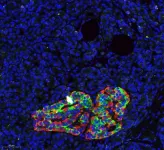
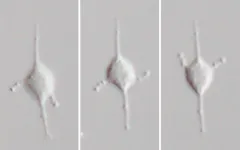
(Press-News.org) Italian scientists from Università Cattolica at Rome discovered an important genetic mechanism that pancreatic cancer cells employ to evade therapies, paving the way to new drugs for a killer disease. The tumor evades treatments by implementing a 'favorable genetic reshuffling,' strategically playing its best cards to thwart cures. This finding is the result of a study published today in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, coordinated by Claudio Sette, Professor of Human Anatomy at the Catholic University, and Director of the "Organoids Facility" at the Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS.
"We have discovered a mechanism based on the regulation of messenger RNAs that contributes to chemotherapy resistance," Sette explains. "There are already RNA-targeting drugs, used with other medical indications, to counteract this type of regulation. These drugs could potentially be developed as anti-tumor agents for resistant patients."
Background
Pancreatic cancer affects approximately 500,000 people worldwide each year. Despite being the 14th most common cancer by incidence, today it is unfortunately the seventh leading cause of cancer-related death. The 5-year survival rate is less than 10%, mostly limited to patients who are eligible for surgery (around 20-30% of the total).
When the genetic code is transcribed into RNA for protein synthesis, "alternative splicing" can occur. This means that different transcripts can be produced from the same gene, depending on the selected genetic 'cards' (exons, the gene's coding part for amino acids in proteins) to be 'played.' Splicing leads to the production of diverse proteins with different roles through the alternative assortment of exons of the original gene. Splicing is generally altered in tumors, including pancreatic cancer.
"Comparing pancreatic tumors of different subtypes," Professor Sette explains, "we observed that the therapy-resistant cancer is associated with a specific splicing regulation, leading to the synthesis of proteins associated with resistance to chemotherapies. Our study, funded by the Italian Association for Cancer Research, has also identified a splicing regulator called 'Quaking' that is expressed in more aggressive pancreatic tumors and promotes the synthesis of proteins conferring chemoresistance."
There are already existing splicing-regulating drugs that could be potentially employed for this type of cancer; including therapies for individual splicing events, such as the drug nusinersen that is currently used in spinal muscular atrophy.
"Our discovery opens up new treatment possibilities for a type of tumor that generally does not respond to existing therapies," the professor concludes.
END
Pancreatic Cancer: Italian scientists found out how the tumor escapes therapies
Results from a study published in the journal "Cell Reports Medicine," from the Catholic University, Rome campus, and Policlinico A. Gemelli IRCCS, reveal a mechanism of resistance. This discovery could pave the way for the development of new drugs target
2024-02-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gun violence exposure and suicide among black adults
2024-02-06
About The Study: Gun violence exposure among Black adults in the U.S. was significantly associated with lifetime suicidal ideation and behavior in this study that included 3,015 Black adults. Public health efforts to substantially reduce interpersonal gun violence may yield additional benefits by decreasing suicide among Black individuals in the U.S.
Authors: Daniel C. Semenza, Ph.D., of Rutgers University in Camden, New Jersey, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.54953)
Editor’s ...
Cancer risk following smoking cessation
2024-02-06
About The Study: Sustained smoking cessation was associated with a significantly reduced risk of cancer after 10 years since quitting in this study of 2.9 million Korean adults. Quitting at any age helped reduce the cancer risk, and especially for lung cancer, early cessation before middle age exhibited a substantial risk reduction.
Authors: Jin-Kyoung Oh, Ph.D., of the National Cancer Center Graduate School of Cancer Science and Policy in Goyang, Republic of Korea, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
Understanding the moon’s history with Chang’e-5 sample
2024-02-06
WASHINGTON, Feb. 6, 2024 – Earth’s moon achieved its Swiss cheese appearance from celestial objects crashing into its surface, forming impact craters. But craters weren’t all that was left behind; the intense pressure and temperature of such a collision also impacts the rocks and dust covering the lunar surface, known as regolith, altering its mineral composition and structure. Analyzing the resulting minerals provides modern researchers clues to the moon’s past.
China’s Chang’e-5, the first lunar sample ...
Inner ear of miocene fossil ape gives clues to evolution of bipedalism
2024-02-06
A new study of a 7–8-million-year-old extinct fossil ape from China called Lufengpithecus offers new insights into the evolution of human bipedalism.
