(Press-News.org) Cell death is fundamental to life and, thus, healthy aging. In the realm of cellular biology, ferroptosis (a form of programmed cell death) has emerged not only as a focal point of research for its potential in eliminating cancer cells, but also its role in a plethora of other diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, eye diseases such as Retinitis pigmentosa and age-related macular degeneration, as well as ischemia, cardiovascular disease, liver disease, acute kidney injury and inflammation.
While studies of other forms of cell death such as apoptosis focus largely on the roles of proteins, a hallmark of ferroptosis is lipid oxidation and, hence, metabolomics — the study of all small molecules in cells — and lipidomics — the study of lipid metabolites and the proteins that create, modify and break them.
In a groundbreaking study, researchers have identified a dual role in the intricate dance of cell survival and death. The enzyme 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7) is unveiled as a pro-ferroptotic player, while its substrate, 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC), surprisingly demonstrates a pro-survival function in cancer cells. This knowledge provides key information for future cancer-fighting studies.
The study is an international collaboration between five countries. The senior author is Jose Pedro Friedmann Angeli of the Rudolf Virchow Center for Integrative and Translational Bioimaging at the University of Würzburg in Germany. ASU's contribution comes from Professor Judith Klein-Seetharaman, who has a dual appointment in ASU’s School of Molecular Sciences and the College of Health Solutions. Klein-Seetharaman is also a faculty member of the Biodesign Institute’s Center for Applied Structural Discovery.
Klein-Seetharaman’s research uniquely combines protein structural biology with metabolomics. Her expertise in biology and chemistry serves her interdisciplinary research in machine learning-driven multi-omics and the integration of computational and experimental approaches in systems and structural biology of proteins. Klein-Seetharaman’s former postdoc Lokender Kumar, currently a professor at Shoolini University in Solan Himachal Pradesh, India, also contributed to the research.
Klein-Seetharaman became involved in this international collaboration through the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP), which promotes international collaboration in basic research through their grant entitled “Oxidized lipidome: the unspoken language of non-apoptotic cell death." Klein-Seetharaman, together with Raj Reddy at Carnegie Mellon University, had pioneered more than 20 years ago an analogy between biology and language that focused on the study of proteins in an NSF-funded large-scale center on biological language modeling (NSF awards 0225656 and 0225636). Today, large language models (LLMs) have become a mainstay of prediction of protein structure, interactions and functions trained on large protein sequence datasets.
The work on DHCR7’s role in the lipidome language and ferroptosis in cancer has just been published today in the journal Nature.
The research
7-DHC is the precursor to the production of cholesterol in our bodies. The production of low-density lipoproteins, or LDLs (so-called bad cholesterol), versus high-density lipoproteins, or HDLs (good cholesterol), is totally dependent on which protein attaches to the cholesterol in our blood.
Klein-Seetharaman’s principal contribution involves prediction of the functional consequences of mutations in DHCR7 that are associated with a very rare type of cancer. Klein-Seetharaman needed to structurally model the DHCR7 protein because there was no known crystal structure available.
“We used computational tools to predict DHCR7’s structure and orientation in the membrane,” explained Klein-Seetharaman. “It was very obvious from a membrane protein perspective which mutations would likely cause misfolding of the protein and which ones wouldn't. We made the prediction that two out of four known amino acids would cause misfolding.” The paper shows successful experimental validation of Klein-Seetharaman’s predictions — which is a modeler’s dream come true.
Klein-Seetharaman has worked a lot with membrane proteins since her doctoral work with the late Nobel laureate H. Gobind Khorana on the G protein-coupled receptor, rhodopsin. Mutations in rhodopsin associated with Retinitis pigmentosa cause misfolding. Klein-Seetharaman has since developed a conceptual model for folding of membrane proteins that has been able to anticipate disease-causing mutations, even before they have been found in Retinitis pigmentosa patients. This strongly supports the utility of computational structural biology in understanding disease mechanisms.
Klein-Seetharaman began using computational language techniques in 2000, when the human genome was published and hailed as “the book of life.” She explains the approach by giving the example of “New York.” In human language technologies, the co-occurrence of words is exploited in so-called n-gram models. For example, in “New York,” there is a higher chance of finding the word “York” after “New.” “New York” is an n-gram with n=2, because you have two words and you can predict the second word after seeing the first.
