(Press-News.org) A study published in the Journal of Field Robotics assessed the world’s first unmanned machine designed for autonomous forestry operations. Investigators demonstrated that using computer vision, autonomous navigation, and manipulator control algorithms, their newly developed machine can safely, accurately, and efficiently pick up logs from the ground and maneuver through various forest terrains without the need for human intervention.
The research represents a significant milestone in the field of autonomous outdoor robotics, which could reduce the need for human labor, thereby increasing productivity and reducing labor costs, while also minimizing the environmental impact of timber harvesting.
“Besides its short-term effect on forestry, the technological advancements that come with autonomous forestry machines have the potential to address current environmental issues. As demonstrated in this study, by embracing cutting-edge technologies like autonomous navigation and manipulation algorithms, the unmanned machine provides not only timber harvesting with greater efficiency but also promotes sustainable forestry,” said corresponding author Pedro La Hera, PhD, of the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences. “Automated operations can be highly accurate and effective in terms of collateral damage to adjacent ecosystems, which helps us to be more ecologically friendly than we currently are.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/rob.22300
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
The Journal of Field Robotics is an applied robotics journal publishing impactful research on the fundamentals of robotics in unstructured and dynamic environments. We welcome theoretical and practical papers on robotics used in real-world applications such as construction, forestry, agriculture, mining, environment, nuclear, subsea, intelligent highways, healthcare, search and rescue, military, and space (orbital and planetary). We also cover technical and scientific topics such as sensing, mechanical design, computing architectures, learning and control, human-robot interaction, and security.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Researchers develop and test the first unmanned forestry machine
2024-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
KIST-LLNL raises expectations for commercialization of high-energy-density all-solid-state batteries
2024-02-07
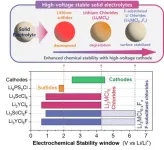
Researchers are actively working on non-flammable solid electrolytes as a safer alternative to liquid electrolytes commonly found in lithium-ion batteries, which are vulnerable to fires and explosions. While sulfide-based solid electrolytes exhibit excellent ionic conductivity, their chemical instability with high-voltage cathode materials necessary for high-energy-density batteries has impeded their commercial viability. Consequently, there has been a growing interest in chloride-based solid electrolytes, which are stability in high-voltage conditions due to their strong bonding ...
Survey finds most don’t know the numbers that help predict heart disease
2024-02-07
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Keeping track of blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels can help identify risk factors for heart disease. However, a national survey by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center found that while many adults know their childhood address or best friend’s birthday, less than half know their blood pressure or ideal weight, and fewer than 1 in 5 know their cholesterol or blood sugar levels.
“Recognizing heart disease risk factors early and adequately treating ...
Artificial intelligence helps predict whether antidepressants will work in patients
2024-02-07
In patients with major depression disorder it is, thanks to use of artificial intelligence, now possible to predict within a week whether an antidepressant will work. With the help of an AI algorithm, a brain scan and an individual's clinical information, researchers from Amsterdam UMC and Radboudumc could see up to 8 weeks faster whether or not the medication would work. The results of this study are published today in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
"This is important news for patients. Normally, ...
Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on soil nematode community of soybean farmland
2024-02-07
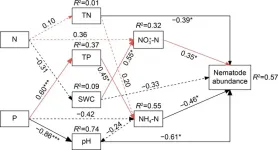
As a predator of soil microorganisms, nematodes respond rapidly to changes in soil environment, which can reflect climate conditions, ecosystem succession status, nutrient cycling and soil ecosystem health. In agroecosystems, nitrogen and phosphate fertilizers are often applied in large quantities. Therefore, studying the effect of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil nematode communities is helpful to understand how nitrogen and phosphorus addition affects the growth and development of crops in farmland ecosystems. This study demonstrates that the addition of nitrogen and phosphorus significantly ...
High-performance photoelectrochemical cells with MoS2 nanoflakes/TiO2 photoanode on 3D porous carbon spun fabric
2024-02-07
This research is led by Donghee Park (Center for Opto-Electronic Materials and Devices, Post-Silicon Semiconductor Institute, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Republic of Korea) and Dong Ick Son (Institute of Advanced Composite Materials, Korea Institute of Science and Technology; KIST School, Department of Nanomaterials and Nano Science, University of Science and Technology, Republic of Korea)
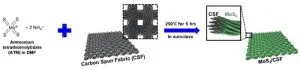
Recently, many scientists have been developing eco-friendly energy sources to replace fossil fuels to minimize global warming that threatens the global ecosystem. One of the notable studies is photoelectrochemical (PEC) cells that use infinite solar energy as ...
SORA combined with FGF21 can inhibit the growth and promote apoptosis of HCC cells through Smad3
2024-02-07
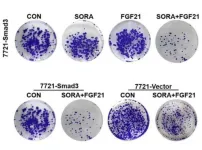
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common disease in human history and one of the main causes of cancer-related death. Sorafenib (SORA) is the best representative of angiogenesis inhibitors and is currently being commonly used in the treatment of advanced HCC as a first-line drug. Although SORA improves the overall survival rate of patients with liver cancer, acquired resistance to SORA has been found in patients with liver cancer and this has led to poor treatment outcomes. Hypoxia is one of the inducements of SORA resistance. Since ...
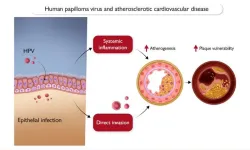
Women with HPV infection face higher risk of death from cardiovascular disease
2024-02-07
Women have a four times higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease if they have an infection with a high-risk strain of the human papillomavirus (HPV), according to research published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Wednesday).
HPV is a very common infection and high-risk strains are known to cause cervical cancer. Previous research has suggested that HPV may also contribute to the build-up of dangerous plaque in the arteries. However, this is the first study to show a link between high-risk HPV infection and deaths from cardiovascular disease.
The research was led by Professors ...
ORNL’s Sholl elected to National Academy of Engineering
2024-02-07
David Sholl, director of the Transformational Decarbonization Initiative at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been elected a member of the National Academy of Engineering for his contributions in addressing large-scale chemical separation challenges, including carbon dioxide capture, using quantitative materials modeling.
Being elected to the National Academy of Engineering is among the highest professional distinction accorded to an engineer. New members are selected by their peers, with this new class bringing total U.S. membership to 2,310. The newly elected class will be formally inducted during ...
Rice’s James Tour named to National Academy of Engineering
2024-02-07
HOUSTON – (Feb. 6, 2024) – Rice University chemist James Tour was named to the National Academy of Engineering (NAE), one of the highest professional distinctions accorded “in recognition of distinguished contributions” to the field.
Tour, the T.T. and W.F. Chao Professor, professor of chemistry and of materials science and nanoengineering and of computer science, was recognized for his research on the “synthesis, fabrication, properties, applications and commercialization of novel forms ...
Preterm births linked to ‘hormone disruptor’ chemicals may cost united states billions
2024-02-07
Daily exposure to chemicals used in the manufacture of plastic food containers and many cosmetics may be tied to nearly 56,600 preterm births in the U.S. in 2018, a new study shows. The resulting medical costs, the authors of the report say, were estimated to reach a minimum of $1.6 billion and as much as $8.1 billion over the lifetime of the children.
For decades, the chemicals, called phthalates, have been shown to interfere with the function of certain hormones, or signaling compounds that circulate in the blood and guide much of the body’s processes. Exposure to these toxins, which is believed to occur as consumer products break down and are ingested, has been linked ...