oral leukemia therapy
2024-01-31
Researchers at Hackensack Meridian’s John Theurer Cancer Center (JTCC), are part of a published Phase 3 study reporting on the equivalent safety and effectiveness in the oral treatment of blood cancers–such as myelodysplastic syndrome and/or chronic myelomonocytic leukemia–to its previously inpatient, intravenous treatment counterparts.
John Theurer Cancer Center is part of the NCI-designated Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center at Georgetown University.
Dr. James K. McCloskey, M.D., led JTCC’s ...
UC Irvine scientists make breakthrough in quantum materials research
2024-01-31
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 31, 2024 — Researchers at the University of California, Irvine and Los Alamos National Laboratory, publishing in the latest issue of Nature Communications, describe the discovery of a new method that transforms everyday materials like glass into materials scientists can use to make quantum computers.
“The materials we made are substances that exhibit unique electrical or quantum properties because of their specific atomic shapes or structures,” said Luis A. Jauregui, professor of physics & astronomy ...
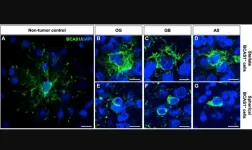
BCAS1 defines a heterogeneous cell population in diffuse glioma patients
2024-01-31
“[...] this is the first study describing a BCAS1+ cell population in a large cohort of diffuse glioma patients.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 31, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on January 24, 2024, entitled, “BCAS1 defines a heterogeneous cell population in diffuse gliomas.”
Oligodendrocyte precursor markers have become of great interest to identify new diagnostic and therapeutic targets for diffuse gliomas, since state-of-the-art studies point towards immature oligodendrocytes as a possible source of gliomagenesis. Brain enriched myelin associated ...
Microgreens made to order: Italian scientists have tailored iodine and potassium content of radishes, peas, rocket and chard
2024-01-31
In a significant development for personalised nutrition, researchers in Italy have cultivated microgreens with bespoke nutritional profiles to serve individual dietary requirements.
The study, published in the Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture (doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13222), provides a blueprint for the soilless cultivation of nutritionally enriched plants in a commercial greenhouse setting.
Co-authors Massimiliano D’Imperio and Francesco Serio, both at the Institute of Sciences of Food Production (ISPA) National Council ...
How to make bright quantum dots even brighter
2024-01-31
Quantum dots are a kind of artificial atom: just a few nanometres in size and made of semiconductor materials, they can emit light of a specific colour or even single photons, which is important for quantum technologies. The discoverers and pioneers of the commercial production of quantum dots were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2023. In recent years, quantum dots made of perovskites have attracted particular attention. Perovskites belong to a class of materials that have a similar structure to the mineral perovskite ...
Method combines artificial intelligence and satellite imagery to map crop-livestock integration systems
2024-01-31
Crop-livestock integration (CLI) systems combine the growing of crops in rotation or consortium, especially grain crops such as soybeans, corn and sorghum, and forage plants used to feed cattle and pigs, with the raising of livestock, typically beef cattle. The crops provide most of the cash income, while the livestock has food available during the dry season and facilitates seed management. CLI improves soil fertility, raises yields and helps rehabilitate degraded areas while reducing the use of pesticides, mitigating the risk of erosion and the seasonality of production, and lowering ...
Pedestrian injuries from falls versus motor vehicle collisions: are we lacking critical policy and interventions?
2024-01-31
January 31, 2024—Using Emergency Medical Services (EMS) data, researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health compared the national burden of pedestrian injuries from motor vehicles to that of pedestrian falls occurring on streets and sidewalks and found that the probability of a pedestrian suffering a severe injury is higher for motor vehicle collisions as compared to falls. Yet, the public health burden of the number of pedestrians injured from a fall – severe or otherwise - is significantly higher compared to the number of pedestrians injured by a motor ...
Treatment of aggressive breast cancer: discovery of a new protein involved in the development of metastases
2024-01-31
A protein found abundantly in breast cancers that are refractory to conventional treatments is thought to cause the development of metastasis. Targeting it would prevent metastatic spread and therefore increase patients survival. These are the findings of a study conducted by a French-American team and led by a biologist at CNRS1. The study, the results of which appear on 31st January in Cell Discovery, aims to better understand the mechanisms at play in the development of primary tumours in aggressive ...
Worldwide prevalence and disability from mental disorders across childhood and adolescence
2024-01-31
About The Study: In this analysis using data from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease study, there was a high prevalence of mental disorders affecting children and youths, indicating that more than 1 of 10 (or 293 million) individuals ages 5 to 24 globally live with a diagnosable mental disorder. In terms of burden, around one-fifth of all disease-related disability (considering all causes) was attributable to mental disorders among this population. Additionally, this age period encompasses about one-fourth of the mental disorder burden across the entire life course.
Authors: Christian Kieling, M.D., Ph.D., of the Universidade ...
1 of 10 veterans diagnosed with dementia may instead have cognitive decline from cirrhosis
2024-01-31
RICHMOND, Va. (Jan. 31, 2024) – As many as 10% of older U.S. veterans diagnosed with dementia may suffer instead from reversible cognitive decline caused by advanced liver disease, according to an analysis from the Virginia Commonwealth University’s School of Medicine and the Richmond VA Medical Center.
It can be difficult for physicians to differentiate dementia from the cognitive decline caused by cirrhosis, called hepatic encephalopathy. If undetected, patients may not receive appropriate treatment that can reverse or halt the impairment. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
[Press-News.org] Researchers uncover potential non-opioid treatment for chronic painA new approach to treating neuropathic pain is making a key step forward thanks to researchers at The University of Texas at Austin