Jun Wu receives the 2024 ISSCR Outstanding Young Investigator Award for his innovative work on stem cell-based embryo and chimera models
2024-02-06
(Press-News.org) Evanston, IL—The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) is honoring Jun Wu, Ph.D. with the 2024 ISSCR Outstanding Young Investigator Award. Dr. Wu is an associate professor in the Department of Molecular Biology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, U.S.A. and a New York Stem Cell Foundation–Robertson Investigator.
The award recognizes the exceptional achievements of an investigator in the early part of his or her independent career in stem cell research. Dr. Wu will present his work during Plenary II, New Technologies to Engineer and Phenotype Stem Cell Systems, on 10 July during the ISSCR 2024 Annual Meeting taking place in Hamburg, Germany. ISSCR 2024 is the world’s leading gathering of the brightest minds in stem cell research and regenerative medicine.
“Dr. Wu is one of the most insightful and innovative independent stem cell scientists today,” ISSCR President Amander Clark, Ph.D. said. “I have no doubt that Jun will continue to make great contributions to the stem cell field long into the future. Congratulations on all of your work and success.”
“I am deeply honored and grateful to receive this prestigious award from the ISSCR,” said Dr. Wu. "This recognition is a testament to the dedication and hard work of my entire team. I owe a great deal to the exceptional collaborative research environment at UT Southwestern and unwavering support from the Department of Molecular Biology.”
Jun Wu is recognized for his innovative work on creating novel embryonic and extraembryonic stem cells, exploring the mechanisms that limit interspecies chimera formation with human pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), and developing human PSC-based embryo models. Dr. Wu has broadened the understanding of pluripotency by deriving and studying several new types of PSCs with distinct molecular and phenotypic features from different species. His work also includes the generation of PSC-derived interspecies chimeras and the development of an effective and versatile interspecies blastocyst complementation system for the generation of organs and tissues from one species inside another species. Most recently, Dr. Wu's group has developed strategies to generate stem cell-based embryo models from several species, including humans, for studying peri-implantation and peri-gastrulation development in vitro.
ISSCR 2024, co-sponsored by the City of Hamburg, Life Science Nord, Bayer, and BlueRock Therapeutics, will take place 10-13 July 2024 in Hamburg, Germany.
About the International Society for Stem Cell Research (www.isscr.org)
With nearly 5,000 members from 80 countries, the International Society for Stem Cell Research is the preeminent global, cross-disciplinary, science-based organization dedicated to stem cell research and its translation to the clinic. The ISSCR mission is to promote excellence in stem cell science and applications to human health. Additional information about stem cell science is available at AboutStemCells.org, an initiative of the Society to inform the public about stem cell research and its potential to improve human health.
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-06
Evanston, IL— The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) will present this year’s ISSCR Momentum Award to Sergiu P. Paşca, M.D., Kenneth T. Norris, Jr. Professor and the Uytengsu Director of Stanford Brain Organogenesis, Stanford University, U.S.A. The award recognizes the exceptional achievements of a mid-career investigator whose innovative research has established a major area of stem cell-related research with a strong trajectory for future success.
Dr. Paşca will present his research during Plenary VII on 13 July 2024 during the ISSCR 2024 Annual Meeting in Hamburg, Germany. ISSCR 2024 is the world’s leading ...
2024-02-06
A new study has provided insight into how experiences and features of neurodiversity vary amongst adults in the UK.
There is variation in people’s attributes and experiences across all populations. Neurodivergent people, such as people with a diagnosis of ADHD, dyslexia, dyspraxia, or autism, may experience the world in distinctive ways. But, we are only beginning to appreciate how traits and experiences associated with neurodivergence differ across the whole population.
Now, new research from the University of Birmingham has provided a more detailed picture of what neurodiversity looks like amongst adults in the UK.
The research is published in JCPP Advances.
Ian Apperly, ...
