(Press-News.org) Hidden beneath the heavily cratered surface of Mimas, one of Saturn's smallest moons, lies a secret: a global ocean of liquid water. This astonishing discovery, led by Dr. Valéry Lainey of the Observatoire de Paris-PSL and published in the journal Nature, reveals a "young" ocean formed just 5 to 15 million years ago, making Mimas a prime target for studying the origins of life in our Solar System.
“Mimas is a small moon, only about 400 kilometers in diameter, and its heavily cratered surface gave no hint of the hidden ocean beneath," says Dr Nick Cooper, a co-author of the study and Honorary Research Fellow in the Astronomy Unit of the School of Physical and Chemical Sciences at Queen Mary University of London. "This discovery adds Mimas to an exclusive club of moons with internal oceans, including Enceladus and Europa, but with a unique difference: its ocean is remarkably young, estimated to be only 5 to 15 million years old."
This young age, determined through detailed analysis of Mimas's tidal interactions with Saturn, suggests the ocean formed recently, based on the discovery of an unexpected irregularity in its orbit. As a result, Mimas provides a unique window into the early stages of ocean formation and the potential for life to emerge.
“The existence of a recently formed liquid water ocean makes Mimas a prime candidate for study, for researchers investigating the origin of life,” explains Dr Cooper. The discovery was made possible by analysing data from NASA's Cassini spacecraft, which meticulously studied Saturn and its moons for over a decade. By closely examining the subtle changes in Mimas's orbit, the researchers were able to infer the presence of a hidden ocean and estimate its size and depth.
Dr Cooper continues: “This has been a great team effort, with colleagues from five different institutions and three different countries coming together under the leadership of Dr Valéry Lainey to unlock another fascinating and unexpected feature of the Saturn system, using data from the Cassini mission.”
The discovery of Mimas's young ocean has significant implications for our understanding of the potential for life beyond Earth. It suggests that even small, seemingly inactive moons can harbor hidden oceans capable of supporting life-essential conditions. This opens up exciting new avenues for future exploration, potentially leading us closer to answering the age-old question: are we alone in the universe?
END
Mimas' surprise: Tiny moon holds young ocean beneath icy shell
2024-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Quantum materials: Discovered new state of matter with chiral properties
2024-02-07
An international research group has discovered a new state of matter characterized by the existence of a quantum phenomenon called chiral current. These currents are generated on an atomic scale by a cooperative movement of electrons, unlike conventional magnetic materials whose properties originate from the quantum characteristic of an electron known as spin and their ordering in the crystal.
Chirality is a property of extreme importance in science, for example, it is fundamental also to understand DNA. ...
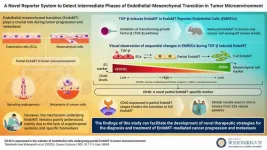
Towards a better understanding of endothelial cell transformation in cancer progression
2024-02-07
In a new study, Tokyo Medical and Dental University researchers shed light on partial endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the tumor microenvironment
Tokyo, Japan - Endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT, also termed as EndMT), a biological process resulting in the formation of mesenchymal (or lineage-committed) phenotypes from endothelial cells (lining blood vessels), plays a crucial role in tumor progression. Despite the important role of EndoMT, the underlying mechanism and characteristics of cells in intermediate/partial EndoMT remain largely unexplored. Now, researchers from Japan have developed a system to study these EndoMT stages.
In ...
After prison, perpetrators of genocide say they’ve changed
2024-02-07
COLUMBUS, Ohio – After serving decades in prison, Rwandans convicted of crimes of genocide returned to their communities articulating a “narrative of redemption,” saying they were good people, despite their past crimes.
And they were hopeful about their prospects for reintegrating into their communities.
Many of these former prisoners had been convicted of murder, often of their own neighbors, connected to the 1994 genocide in Rwanda. But they said they had changed – even while minimizing their role in the killings.
In ...