In studies of lipid oxidation in ferroptosis, Klein-Seetharaman and her team created N-Gram models for cardiolipin, which has three fatty acid tails. So, for every cardiolipin, you can have a combination of three tails — a n-gram with n=3. The team created N-gram models for the lipid species to see what kind of combinations of oxidized lipids are observed, and then they found those associated with cancer development. Furthermore, they have created the first in silico model of a lipid droplet and were able to observe the effects of lipid peroxidation and subsequent fragmentation on lipid droplet structure and dynamics through molecular dynamics simulations.
These are the kinds of cellular effects that are prevented when DHCR7 is inhibited; its substrate 7-DHC accumulates and shields lipids from oxidation and fragmentation. The point mutations in DHCR7 that cause misfolding of the enzyme would lead to accumulation of 7-DHC, preventing lipid peroxidation and thus suppressing ferroptosis. That’s why the mutations are associated with cancer because the loss of this enzyme gives cancer cells the ability to escape programmed cell death. Klein was the only computational biologist on the team. Her expertise was important in the study of DHCR7 structure and its folding, as well as lipid metabolite binding to this protein.
Klein-Seetharaman has devoted much of her career to the mapping of protein sequence to structure space. With the incredible amount of genome sequence data out there, as well as efforts made with structural proteomics accumulating experimental protein structures, she believes that the next frontier is to use the experimental and predicted structures to map the structure space of all proteins in an organism, like the 20,000 genes encoding proteins in a human, as well as interactions with other biomolecules, which is at the heart of biological function.
“What's interesting are the metabolites like the lipids that we are talking about in this study. We want to know what these metabolites do, which targets and where on their structures they bind, and how they manipulate the cell,” explained Klein-Seetharaman. “The metabolite identities and concentrations are what makes organisms most resilient to environmental change, because ligand binding and enzymatic reactions are the fastest way an organism can respond to its environment.”
Contrary to earlier notions associating elevated 7-DHC levels with cytotoxicity in developing neurons, this research establishes 7-DHC accumulation as a robust pro-survival mechanism in cancer cells, making cancer cells resilient to death by ferroptosis. The key lies in 7-DHC's remarkable reactivity against peroxyl radicals, effectively shielding phospholipids from autoxidation and fragmentation. Understanding this process altering metabolite concentrations will allow us to address it and make patients resilient to cancer.
The study further validates these findings in neuroblastoma and Burkitt lymphoma, shedding light on 7-DHC's potential to induce a death-resistant state in tumors, ultimately contributing to a more aggressive cancer phenotype. This discovery unveils a previously unrecognized anti-ferroptotic activity of 7-DHC, presenting a cell-intrinsic mechanism that cancer cells might exploit to evade death.
END
Cheating death: How cancer cells escape
Key enzyme that stops cancer cell death paves way for future treatments
2024-02-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
JMIR Medical Informatics invites submissions on AI language models in health care
2024-02-01
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce a new section titled, “AI Language Models in Health Care” in JMIR Medical Informatics. This leading peer-reviewed journal is indexed in PubMed and has a unique focus on clinical informatics and the digitization of care processes. This section will have a broad focus and encompass topics about the successful implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) language models in diverse health care settings. The topics will include details about the process, use, outcomes, and ...
Human cells building ‘molecular highways’ captured for first time
2024-02-01
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona and the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) in Madrid have captured the world’s first high-resolution images of the earliest moments of microtubule formation inside human cells. The findings, published today in the journal Science, lay the foundations for potential breakthroughs in treating many different types of diseases ranging from cancer to neurodevelopmental disorders.
“Microtubules are critical components of cells, but all the images we see in textbooks describing the first moments of their creation are models or cartoons based ...
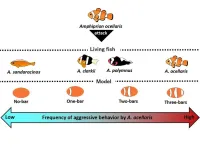
Clown anemonefish seem to be counting bars and laying down the law
2024-02-01
We often think of fish as carefree swimmers in the ocean, reacting to the world around them without much forethought. However, new research from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) suggests that our marine cousins may be more cognizant than we credit them for.
By observing how a colony of clown anemonefish (Amphiprion ocellaris) – the species of the titular character in Finding Nemo – reacts to intruders in their sea anemone home, OIST researchers have found that ...
