(Press-News.org) Tiny external structures in the wax coating of blueberries give them their blue colour, researchers at the University of Bristol can reveal.
This applies to lots of fruits that are the same colour including damsons, sloes and juniper berries.
In the study, published today in Science Advances, researchers show why blueberries are blue despite the dark red colour of the pigments in the fruit skin. Their blue colour is instead provided by a layer of wax that surrounds the fruit which is made up of miniature structures that scatter blue and UV light. This gives blueberries their blue appearance to humans and blue-UV to birds. The chromatic blue-UV reflectance arises from the interaction of the randomly arranged crystal structures of the epicuticular wax with light.
Rox Middleton, Research Fellow at Bristol’s School of Biological Sciences, explained: “The blue of blueberries can’t be ‘extracted’ by squishing – because it isn’t located in the pigmented juice that can be squeezed from the fruit. That was why we knew that there must be something strange about the colour.
“So we removed the wax and re-crystallised it on card and in doing so we were able to create a brand new blue-UV coating.”
The ultra-thin colorant is around two microns thick, and although less reflective, it’s visibly blue and reflects UV well, possibly paving the way for new colorant methods.
“It shows that nature has evolved to use a really neat trick, an ultrathin layer for an important colorant," added Rox.
Most plants are coated in a thin layer of wax which has multiple functions, many of which scientists still don’t understand. They know that it can be very effective as a hydrophobic, self-cleaning coating, but it's only now they realise how important the structure is for visible coloration.
Now the team plan to look at easier ways of recreating the coating and applying it. This could lead to a more sustainable, biocompatible and even edible UV and blue-reflective paint.
Furthermore these coatings could have the same multiple functions as natural biological ones that protect plants.
Rox added: “It was really interesting to find that there was an unknown coloration mechanism right under our noses, on popular fruits that we grow and eat all the time.
“It was even more exciting to be able to reproduce that colour by harvesting the wax to make a new blue coating that no-one’s seen before.
“Building all that functionality of this natural wax into artificially engineered materials is the dream!”
Paper:
‘Self-assembled, Disordered Structural Colour from Fruit Wax Bloom’ by Rox Middleton et al in Science Advances.
END
Scientists reveal why blueberries are blue
2024-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
McMaster and ALK researchers discover new cell that remembers allergies
2024-02-07
Researchers with McMaster University and Denmark-based pharmaceutical company ALK-Abello A/S have made a groundbreaking discovery: a new cell that remembers allergies.
The discovery gives scientists and researchers a new target in treating allergies and could lead to new therapeutics. The research, published in Science Translational Medicine on Feb. 7, 2024, coins the brand-new cell as a type-2 memory B cell (MBC2).
“We’ve discovered a type of memory B cell that had unique characteristics and a unique gene ...
England’s oldest became frailer during austerity, study suggests
2024-02-07
The speed at which England’s oldest adults became frailer accelerated during the UK Government’s era of austerity politics, according to a new study.
Researchers say that the rate of frailty in people aged 85 and over in England increased 50 per cent faster per year between 2012 and 2018 compared with the preceding eight years.
The impact of frailty – a decline in a person’s mental and physical resilience to illness and injury – on the oldest in society must be considered should any new austerity measures be introduced, experts warn.
The study, led by researchers from the University of Edinburgh’s ...
Exceptionally rapid tooth development and ontogenetic changes in the feeding apparatus of the Komodo dragon
2024-02-07
Tea Maho and Robert R. Reisz
University of Toronto Mississauga
Kilat, the largest living lizard at the Toronto Metro Zoo, like other members of his species (Varanus komodoensis), truly deserves to be called the Komodo Dragon! Its impressive size and the way it looks at you and tracks your every move makes you realize that it is an apex predator, not unlike a ferocious theropod dinosaur. So, it is not surprising when you look around at his enclosure to find that there are shed teeth sparkling on the ground, a common find when ...