Japan's electric vehicle transition by 2035 may be insufficient to combat the climate crisis, but there are solutions
2024-02-07
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers at Kyushu University have found that Japan's current policy of stopping the sale of gas vehicles by 2035 and transitioning only to hybrids and electric vehicles may be insufficient to reduce the country's CO2 emissions and prevent it from reaching its decarbonization target goals. In fact, emissions may temporarily increase.
The team's analysis showed that along with the policy, the Japanese government must simultaneously work to increase production of clean ...
From the research bench to the patient’s bedside: Project on Medical Microwave Imaging awarded with 1.5M€
2024-02-07
The European project entitled “Bone, Brain, Breast and Axillary Medical Microwave Imaging Twinning (3BAtwin)” has been awarded with €1.5M to reinforce our training on Medical Microwave Imaging (MMWI). The project is led by the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Ciências ULisboa) (Portugal), in collaboration with University of Galway (Ireland) and Turin Polytechnic University (Italy).
The goal of this twinning project is to accelerate the transition of Medical Microwave Imaging “from the research bench ...
New resource for selecting best treatment path for young children with cancerous tumors published by NCCN
2024-02-07
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [February 7, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—today published its first ever set of treatment recommendations pertaining to neuroblastoma. Neuroblastoma is a type of solid tumor cancer that typically occurs in early childhood, with the majority diagnosed before age five.[1] Neuroblastoma is the most common type of solid tumor (outside of brain tumors) in children, with more than 700 cases diagnosed in the United States every year.[2] Research innovations ...
Gut microbiome changes during pregnancy may influence immune system response
2024-02-07
Highlights:
Alterations in gut microbiota may influence immune system changes during pregnancy.
However, the connection isn’t well known.
Researchers in China analyzed gut microbiota, metabolites and cytokines in healthy pregnant and non-pregnant young women.
The new study identifies numerous pathways by which the gut microbiome may change the immune system.
Washington, D.C.—During pregnancy, a woman’s immune system changes dramatically but researchers don’t yet understand all the underlying mechanisms. A new study shows how the gut microbiota may play a role.
In a paper published this week in mSystems, researchers in China report that during pregnancy, ...
Warmer water may help rivers keep antimicrobial resistance at bay
2024-02-07
Highlights:
Wastewater, even when treated, can deliver antimicrobial resistance genes to rivers.
Further research is needed on if rivers function as a protective barrier.
Researchers subjected biofilms from pristine rivers to wastewater.
Antibiotic resistant bacteria from wastewater successfully integrated at first, but in the warmest water were edged out by naturally occurring microbes.
The study suggests that temperature can influence the microbial competition in rivers.
Washington, D.C.—Antimicrobial resistant genes (ARGs) from wastewater can end up in natural biofilms in rivers, but they may not stick around very long. This week in mSphere, ...
AIM-HI Accelerator Fund celebrates Yiviva's milestone collaboration with AstraZeneca China, furthering technology platforms for multiple cancers
2024-02-07
Accelerating Innovation in Medicine - Health Initiative (AIM-HI) is proud to celebrate a significant milestone in the journey of one of its esteemed portfolio companies, Yiviva. A clinical-stage platform biotechnology company, Yiviva has entered into a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with AstraZeneca China, a multinational biopharmaceutical leader.
AIM-HI exists to support bold new ideas in treating and preventing cancer. So when Yale Professor Yung-Chi Cheng approached us years ago about mining ancient Chinese herbs for modern therapies, we took notice. Other investors ...
New scientific research will test PREVENT risk calculator among diverse groups
2024-02-07
DALLAS, Feb. 7, 2024 — Research teams from Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, New York University and Duke University will work together to assess the accuracy of the American Heart Association’s new PREVENTTM risk calculator with funding from the Association’s De-biasing Clinical Care Algorithms project.
The American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of service in 2024, is the single largest non-government supporter of heart and brain health research in the U.S. The de-biasing project is funded by a grant from the Doris Duke Foundation to study the role of race and ethnicity in clinical equations and their ...