2024-02-06
American Geophysical Union
6 February 2024
AGU Release No. 24-04
For Immediate Release
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/seattle-fault-may-have-origins-in-an-ancient-tear-in-the-continent
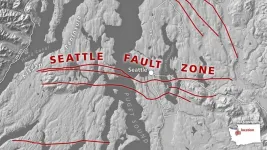
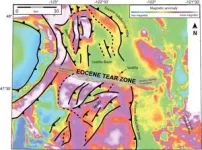
Seattle fault may have origins in an ancient tear in the continent
Magnetic data suggest the hazardous Seattle fault zone developed as the edge of the continent tore itself in two more than 50 million years ago, providing a possible new origin story for the fault
AGU ...
2024-02-06
Black holes not only existed at the dawn of time, they birthed new stars and supercharged galaxy formation, a new analysis of James Webb Space Telescope data suggests.
The insights upend theories of how black holes shape the cosmos, challenging classical understanding that they formed after the first stars and galaxies emerged. Instead, black holes might have dramatically accelerated the birth of new stars during the first 50 million years of the universe, a fleeting period within its 13.8 billion—year history.
"We know these monster black holes ...
2024-02-06
Xuan Wang, Assistant Professor, Electrical and Computer Engineering, is designing a framework for Multi-Autonomous Multi-Human (MAMH) systems.
The operation of many real-world systems involves the co-existence of human and autonomous agents. Inadequate coordination among these agents can lead to significant performance degradation or safety risks.
In this project, Wang aims to develop a novel framework for Multi-Autonomous Multi-Human coordination, which could enhance algorithmic scalability and ...
2024-02-06
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- When diagnosing skin diseases based solely on images of a patient’s skin, doctors do not perform as well when the patient has darker skin, according to a new study from MIT researchers.
The study, which included more than 1,000 dermatologists and general practitioners, found that dermatologists accurately characterized about 38 percent of the images they saw, but only 34 percent of those that showed darker skin. General practitioners, who were less accurate overall, showed a similar decrease in accuracy ...
2024-02-06
The Vilcek Foundation announces the recipients of the 2024 Vilcek Foundation Prizes in Biomedical Science. Awarded annually since 2006, the prizes recognize outstanding immigrant scientists at the forefront of their fields, and celebrate the importance of immigrant contributions to scientific research and discovery in the United States. In 2024, the foundation awards $250,000 in prizes to Luciano Marraffini (b. Argentina), Gerta Hoxhaj (b. Albania), Tomasz Nowakowski (b. Poland) and Takanori Takebe (b. Japan).
“With the 2024 Vilcek Foundation Prizes in Biomedical Science, we honor scientists who have ...
2024-02-06
No increased risks for babies, and for some serious neonatal complications lower risks. This is the result of the largest study to date on the safety of newborn babies whose mothers were vaccinated against COVID-19 during pregnancy. The study is a collaboration between Swedish and Norwegian researchers and is published in the journal JAMA.
COVID-19 vaccination in pregnancy was not associated with any increased risks in newborn infants. On the contrary, the study of nearly 200,000 newborns in Sweden and Norway showed that babies born by women who chose to be vaccinated ...
2024-02-06
About The Study: In this population-based study from Sweden and Norway that included 94,000 infants exposed to COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy and 102,000 control infants born between June 2021 and January 2023, vaccination of pregnant individuals with mRNA COVID-19 vaccines was not associated with increased risks of neonatal adverse events in their infants.
Authors: Mikael Norman, M.D., Ph.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.26945)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
2024-02-06
About The Study: The bivalent COVID-19 vaccines protected children and adolescents against SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptomatic COVID-19 in this study including 2,959 participants ages 5 to 17 years. These data demonstrate the benefit of COVID-19 vaccine in children and adolescents. All eligible children and adolescents should remain up to date with recommended COVID-19 vaccinations.
Authors: Leora R. Feldstein, Ph.D., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Jun Wu receives the 2024 ISSCR Outstanding Young Investigator Award for his innovative work on stem cell-based embryo and chimera models