(Press-News.org)
Forests, which cover a third of Earth's land surface, are pivotal in carbon storage and the water cycle, though the full scope of their impact remains to be fully understood. In a new study published in Nature Communications, researchers from Stockholm University and international colleagues provide new insights into the complex role forests play in the climate system and water cycle.
The research, involving scientists from 11 institutions across five countries, including Sweden, the UK, Finland, Germany, and Brazil, highlights the intricate relationship between forests, particularly their emission of organic gases, and the formation of reflective clouds that could influence global temperatures.
Comparing boreal and tropical forests
The unique aspect of this study is its focus on both boreal and tropical forests, which constitute 27% and 45% of the Earth's forested area, respectively. These ecosystems differ in their emissions and cloud formation processes, leading to varying impacts on the forest-cloud-climate feedback loop.
"This study, utilizing long-term data from diverse forest environments in Finland and Brazil, marks the first time observational evidence has been presented for these interactions in tropical rainforests," says lead author Sara Blichner, postdoctoral scientist at the Department of Environmental Sciences at Stockholm University.
Underrepresentation of forests in climate models
The study emphasizes the need for improved climate models to accurately represent these complex interactions. "Our findings suggest that current models may underestimate the impact of forests on cloud formation and climate, especially in tropical regions, which are crucial due to high amount of solar radiation these areas receive at these latitudes," Blichner explains.
However, Blichner stresses that while the study highlights areas for improvement in climate modeling, it does not undermine the overall reliability of these models. "Climate models are highly trustworthy in representing the main processes of climate change. Our research aims to refine these models, reducing uncertainties in future climate projections," she asserts.
Natural particles and global warming
The research also points out that as man-made particle emissions decrease due to air quality policies, the natural particles from forests become increasingly significant. These feedbacks are more potent in cleaner air environments and could play an important role in moderating global warming.
This collaborative study underscores the need for continued research and improvement in climate modeling to better predict future climate scenarios. Additionally, the findings highlight that these types of effects must be considered when assessing forest conservation as a key strategy in climate change mitigation.
About forest emissions and climate regulation
Forests release substantial amounts of organic gases, particularly noticeable as the distinctive scent of a pine forest on a warm day. These gases, once released into the atmosphere, contribute to particle formation.
Clouds are composed of minuscule water droplets and each of these droplets nucleate around a particle in the air. An increase in atmospheric particles results in clouds with more droplets, enhancing their reflectivity of sunlight and leading to cooler surface temperatures.
As climate change raises temperatures, forests are anticipated to emit more of these gases, thereby creating more particles and potentially more reflective clouds.
Contact:
Sara Blichner, postdoctoral scientist at the Department of Environmental Sciences, Stockholm University
Phone: +46 793503771 Email: sara.blichner@aces.su.se
Ilona Riipinen, professor at the Department of Environmental Sciences and director of the Bolin Centre Climate Research, Stockholm University
Phone: +46-73-5859251 Email: ilona.riipinen@aces.su.se
END
Capsaicin, derived from hot chili pepper plants, has been used to treat various types of pain, and a high concentration capsaicin patch (HCCP) is approved for the treatment of nerve (or neuropathic) pain. In a real-world study published in Pain Practice that included 97 outpatients in Germany diagnosed primarily with neuropathic back pain, postoperative/posttraumatic neuropathic pain, or postherpetic neuralgia (shingles pain), patients appeared to benefit from multiple HCCP applications.
Among the ...
An analysis of relevant published studies indicates that across all ages, food allergy negatively affects individuals’ quality of life to a greater extent in females than in males.
The analysis, which is published in Clinical and Experimental Allergy, included 34 studies. In the studies, women and the parents of girls tended to report a greater impact of food allergy on health-related quality of life than men or parents of boys.
Evidence also showed that improvements in quality of life over the course of treatment for food allergy can be different for males and females, with weak evidence suggesting that male children may experience more improvements ...
