(Press-News.org) Women have a four times higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease if they have an infection with a high-risk strain of the human papillomavirus (HPV), according to research published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Wednesday).
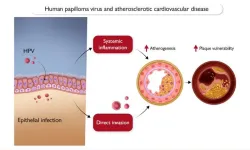
HPV is a very common infection and high-risk strains are known to cause cervical cancer. Previous research has suggested that HPV may also contribute to the build-up of dangerous plaque in the arteries. However, this is the first study to show a link between high-risk HPV infection and deaths from cardiovascular disease.
The research was led by Professors Seungho Ryu, Yoosoo Chang and Hae Suk Cheong from the Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. Prof. Ryu said “Despite remarkable advances in controlling well-known risk factors for heart disease – such as smoking, high cholesterol, hypertension, and diabetes – heart disease continues to be a major cause of death. Interestingly, these conventional risk factors don't explain all heart disease cases; about 20% occur in people who don't have these issues. This highlights the need to investigate other changeable risk factors. Our research focuses on examining the impact of HPV, particularly in relation to cardiovascular mortality, as a potential risk factor for heart disease.”
The research included 163,250 young or middle-aged Korean women who had no cardiovascular disease at the start of the study. The women were given a variety of health screening tests, including cervical screening for 13 high-risk strains of HPV. The women returned for health checks every year or two for an average of eight and half years.
Researchers were able to combine data on the women’s HPV test results with national data on deaths from cardiovascular disease, including heart disease and stroke.
As a group of relatively young, healthy women, their risk of dying of cardiovascular disease was generally low (9.1 in 100,000 overall).
However, after taking account for other factors that are known to increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, researchers found that women with high-risk HPV had a 3.91 times greater risk of blocked arteries, a 3.74 times greater risk of dying from heart disease and a 5.86 times greater risk of dying from a stroke, compared to women who did not have a high-risk HPV infection. Researchers also found that the risk was higher still in women who had a high-risk HPV infection and obesity.
Prof. Cheong said: “We know that inflammation plays a pivotal role in the development and progression of cardiovascular disease and viral infections are potential triggers of inflammation. HPV is known for its link to cervical cancer, but research is starting to show that this virus can also be found in the blood stream. It could be that the virus is creating inflammation in the blood vessels, contributing to blocked and damaged arteries and increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
“This study highlights the importance of comprehensive care for patients with high-risk HPV. Clinicians should monitor cardiovascular health in patients with high-risk HPV, particularly those with obesity or other risk factors. It's important for people with high-risk HPV to be aware of the potential for both heart disease and cervical cancer risks. They should engage in regular health screenings and adopt a healthy lifestyle to mitigate their risk of cardiovascular disease.”
The researchers say more work is needed to find out whether high-risk HPV infection has similar effects on men and to see if the HPV vaccine can prevent deaths from heart disease. Prof. Ryu added: “If these findings are confirmed, they could have substantial implications for public health strategies. Increasing HPV vaccination rates may be an important strategy in reducing long-term cardiovascular risks.”
In an accompanying editorial [2] Prof. James S. Lawson from the University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia, and colleagues said: “The evidence that viruses in general and HPV in particular increase the risk of adverse outcomes from atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease has become compelling enough to add to the already strong case for vaccination against influenza virus, SARS-CoV-2, and HPV. The evidence that HPV is causal in the initiation or progression of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is highly suggestive but would become definitive if the results of randomized trials evaluating HPV vaccines for prevention of cervical cancer showed a reduction in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
“These findings, when added to other evidence linking HPV and other viruses to higher cardiovascular disease mortality, make a strong case for accepting viruses as risk factors for adverse outcomes from atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.”
END
Women with HPV infection face higher risk of death from cardiovascular disease
2024-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ORNL’s Sholl elected to National Academy of Engineering
2024-02-07
David Sholl, director of the Transformational Decarbonization Initiative at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been elected a member of the National Academy of Engineering for his contributions in addressing large-scale chemical separation challenges, including carbon dioxide capture, using quantitative materials modeling.
Being elected to the National Academy of Engineering is among the highest professional distinction accorded to an engineer. New members are selected by their peers, with this new class bringing total U.S. membership to 2,310. The newly elected class will be formally inducted during ...
Rice’s James Tour named to National Academy of Engineering
2024-02-07
HOUSTON – (Feb. 6, 2024) – Rice University chemist James Tour was named to the National Academy of Engineering (NAE), one of the highest professional distinctions accorded “in recognition of distinguished contributions” to the field.