The study, published in The Innovation, was conducted by a team from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Yunnan Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology (YICRA), and New York University (NYU).
Humans and our closest relatives, the living apes, display a remarkable diversity of locomotor abilities, from walking upright on two legs to climbing and clambering in trees to walking using all four limbs. Scientists have long been fascinated ...
GPT-3 transforms chemical research
2024-02-06
Artificial intelligence is growing into a pivotal tool in chemical research, offering novel methods to tackle complex challenges that traditional approaches struggle with. One subtype of artificial intelligence that has seen increasing use in chemistry is machine learning, which uses algorithms and statistical models to make decisions based on data and perform tasks that it has not been explicitly programmed for.
However, to make reliable predictions, machine learning also demands large amounts of data, which isn’t always available in chemical research. Small chemical datasets simply do not provide enough information for these algorithms to train on, which limits their effectiveness.
In ...
Guanine synthesis yields new insights into nitrogen’s role in nanocarbon catalysis
2024-02-06
In recent years, carbon-based catalysts — especially nitrogen-doped nanocarbons — have emerged as sustainable, reliable alternatives to the metal catalysts that have traditionally been used to support chemical reactions. Researchers from the Key Laboratory of Advanced Carbon-Based Functional Materials (Fujian Province University) at Fuzhou University synthesized nanocarbons from guanine molecules to better understand the precise role nitrogen plays in the carbon-based materials and explore the reaction mechanisms of these catalytic systems.
In a recently published study, the research team clarified how different types of nitrogen can modulate oxidative dehydrogenation ...
Baseline findings among hospitalized mucormycosis patients —— A multicentric ambispective cohort study in India
2024-02-06
Mucormycosis is a relatively rare but serious fungal infection increasingly recognised for its poor prognosis and high mortality. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the incidence of mucormycosis reached high levels during 2021–2022 in India.
This study led by Dr. Rizwan Suliankatchi Abdulkader (Indian Council of Medical Research) established a multicentric ambispective cohort of patients hospitalised with mucormycosis across India and reported their baseline profile, clinical characteristics, and outcomes at discharge.
Mucormycosis was diagnosed based on mycological confirmation on direct microscopy (KOH/Calcofluor white stain), ...
New DNA methylation-based method for precise assessment of pancreas cell composition
2024-02-06
Research introduces new DNA methylation-based method for accurately assessing cell composition in the human pancreas, addressing a critical gap in diabetes research. By overcoming limitations of traditional protein marker-based approaches, the study provides a more precise means to identify specific cell types. The findings offer insights into beta-cell dysfunction across diabetes types and have direct clinical implications, enhancing our understanding of diabetes development and potentially guiding more tailored treatment ...
Remarkable cellular architecture and phylogenetic position of the mysterious arm-swinging protist meteora sporadica
2024-02-06
Tsukuba, Japan—Meteora sporadica is a small, unicellular eukaryote (protist) that was discovered in deep Mediterranean sea sediments in 2002. It differs from known protists by the presence of two lateral arms that swing back and forth. However, the ultrastructure and phylogenetic position of M. sporadica remain unknown.
In this study, researchers successfully cultured and analyzed two strains of M. sporadica from marine sediments in detail. Ultratructural observations revealed ...
Mechanism of plants obtain nitrogen by supplying iron to symbiotic bacteria
2024-02-06
Tsukuba, Japan—Leguminous plants have a mechanism (rhizobial symbiosis) to efficiently acquire nitrogen, which is an essential macronutrient for growth, through the nitrogen-fixing bacteria rhizobia. Root nodules are organs on plant roots that facilitate the symbiotic relationship. Rhizobia coloniza these nodules and fix nitrogen by converting nitrogen from air into ammonia. Iron is needed for the enzymes that catalyze nitrogen fixation; however, where and how iron is transported to the nodule and used for nitrogen fixation is largely unknown.
In this study, using the legume model plant Lotus japonicus, a transcriptome ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Pancreatic Cancer: Italian scientists found out how the tumor escapes therapiesResults from a study published in the journal "Cell Reports Medicine," from the Catholic University, Rome campus, and Policlinico A. Gemelli IRCCS, reveal a mechanism of resistance. This discovery could pave the way for the development of new drugs target