(Press-News.org) The gross price of insulin in the U.S. is more than nine times higher than in 33 high-income comparison nations, according to a new RAND report.
Although the cost differences of insulin between the U.S. and other nations varied depending on the comparison country and the type of insulin, U.S. prices were always higher -- often five to 10 times higher -- than those in other countries. The new report updates findings from earlier RAND work about U.S. insulin prices.
After accounting for rebates and other discounts often offered by drug manufacturers, the price of a unit of insulin remained 2.3 times higher in the U.S. than in comparison nations, according to the study.
“Insulin prices in the U.S. have been increasing for many years and are substantially higher than in other middle and high-income nations,” said Andrew Mulcahy, the study’s lead author and a senior health economist at RAND, a nonprofit research organization.
Insulin is a drug most commonly used to control blood sugar levels in people who have insulin-dependent diabetes. The drug is sold in many different forms, with different chemical properties and different duration of effects.
Insulin list prices in the United States have increased dramatically since the early 2010s. For example, one federal analysis found that the average U.S. wholesale-acquisition price for rapid-acting, long-acting, and short-acting insulin increased by 15% to 17% per year from 2012 to 2016.
Medicare enrollees’ financial exposure to out-of-pocket spending for insulin is changing dramatically. Under the Inflation Reduction Act, insulin cost-sharing will be capped at $35 per month beginning in 2024. Congress also is considering proposals to extend the cap to individuals with employer or individual market coverage.
RAND researchers compiled their estimates of international insulin prices by examining industry standard IQVIA MIDAS data on insulin sales and volume for 2017 through 2022, comparing the U.S. to 33 nations that belong to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
The analysis presents separate comparisons using manufacturer gross prices, which may be more relevant to U.S. patients without drug coverage or otherwise paying out of pocket for insulin, and estimated manufacturer net prices after applying rebates paid by manufacturers.
The report presents volume and sales by type of insulin separately for the United States and 33 comparison OECD countries.
Researchers found that U.S. manufacturer gross prices per 100 international units of insulin were on average 9.71 times those in OECD comparison countries combined. After estimating gross-to-net discounts for insulins, U.S. net prices remained 2.33 times of those in comparison countries combined.
U.S. manufacturer gross prices ranged from 4.57 times those in Mexico to 37.99 times those in Turkey. Comparisons of U.S. insulin prices to prices in other countries were fairly constant from 2017 through 2022.
The study was sponsored by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The report, “Comparing Insulin Prices in the United States to Other Countries: Results from a Price Index Analysis,” is available on the website of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and on www.rand.org.
Other authors of the report are Daniel Schwam and Nate Edenfield.
RAND Health Care promotes healthier societies by improving health care systems in the United States and other countries.
END
Insulin prices in US are nine times higher than in other wealthy nations, study finds
Depending on type of insulin, some U.S. prices can be even higher
2024-02-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Diabetes and liver cancer — Stanford Medicine study suggests new screening guidelines
2024-02-01
For centuries, doctors have used their hands as essential diagnostic tools — exploring joints and palpating abdomens to assess a patient’s health. Often a cancer will reveal itself as a lump or unusual stiffness in a normally bouncy tissue or organ.
More recently, the relationship between stiffness and cancer has been documented through biophysical studies and clinical trials, particularly in liver and breast cancer. For example, stiffness is a primary hallmark of liver cirrhosis, which can progress to liver cancer.
Now researchers ...
Researchers take new ‘mixed reality’ headsets for a spin
2024-02-01
Among the buzziest consumer technologies right now are “mixed reality” or “spatial computing” headsets that convincingly blend views of the real world with digital content.
A key enabling technology behind these gizmos is passthrough video, which involves blocking out all light so users must rely on cameras on the headsets to see the external world around them via real-time video playing on tiny screens. The arrangement allows users to physically interact with their environments and go about daily activities but with added digital content displayed, ranging from familiar device apps to innovative gaming scenarios. ...