New research shows that the arrangement of bacteria in biofilms affects their sensitivity to antibiotics
2024-02-01
Bacteria are traditionally imagined as single-cell organisms, spread out sparsely over surfaces or suspended in liquids, but in many environments the true bacterial mode of growth is in sticky clusters called biofilms. Biofilm formation can be useful to humans—it is integral, for example, to the production of kombucha tea. But it is more often problematic, because it makes it more difficult to control bacterial growth: When bacterial cells produce a biofilm, it acts as a shield against outside invaders, making the bacteria more ...
First atomic-scale 'movie' of microtubules under construction, a key process for cell division
2024-02-01
· Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) , the Spanish National Cancer Research Center (CNIO) and the IBMB-CSIC solve a key problem in biology: how human cells build their microtubules
· During cell division, microtubules function as nanometer-thick long ‘ropes' inside cells that pull chromosomes apart so that each daughter cell receives a copy of the genetic material
· The work published in Science lays the groundwork for future breakthroughs in the treatment of diseases ranging from cancer to neurodevelopmental disorders
Cells in the human body are constantly dividing. With each division the genetic information contained in the ...
Mapping the structure and organization of hippocampal neurons in the mouse brain
2024-02-01
Single-cell projectome analysis has revealed previously unknown spatial organization principles of the brain-wide structure and connectivity of more than 10,000 individual hippocampal neurons in the mouse brain, according to a new study. Specialized projections called axons allow neurons to transmit signals to other neurons across the brain. The hippocampus (HIP) – one of the most extensively studied brain regions – plays a crucial role in many crucial brain functions, including learning, memory, ...
Large herbivores’ effects on ecosystems depend more on size and diet than on herbivore origin
2024-02-01
The effect of large herbivores on plant abundance and diversity depends more on their size and diet than whether they are native or introduced into their host ecosystems, according to a meta-analysis of more than 200 studies worldwide. The findings counter the widely held notion that the impacts of introduced megafauna are distinct and more harmful than those of native megafauna and suggest that trait-based ecology provides better insight into megaherbivore-plant interactions than concepts of species origin. Large mammal herbivores play a key role in shaping ecosystems and biodiversity by consuming vegetation, dispersing seeds and nutrients, and creating ...
The evolution of sign languages globally revealed through computational analyses
2024-02-01
A computational analysis has highlighted the poorly understood relationships and elusive histories of modern sign languages worldwide, revealing two major sign language families shaped by geopolitical forces and relevant signing communities. The findings show that the computational methods applied – which have been useful in understanding spoken languages – can be extended to the study of sign languages; as such, they offer promise for addressing the disparities in our understanding of other marginalized and diverse ...
AI system reveals new insights into early language acquisition through the experience of a single child
2024-02-01
A new machine learning model – trained on video and audio recorded from the first-person perspective of one young child for over a year – has provided new insights into early language acquisition. Not only do the findings offer a valuable framework to understand how children learn words and concepts, but they could be critical in developing artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can learn language in more human-like ways. Beginning around 6 to 9 months of age, children begin acquiring their ...
Targeting treatment resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
2024-02-01
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL FEB. 1, 2024, AT 2 P.M. ET) – New research from Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and collaborating organizations has identified a next-generation BTK degrader that could help overcome treatment resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and related blood cancers.
Their findings, published Feb. 2 in the journal Science, could offer a therapeutic option for CLL patients whose tumors become drug-resistant or are unresponsive to frontline treatment.
“This new compound not only inhibits the cellular molecule BTK, but goes further by taking aim at the target ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
New discovery of younger Ediacaran biota
Lymphovenous bypass: Potential surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
When safety starts with a text message
CSIC develops an antibody that protects immune system cells in vitro from a dangerous hospital-acquired bacterium
New study challenges assumptions behind Africa’s Green Revolution efforts and calls for farmer-centered development models
Immune cells link lactation to long-lasting health
Evolution: Ancient mosquitoes developed a taste for early hominins
Pickleball players’ reported use of protective eyewear
Changes in organ donation after circulatory death in the US
Fertility preservation in people with cancer
A universal 'instruction manual' helps immune cells protect our organs
Fifteen-year results from SWOG S0016 trial suggest follicular lymphoma is curable
The breasts of a breastfeeding mother may protect a newborn from the cold – researchers offer a new perspective on breast evolution
More organ donations now come from people who die after their heart stops beating
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
[Press-News.org] Cheating death: How cancer cells escapeKey enzyme that stops cancer cell death paves way for future treatments