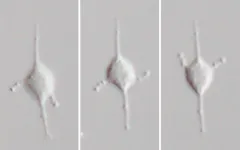
(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan—Meteora sporadica is a small, unicellular eukaryote (protist) that was discovered in deep Mediterranean sea sediments in 2002. It differs from known protists by the presence of two lateral arms that swing back and forth. However, the ultrastructure and phylogenetic position of M. sporadica remain unknown.
In this study, researchers successfully cultured and analyzed two strains of M. sporadica from marine sediments in detail. Ultratructural observations revealed that M. sporadica has a complex cytoskeleton, with lateral arms that are supported by microtubules extending from multiple microtubule-organizing centers (MTOCs) located in the center of the cell. A large-scale molecular phylogenetic analysis using amino acid sequences of 254 genes revealed that M. sporadica is not associated with any of the major eukaryotic lineages (supergroups) identified to date, but is closely related to Hemimastigophora, a group of protists considered to be one of the most deep-branching eukaryotes.
Interestingly, Hemimastigophora is composed of large protists with numerous flagella and no arms or MTOCs. This study demonstrates that Meteora and Hemimastigophora represent a morphological diversity that is comparable to other supergroups. Identifying and analyzing poorly-studied protists, such as M. sporadica, is essential for elucidating the phylogeny and diversity of eukaryotes.
###
This study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Numbers: 13J00587, 18J02091, by NSERC discovery grant 298366-2019 (to AGBS), and NSERC Discovery grant RGPIN-2022-05430 (to AJR).
Original Paper
Title of original paper:
Meteora sporadica, a protist with incredible cell architecture, is related to Hemimastigophora
Journal:
Current Biology
DOI:
10.1016/j.cub.2023.12.032
Correspondence
Assistant Professor SHIRATORI, Takashi
Institute of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Tsukuba
Related Link
Institute of Life and Environmental Sciences
END
Remarkable cellular architecture and phylogenetic position of the mysterious arm-swinging protist meteora sporadica
2024-02-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mechanism of plants obtain nitrogen by supplying iron to symbiotic bacteria
2024-02-06
Tsukuba, Japan—Leguminous plants have a mechanism (rhizobial symbiosis) to efficiently acquire nitrogen, which is an essential macronutrient for growth, through the nitrogen-fixing bacteria rhizobia. Root nodules are organs on plant roots that facilitate the symbiotic relationship. Rhizobia coloniza these nodules and fix nitrogen by converting nitrogen from air into ammonia. Iron is needed for the enzymes that catalyze nitrogen fixation; however, where and how iron is transported to the nodule and used for nitrogen fixation is largely unknown.
In this study, using the legume model plant Lotus japonicus, a transcriptome ...
11 leading stroke scientists to receive American Stroke Association honors
2024-02-06
PHOENIX, Feb. 6, 2024 – Eleven scientists leading the way in stroke research will be recognized during the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2024 for their exceptional professional achievements. The meeting will be held in Phoenix, Feb. 7-9, and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
The illustrious group of awardees includes four groundbreaking scientists who have devoted their careers to stroke research and six scientists will be recognized for their notable new research. The awards include the Ralph L. Sacco Outstanding Stroke Research ...
Powerful answers to energy questions may be blowing in the wind
2024-02-06
While wind farms have become a widely popular method of generating energy, researchers are now looking at the impact of these large farms on wind patterns and the surrounding environment.
Using large-scale simulations to better understand the way air moves across and within wind farms, researchers from UBC Okanagan and Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) in the Netherlands have developed a modelling framework that will help improve wind energy forecasts and productivity.
The researchers also hope to learn how large wind farms can alter natural wind patterns.
“Wind farms are getting so large that ...
Discover BMB announces exciting lineup of speakers
2024-02-06
Be front and center for the hottest research findings in the molecular life sciences at Discover BMB, the annual meeting of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, to be held March 23–26 in San Antonio.