How leafcutter ants cultivate a fungal garden to degrade plants and provide insights into future biofuels
2024-02-01
By Maegan Murray
Scientists have spent decades finding ways to efficiently and affordably degrade plant materials so that they can be converted into useful bioproducts that benefit everyday life.
Bio-based fuels, detergents, nutritional supplements, and even plastics are the result of this work. And while scientists have found ways to degrade plants to the extent needed to produce a range of products, certain polymers such as lignin, which is a primary ingredient in the cell wall of plants, remain incredibly difficult to affordably break down without adding pollutants back into the environment. These polymers can be left behind as waste products with ...
UC Davis establishes bird flight research center
2024-02-01
Researching how bird flight can inform aircraft design is the goal of a new center to be established at the University of California, Davis.
Christina Harvey, an assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at UC Davis, and Michelle Hawkins, a professor in the School of Veterinary Medicine and director of the California Raptor Center, are launching the bird flight research center with a nearly $3 million grant from the Department of Defense. The new center will utilize motion capture and photogrammetry ...
ADA releases updated recommendations to enhance radiography safety in dentistry
2024-02-01
CHICAGO, Feb. 1, 2024 – The use of lead abdominal aprons or thyroid collars on patients when conducting dental X-rays is no longer recommended, according to an expert panel established by the American Dental Association (ADA) Council on Scientific Affairs. Additionally, dentists should take into consideration the diagnostic information needed from X-rays to benefit patient care or substantially improve clinical outcomes.
The Journal of the American Dental Association published the new recommendations today, which aim to improve radiation ...
Cheating death: How cancer cells escape
2024-02-01
Cell death is fundamental to life and, thus, healthy aging. In the realm of cellular biology, ferroptosis (a form of programmed cell death) has emerged not only as a focal point of research for its potential in eliminating cancer cells, but also its role in a plethora of other diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, eye diseases such as Retinitis pigmentosa and age-related macular degeneration, as well as ischemia, cardiovascular disease, liver disease, acute kidney injury and inflammation.
While studies of other forms of cell death such as apoptosis focus largely on ...
JMIR Medical Informatics invites submissions on AI language models in health care
2024-02-01
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce a new section titled, “AI Language Models in Health Care” in JMIR Medical Informatics. This leading peer-reviewed journal is indexed in PubMed and has a unique focus on clinical informatics and the digitization of care processes. This section will have a broad focus and encompass topics about the successful implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) language models in diverse health care settings. The topics will include details about the process, use, outcomes, and ...
Human cells building ‘molecular highways’ captured for first time
2024-02-01
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona and the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) in Madrid have captured the world’s first high-resolution images of the earliest moments of microtubule formation inside human cells. The findings, published today in the journal Science, lay the foundations for potential breakthroughs in treating many different types of diseases ranging from cancer to neurodevelopmental disorders.
“Microtubules are critical components of cells, but all the images we see in textbooks describing the first moments of their creation are models or cartoons based ...
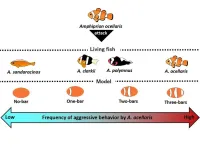
Clown anemonefish seem to be counting bars and laying down the law
2024-02-01
We often think of fish as carefree swimmers in the ocean, reacting to the world around them without much forethought. However, new research from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) suggests that our marine cousins may be more cognizant than we credit them for.
By observing how a colony of clown anemonefish (Amphiprion ocellaris) – the species of the titular character in Finding Nemo – reacts to intruders in their sea anemone home, OIST researchers have found that ...
New research shows that the arrangement of bacteria in biofilms affects their sensitivity to antibiotics
2024-02-01
Bacteria are traditionally imagined as single-cell organisms, spread out sparsely over surfaces or suspended in liquids, but in many environments the true bacterial mode of growth is in sticky clusters called biofilms. Biofilm formation can be useful to humans—it is integral, for example, to the production of kombucha tea. But it is more often problematic, because it makes it more difficult to control bacterial growth: When bacterial cells produce a biofilm, it acts as a shield against outside invaders, making the bacteria more ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] Insulin prices in US are nine times higher than in other wealthy nations, study findsDepending on type of insulin, some U.S. prices can be even higher