(Press-News.org) Single-cell projectome analysis has revealed previously unknown spatial organization principles of the brain-wide structure and connectivity of more than 10,000 individual hippocampal neurons in the mouse brain, according to a new study. Specialized projections called axons allow neurons to transmit signals to other neurons across the brain. The hippocampus (HIP) – one of the most extensively studied brain regions – plays a crucial role in many crucial brain functions, including learning, memory, and emotional behaviors. The core circuits within the HIP are connected with various other brain areas by axon projections. However, the spatial organization of intra- and extra-HIP axon projections remains largely unknown. Mapping the connectivity of neurons in the HIP is essential for understanding the region’s neural circuitry and underlying brain functions. Combining sparse-labeling methods with fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography (fMOST), Shou Qiu and colleagues systematically mapped 10,100 single-neuron axon projections and their arborization patterns throughout the entire mouse HIP, creating a comprehensive three-dimensional single-cell atlas of the region and its connections. Qiu et al.’s reconstruction revealed 43 projectome subtypes with distinct projection patterns based on axon or dendrite morphology and axon arborization at target areas. Spatial transcriptomic analysis of hippocampal sections also showed that the number of projection targets and axon-tip distribution for HIP neurons was correlated with the location of each cell’s soma along longitudinal and transverse axes. Qiu et al. created an open online database that enables interactive visualization and analysis of the study’s data.
END
Mapping the structure and organization of hippocampal neurons in the mouse brain
2024-02-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Large herbivores’ effects on ecosystems depend more on size and diet than on herbivore origin
2024-02-01
The effect of large herbivores on plant abundance and diversity depends more on their size and diet than whether they are native or introduced into their host ecosystems, according to a meta-analysis of more than 200 studies worldwide. The findings counter the widely held notion that the impacts of introduced megafauna are distinct and more harmful than those of native megafauna and suggest that trait-based ecology provides better insight into megaherbivore-plant interactions than concepts of species origin. Large mammal herbivores play a key role in shaping ecosystems and biodiversity by consuming vegetation, dispersing seeds and nutrients, and creating ...
The evolution of sign languages globally revealed through computational analyses
2024-02-01
A computational analysis has highlighted the poorly understood relationships and elusive histories of modern sign languages worldwide, revealing two major sign language families shaped by geopolitical forces and relevant signing communities. The findings show that the computational methods applied – which have been useful in understanding spoken languages – can be extended to the study of sign languages; as such, they offer promise for addressing the disparities in our understanding of other marginalized and diverse ...
AI system reveals new insights into early language acquisition through the experience of a single child
2024-02-01
A new machine learning model – trained on video and audio recorded from the first-person perspective of one young child for over a year – has provided new insights into early language acquisition. Not only do the findings offer a valuable framework to understand how children learn words and concepts, but they could be critical in developing artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can learn language in more human-like ways. Beginning around 6 to 9 months of age, children begin acquiring their ...
Targeting treatment resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
2024-02-01
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL FEB. 1, 2024, AT 2 P.M. ET) – New research from Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and collaborating organizations has identified a next-generation BTK degrader that could help overcome treatment resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and related blood cancers.
Their findings, published Feb. 2 in the journal Science, could offer a therapeutic option for CLL patients whose tumors become drug-resistant or are unresponsive to frontline treatment.
“This new compound not only inhibits the cellular molecule BTK, but goes further by taking aim at the target ...
Sustainable carbon removals limits identified, huge climate mitigation challenge revealed
2024-02-01
*Embargoed until 14:00 US Eastern / 19:00 UK GMT / 20:00 Europe CET – Thursday 1 February*
Governments and businesses are relying on dangerous amounts of future removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, instead of more rapidly reducing emissions and phasing out fossil fuels. This problem is partly due to an incomplete picture1 of the damaging consequences of carbon dioxide removal for people, food security and natural ecosystems, according to new research published in Science.
The paper finds that the carbon dioxide removal potential currently reported by the UN ...
Whole-brain projection patterns of single neurons in mouse hippocampus unveiled
2024-02-01
A study published in Science on Feb. 1 reported a comprehensive database of single-neuron projectomes consisting of over 10,000 mouse hippocampal neurons, thus revealing the spatial connectivity patterns of mouse hippocampal neurons at the mesoscopic level.
The study was conducted by teams from the Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology (CEBSIT), the Institute of Neuroscience of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), the HUST-Suzhou Institute for Brainsmatics, Hainan University, the Kunming Institute of Zoology of CAS, Lingang Laboratory, and the Shanghai Center for ...
New study suggests culling animals who ‘don’t belong’ can be a flawed nature conservation practice
2024-02-01
New research published today in the journal Science has concluded that eradicating animals on the basis that they are not native in order to protect plant species, can be a flawed practice costing millions of dollars, and resulting in the slaughter of millions of healthy wild animals.
Introduced large herbivores, or megafauna, are claimed to have distinct and harmful ecological impacts, including damaging sensitive plants and habitats, reducing native plant diversity, and facilitating introduced plants. However, up to now these impacts have been studied without comparison to a proper ...
IU surgeon-scientist studying physiological effect of microorganisms in sinuses of chronic rhinosinusitis patients
2024-02-01
INDIANAPOLIS—An Indiana University School of Medicine surgeon-scientist is leading a multi-institutional grant investigating the role of the sinus microbiome in chronic rhinosinusitis, an inflammatory disease that causes the lining of the sinuses to swell. The research team will study biospecimens from human sinus surgery patients in the lab and examine how bacteria in the microbiome shape the disease process and might offer novel therapeutic strategies.
Vijay Ramakrishnan, MD, professor of otolaryngology—head ...
Stand Up to Cancer announces changes to scientific advisory committee
2024-02-01
LOS ANGELES – February 1, 2024 – Stand Up To Cancer® (SU2C) today announced changes to its Scientific Advisory Committee (SAC), which oversees SU2C’s scientific research.
Composed of cancer research leaders from academic, government, industry, and advocacy fields, SU2C’s SAC sets direction for research initiatives, reviews proposals for new grant awards, and conducts rigorous oversight of all active grants in the SU2C research portfolio in collaboration with SU2C’s president and CEO Julian Adams, Ph.D.
World renowned cancer researcher and Nobel laureate Phillip A. Sharp, Ph.D., who has chaired the SAC since SU2C launched in ...
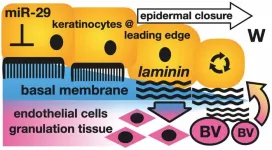
Small RNAs take on the big task of helping skin wounds heal better and faster with minimal scarring
2024-02-01
Philadelphia, February 1, 2024 – New findings in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, report that a class of small RNAs (microRNAs), microRNA-29, can restore normal skin structure rather than producing a wound closure by a connective tissue (scar). Any improvement of normal skin repair would benefit many patients affected by large-area or deep wounds prone to dysfunctional scarring.
Because the burden of non-healing wounds is so significant, it is sometimes called a “silent pandemic.” Worldwide, costs associated with wound care are expected to ...