Scientists develop a low-cost device to make cell therapy safer
2024-02-07
CAMBRIDGE, MA – A tiny device built by scientists at MIT and the Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology could be used to improve the safety and effectiveness of cell therapy treatments for patients suffering from spinal cord injuries.
In cell therapy, clinicians create what are known as induced pluripotent stem cells by reprogramming some skin or blood cells taken from a patient. To treat a spinal cord injury, they would coax these pluripotent stem cells to become progenitor cells, which are destined to differentiate into spinal cord cells. These progenitors are then transplanted back into ...
Getting to know the ‘ghost’ inside batteries
2024-02-07
An Argonne team developing materials for solid-state batteries took an unexpected detour to investigate tiny short-circuits known as soft-shorts. Their insights will benefit battery researchers around the world.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have shed important new light on what the early signs of battery failure look like. Their study — which relates to a condition called soft-shorts — provides the research community with valuable knowledge and methods to design better electric vehicle (EV) batteries.
The Argonne team’s research focused on all-solid batteries with anodes (negative electrodes) ...
Predicting neurodevelopmental disease in children from parent’s traits
2024-02-07
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Predicting the trajectory of neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders like autism or schizophrenia is difficult because they can be influenced by many different genetic and environmental factors. A new study, led by Penn State researchers, demonstrates that evaluating parents for their manifestation of traits of these disorders — and related diseases like depression and anxiety — may provide a more accurate method of predicting the prevalence, and potentially severity, of the disorders in affected children than screening for genetic variants alone. This is likely due, at least in part, to genetic variants the parents transmit to the ...
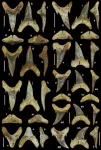
New species of 65 million year old fossil shark discovered in Alabama, USA
2024-02-07
Birmingham, AL (February 7, 2024) – Today, a team of scientists is pleased to announce the discovery of a new fossil shark species from Alabama, USA. The team is led by Jun Ebersole, Director of Collections, McWane Science Center, Birmingham, AL, David Cicimurri, Curator of Natural History, South Carolina State Museum in Columbia, and T. Lynn Harrell, Jr., Paleontologist and Fossil Collections Curator at the Geological Survey of Alabama in Tuscaloosa.
The shark is a new species of Palaeohypotodus (pronounced pale-ee-oh-hype-oh-toe-duss), which means “ancient small-eared tooth,” in reference to the small needle-like fangs present on the sides of the teeth. It has ...
Time to treatment with intravenous thrombolysis before thrombectomy and functional outcomes in acute ischemic stroke
2024-02-07
About The Study: In patients presenting at thrombectomy-capable stroke centers, the benefit associated with intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) plus thrombectomy versus thrombectomy alone was time dependent and statistically significant only if the time from symptom onset to expected administration of IVT was short in this individual participant data meta-analysis (n = 2,313) of six randomized clinical trials.
Authors: Johannes Kaesmacher, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Bern in Bern, Switzerland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Many hookah manufacturers have not complied with FDA-mandated nicotine warning labels
2024-02-07
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
February 7, 2024
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Many Hookah Manufacturers Have Not Complied with FDA-Mandated Nicotine Warning Labels
Only half of the hookah packages assessed in a new study included the required nicotine warnings, two years after this federal regulation was implemented to alert consumers about the health risks of nicotine addiction.
Since August 2018, the US Food & Drug Administration has mandated that all hookah (also known as waterpipe tobacco or shisha) manufacturers include a nicotine warning ...
Endovascular thrombectomy for large ischemic stroke across ischemic injury and penumbra profiles
2024-02-07
About The Study: In this exploratory analysis of a randomized clinical trial of 336 patients with extensive ischemic stroke, endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) improved clinical outcomes across a wide spectrum of infarct volumes, although enrollment of patients with minimal penumbra volume was low. In EVT-treated patients, clinical outcomes worsened as presenting ischemic injury estimates increased.
Authors: Amrou Sarraj, M.D., of University Hospital Cleveland Medical Center—Case Western ...