Don’t miss this opportunity to hear from the top minds in the field. Reporters are invited to register for a complimentary press pass to attend #DiscoverBMB in San Antonio or access press materials electronically. Please note that only a limited number of complementary on-site press passes will be issued, so advance registration is recommended. Find more information in the #DiscoverBMB newsroom.
As part of an exciting program spotlighting the ...
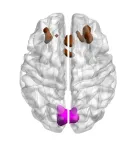
Study finds strongest evidence to date of brain’s ability to compensate for age-related cognitive decline
2024-02-06
Scientists have found the strongest evidence yet that our brains can compensate for age-related deterioration by recruiting other areas to help with brain function and maintain cognitive performance.
As we age, our brain gradually atrophies, losing nerve cells and connections and this can lead to a decline in brain function. It’s not fully understood why some people appear to maintain better brain function than others, and how we can protect ourselves from cognitive decline.
A widely accepted notion is that some people’s brains are able to compensate ...
How T cells combat tuberculosis
2024-02-06
LA JOLLA, CA—La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) is working to guide the development of new tuberculosis vaccines and drug therapies.
Now a team of LJI scientists has uncovered important clues to how human T cells combat Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes TB. Their findings were published recently in Nature Communications.
"This research gives us a better understanding of T cell responses to different stages in tuberculosis infection and helps us figure out is there are additional diagnostic ...
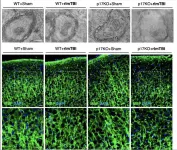
Drug could protect brains from damage after concussions
2024-02-06
Repeat concussions, also referred to as repetitive mild traumatic brain injury, can lead to chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) and raise the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. However, some people who experience repetitive mild traumatic brain injury never develop major disease. Onder Albayram and colleagues investigated the role of a protein known as p17 in protecting brains from long-term pathologies. In stressed neurons, p17 initiates production of C18-Ceramide, a bioactive sphingolipid that acts as a label of damaged mitochondria in neuronal axons. Labelled mitochondria are then detected and removed by autophagosomes. The authors knocked out p17 in mice. Some p17-knockout ...
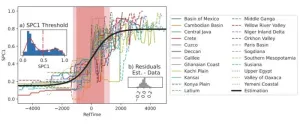
Is there a typical rate of cultural evolution?
2024-02-06
Are cultural evolution rates similar across human societies? The emerging field of Cliodynamics uses mathematical models to study history. Tobias Wand and colleagues used a data-driven approach to estimate the rates of cultural evolution in 23 geographic areas, using data from Seshat: Global History Databank, which records nine “complexity characteristics” for 370 polities over 10,000 years, ending in the nineteenth century. The complexity characteristics are polity population; extent of polity territory; the size of the largest urban center; hierarchical complexity; the ...
Last chance to get hotel discounts for the world’s largest physics meeting
2024-02-06
Next month, scientists from around the world will convene to share new results from across the physical sciences in nearly 11,000 individual presentations. The American Physical Society’s (APS) March Meeting will be held in person in Minneapolis and online everywhere March 3-8.
Discounted hotel rates are available for in-person attendees at select Minneapolis hotels near the Minneapolis Convention Center. Book your hotel by Feb. 9 to receive the discount.
Press Registration
News media with valid APS press credentials may register for the meeting at no cost. To request press credentials, visit APS’s online newsroom. Registration ...
Newly discovered carbon monoxide-runaway gap can help identify habitable exoplanets
2024-02-06
The search for habitable exoplanets involves looking for planets with similar conditions to the Earth, such as liquid water, a suitable temperature range and atmospheric conditions. One crucial factor is the planet's position in the habitable zone, the region around a star where liquid water could potentially exist on the planet's surface. NASA's Kepler telescope, launched in 2009, revealed that 20–50% of visible stars may host such habitable Earth-sized rocky planets. However, the presence of liquid water alone does not guarantee a planet’s habitability. On Earth, ...