Tour, the T.T. and W.F. Chao Professor, professor of chemistry and of materials science and nanoengineering and of computer science, was recognized for his research on the “synthesis, fabrication, properties, applications and commercialization of novel forms ...
Preterm births linked to ‘hormone disruptor’ chemicals may cost united states billions
2024-02-07
Daily exposure to chemicals used in the manufacture of plastic food containers and many cosmetics may be tied to nearly 56,600 preterm births in the U.S. in 2018, a new study shows. The resulting medical costs, the authors of the report say, were estimated to reach a minimum of $1.6 billion and as much as $8.1 billion over the lifetime of the children.
For decades, the chemicals, called phthalates, have been shown to interfere with the function of certain hormones, or signaling compounds that circulate in the blood and guide much of the body’s processes. Exposure to these toxins, which is believed to occur as consumer products break down and are ingested, has been linked ...
We must tackle female ageism in sport and exercise science, urge researchers
2024-02-07
Action is urgently needed to address the dearth of older women in sport and exercise science, not only for the sake of the growing numbers of female athletes, but women’s health in general, urge a group of international researchers in an editorial, published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
There are already far too few sports and exercise science studies that include women, point out the authors, citing their own 2021 report on the sex data gap.
This showed that out of 5261 studies, from across six popular sport and exercise science journals, women and girls made up just over a third of the total number of participants, a figure that is likely ...
Women may find it harder to adjust to later life divorce and break-ups than men
2024-02-07
Women may find it harder to emotionally adjust to divorce or a relationship break-up in later life than men do, if patterns of antidepressant use are indicative, suggests a large long term study published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
While both sexes increased their antidepressant use in the run up to, and immediate aftermath of, a divorce, break-up, or bereavement, women’s use of these drugs was greater than men’s. And while re-partnering was associated with a slight reduction in antidepressant use in both sexes, it was particularly short-lived in women, the study findings indicate.
Due to population ...
High weekly physical activity levels linked to lower kidney disease risk in diabetes + overweight/obesity
2024-02-07
Clocking up high weekly levels of moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity is linked to a lower risk of developing chronic kidney disease in overweight/obese people with type 2 diabetes, finds research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
But boosting the weekly tally by just over an hour is linked to a 33% reduction in risk, with the effects apparent for bouts lasting above or below 10 minutes at a time, the findings indicate.
Diabetes is the leading cause of chronic kidney disease, accounting for 30–50% of all such cases. Diabetes plus chronic kidney disease is associated with a 10-fold or greater increase in the risk of death from any cause ...
Monterey Bay Aquarium study reveals how kelp forests persisted through the large 2014-2016 Pacific marine heatwave
2024-02-07
New research led by Monterey Bay Aquarium and the University of California, Santa Cruz, reveals that denser, and more sheltered, kelp forests can withstand serious stressors amid warming ocean temperatures. Published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, the study also offers the first comprehensive assessment of how declines in kelp abundance affected marine algae, invertebrates, and fishes living in Monterey Bay. The study comes after a multi-year marine heatwave – the product of a 2014 ‘blob’ ...
Early drawing and building skills linked to enhanced education and behaviour in children
2024-02-07
Fine motor skills in young children are linked to better GCSE scores and fewer behavioural problems in childhood and adolescence, according to a new study from the University of Surrey and Birkbeck, University of London. The authors suggest that preschool fine motor skills, including drawing, folding paper and block building, may play an important role in the pathway between infancy and later educational and behavioural outcomes in primary and secondary school.
The study showed that fine motor skills ...
NLR researcher named Fellow of Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE)
2024-02-07
WASHINGTON – U.S. Naval Research Laboratory research physicist Lynda E. Busse, Ph.D., was named a Fellow of SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics, for outstanding technical contributions to the development of novel infrared (IR) optical materials and photonics devices.
Announced December 2023, the 47 new Fellows represent high-profile leaders in academia, industry, and government, and are being honored for their technical achievements as well as for their service to SPIE and the optics and photonics community. Dr. Busse was recognized along with many of the other new Fellows at the 2024 SPIE Photonics West Conference in San Francisco, California ...
A Filipino fruit dove, long part of Peabody collection, reveals its secrets
2024-02-06
In May 1953, Filipino ornithologist D. S. Rabor collected a single female fruit dove on the forested slopes of an active volcano on the Philippine island of Negros. The small apple green bird, which had yellow edgings on its wings and prominent circles of bare skin around its eyes, was unlike any other known pigeon species. In 1954, Rabor and Yale professor Dillon Ripley described the unique specimen as Ptilinopus arcanus, a name inspired by the Latin word for “secret.”
The Negros Fruit Dove, as it is commonly known, has never been ...