A recent analysis of data from nearly all World Health Organization member states clearly demonstrates a link between air pollution and mortality from cardiovascular diseases, with more of such deaths associated with air pollution in low-income countries compared with high-income countries.
In all 183 countries included in the Chronic Diseases and Translational Medicine study, ischemic heart disease-related deaths attributed to air pollution were higher than stroke-related deaths caused by air pollution. In 2019, outdoor air pollution caused 16 ischemic heart disease-related deaths per 100,000 people in high-income countries compared with 70 per 100,000 in low-income countries.
Also, in ...
A study published in the Journal of Field Robotics assessed the world’s first unmanned machine designed for autonomous forestry operations. Investigators demonstrated that using computer vision, autonomous navigation, and manipulator control algorithms, their newly developed machine can safely, accurately, and efficiently pick up logs from the ground and maneuver through various forest terrains without the need for human intervention.
The research represents a significant milestone in the field of autonomous outdoor robotics, which could reduce the need for human labor, thereby increasing productivity and reducing labor costs, while ...
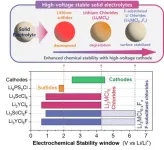
Researchers are actively working on non-flammable solid electrolytes as a safer alternative to liquid electrolytes commonly found in lithium-ion batteries, which are vulnerable to fires and explosions. While sulfide-based solid electrolytes exhibit excellent ionic conductivity, their chemical instability with high-voltage cathode materials necessary for high-energy-density batteries has impeded their commercial viability. Consequently, there has been a growing interest in chloride-based solid electrolytes, which are stability in high-voltage conditions due to their strong bonding ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Keeping track of blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels can help identify risk factors for heart disease. However, a national survey by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center found that while many adults know their childhood address or best friend’s birthday, less than half know their blood pressure or ideal weight, and fewer than 1 in 5 know their cholesterol or blood sugar levels.
“Recognizing heart disease risk factors early and adequately treating ...
In patients with major depression disorder it is, thanks to use of artificial intelligence, now possible to predict within a week whether an antidepressant will work. With the help of an AI algorithm, a brain scan and an individual's clinical information, researchers from Amsterdam UMC and Radboudumc could see up to 8 weeks faster whether or not the medication would work. The results of this study are published today in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
"This is important news for patients. Normally, ...
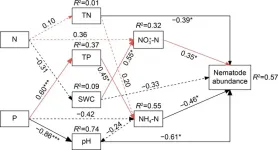
As a predator of soil microorganisms, nematodes respond rapidly to changes in soil environment, which can reflect climate conditions, ecosystem succession status, nutrient cycling and soil ecosystem health. In agroecosystems, nitrogen and phosphate fertilizers are often applied in large quantities. Therefore, studying the effect of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil nematode communities is helpful to understand how nitrogen and phosphorus addition affects the growth and development of crops in farmland ecosystems. This study demonstrates that the addition of nitrogen and phosphorus significantly ...
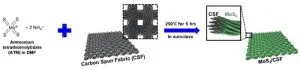
This research is led by Donghee Park (Center for Opto-Electronic Materials and Devices, Post-Silicon Semiconductor Institute, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Republic of Korea) and Dong Ick Son (Institute of Advanced Composite Materials, Korea Institute of Science and Technology; KIST School, Department of Nanomaterials and Nano Science, University of Science and Technology, Republic of Korea)
Recently, many scientists have been developing eco-friendly energy sources to replace fossil fuels to minimize global warming that threatens the global ecosystem. One of the notable studies is photoelectrochemical (PEC) cells that use infinite solar energy as ...
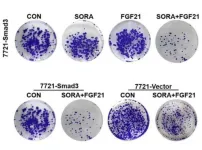
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common disease in human history and one of the main causes of cancer-related death. Sorafenib (SORA) is the best representative of angiogenesis inhibitors and is currently being commonly used in the treatment of advanced HCC as a first-line drug. Although SORA improves the overall survival rate of patients with liver cancer, acquired resistance to SORA has been found in patients with liver cancer and this has led to poor treatment outcomes. Hypoxia is one of the inducements of SORA resistance. Since ...